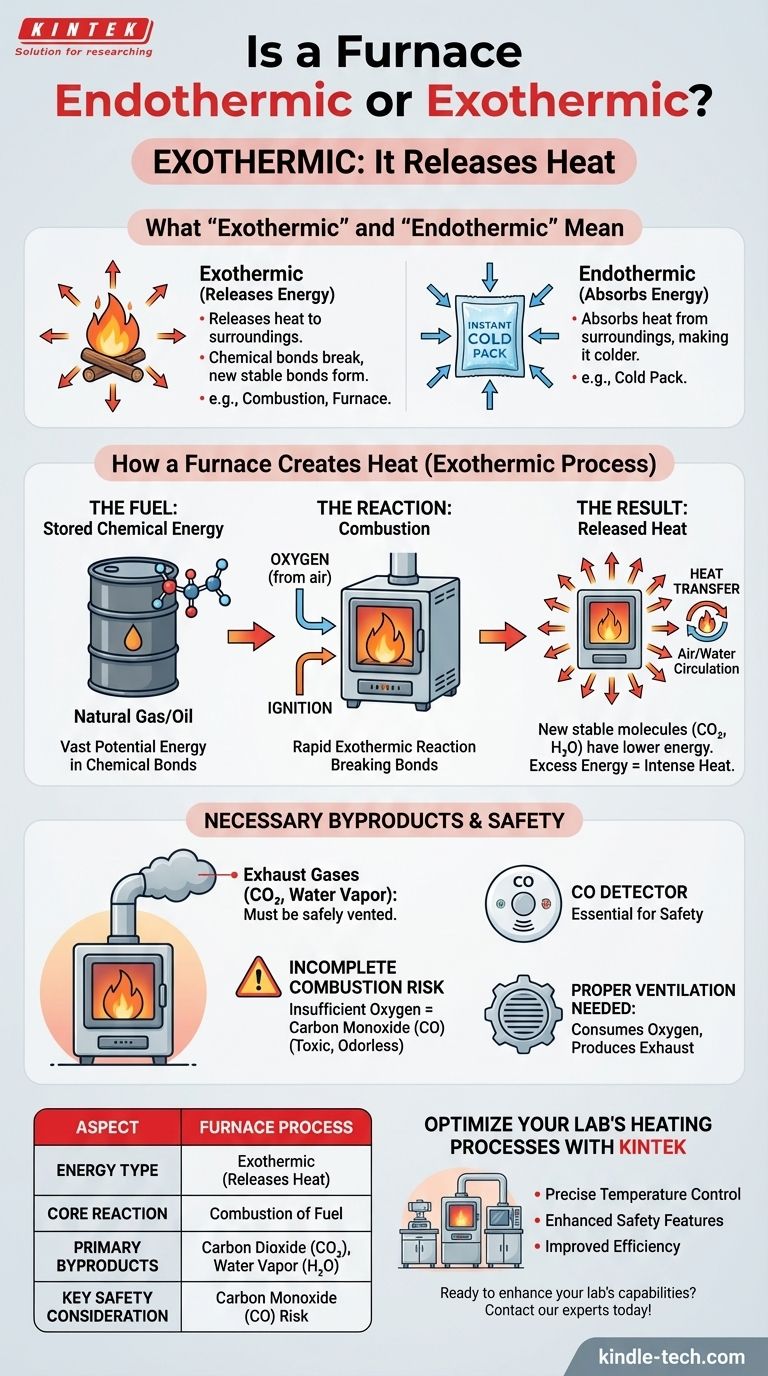
In simple terms, a furnace is exothermic. The entire purpose of a furnace is to generate and release heat into your home, which is the definition of an exothermic process. This is achieved through the combustion of fuel, which converts stored chemical energy into usable thermal energy.
A furnace doesn't just move heat; it creates it. This is done through a controlled chemical reaction (combustion) that releases energy, making the process fundamentally exothermic. Understanding this principle is key to appreciating both its function and its safety requirements.

What "Exothermic" and "Endothermic" Actually Mean
To understand your furnace, we first need to clarify these two scientific terms. They describe how energy moves during a chemical reaction.
Exothermic: Releasing Energy
An exothermic reaction is one that releases energy into its surroundings, usually in the form of heat. Think of a campfire or a lit match. The chemical bonds in the fuel (wood) are broken, and new, more stable bonds are formed, releasing the excess energy as light and heat.
This is the principle all combustion-based heating systems rely on.
Endothermic: Absorbing Energy
An endothermic reaction is the opposite. It absorbs energy from its surroundings, making the environment colder. A common example is the chemical reaction in an instant cold pack.
If a furnace were endothermic, it would draw heat from your home and get colder, making it an air conditioner, not a heater.
How a Furnace Creates Heat: The Exothermic Process
Your furnace is a highly controlled environment for an exothermic reaction. The process can be broken down into three simple stages.
The Fuel: Stored Chemical Energy
Most furnaces use a fuel like natural gas (primarily methane) or oil. This fuel contains a vast amount of potential energy stored within its chemical bonds.
The Reaction: Combustion
The furnace introduces oxygen (from the air) and an ignition source (like a pilot light or electronic igniter) to the fuel. This triggers combustion, a rapid exothermic reaction.
The reaction breaks the bonds in the fuel and oxygen molecules and forms new, more stable molecules—primarily carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
The Result: Released Heat
Because the new molecules (CO₂ and H₂O) are in a lower energy state than the original fuel and oxygen, the excess energy is released as intense heat. This heat is then transferred to the air or water that circulates through your home.
The Necessary Byproducts of an Exothermic System
While the heat is the desired product, the exothermic combustion in a furnace isn't perfectly clean. Understanding the byproducts is crucial for safety and efficiency.
Creation of Exhaust Gases
The primary byproducts of complete combustion are carbon dioxide and water vapor. These gases are not useful for heating and must be safely vented out of your home through a flue or exhaust pipe.
The Risk of Incomplete Combustion
If the furnace doesn't get enough oxygen, incomplete combustion can occur. This dangerous condition produces carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas. This is why carbon monoxide detectors are non-negotiable in any home with a combustion appliance.
The Need for Ventilation
Because a furnace consumes oxygen and produces exhaust, it requires proper ventilation. High-efficiency furnaces often draw combustion air directly from the outside to ensure the reaction is clean and to prevent depressurizing your home.
Why This Distinction Matters for You
Understanding that your furnace is an exothermic system provides a clear framework for operating it safely and efficiently.
- If your primary focus is safety: Recognize that the heat is a product of a chemical reaction that creates harmful byproducts, making proper ventilation and a working carbon monoxide detector absolutely essential.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Know that the goal of a modern furnace is to maximize the heat extracted from the exothermic reaction while safely managing and exhausting the necessary byproducts.
Ultimately, knowing your furnace is exothermic helps you see it not as a magic box, but as a controlled chemical reactor that requires respect and maintenance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Furnace Process |
|---|---|
| Energy Type | Exothermic (Releases Heat) |
| Core Reaction | Combustion of Fuel (e.g., Natural Gas) |
| Primary Byproducts | Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) and Water Vapor (H₂O) |
| Key Safety Consideration | Risk of Carbon Monoxide (CO) from incomplete combustion |
Optimize Your Lab's Heating Processes with KINTEK
Understanding the principles of exothermic reactions is crucial for safe and efficient heating, whether in your home or your laboratory. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab furnaces, ovens, and related equipment that provide precise, reliable, and safe thermal processing for a wide range of applications.
Let us help you achieve superior results:
- Precise Temperature Control: Ensure your experiments and processes have the exact thermal environment they need.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Our equipment is designed with safety as a priority, helping you manage byproducts and prevent hazards.
- Improved Efficiency: Maximize energy use and streamline your workflow with reliable lab equipment.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How hot is a muffle furnace in Celsius? A Guide to Temperature Ranges from 800°C to 1800°C
- What is the meaning of debinding? Master the Critical Step to High-Performance Parts
- What is a muffle furnace used for in a lab? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What are the methods of ash determination? Choosing the Right Technique for Accurate Mineral Analysis
- What are the safety precautions for heat treatment? A Complete Guide to Protecting Personnel and Facilities



















