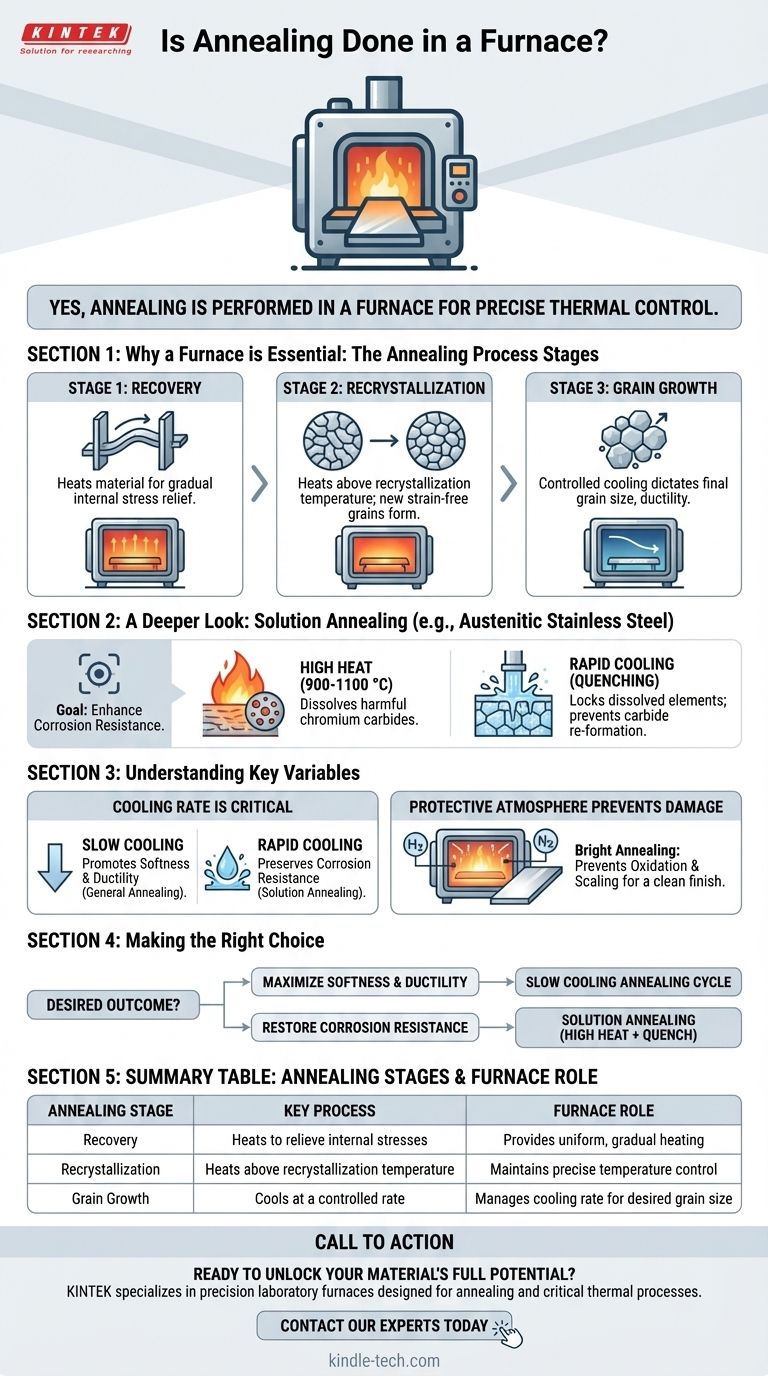
Yes, in virtually all industrial applications, annealing is performed in a furnace. The process requires precise thermal control that only a specialized furnace can provide. This equipment is not merely a heater; it is an engineered environment used to systematically alter a material's internal microstructure to achieve specific mechanical properties.
The core purpose of using a furnace for annealing is to execute a controlled thermal cycle. This involves heating the material to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it at a calculated rate to relieve internal stresses, increase ductility, and refine its grain structure.

Why a Furnace is Essential for Annealing
The annealing process is a sequence of three distinct metallurgical stages, each requiring the precise temperature control and stable environment that a furnace provides.
Stage 1: Recovery
The first step is heating the material within the furnace. As the temperature rises, the furnace allows for a gradual and uniform relief of internal stresses that may have been induced during prior manufacturing processes like bending, machining, or cold working.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
Next, the furnace heats the material above its recrystallization temperature but keeps it safely below its melting point. At this critical temperature, new, strain-free grains begin to form within the material's structure, effectively replacing the deformed grains that contained the internal stresses.
Stage 3: Grain Growth
During the final stage, the material is cooled. The rate of cooling, which is carefully managed by the furnace's control system, dictates the final size of the new grains. A slow cooling process allows the newly formed grains to grow, resulting in a softer, more ductile, and more pliable final product.
A Deeper Look: Solution Annealing
While general annealing aims to soften a material, specialized versions exist for different alloys and goals. Solution annealing is a critical variant used primarily for austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 300 series).
The Goal: Enhance Corrosion Resistance
For these specific steels, the primary goal is not just softening but also maximizing corrosion resistance. The process dissolves harmful chromium carbides that may have precipitated within the material, restoring its protective qualities.
The Process: High Heat and Rapid Cooling
Solution annealing is performed at very high temperatures, typically between 900 °C and 1100 °C. Unlike traditional annealing, this process is followed by a rapid cool-down, or quenching, often in water. This sudden temperature drop locks the dissolved elements in place and prevents the harmful carbides from re-forming.
Understanding the Key Variables
Achieving the desired outcome with annealing depends entirely on controlling the process variables. Mismanagement can lead to undesirable properties.
Cooling Rate is Critical
The speed of cooling is arguably the most critical factor. Slow cooling promotes softness and ductility in general annealing. In contrast, rapid cooling (quenching) is essential for solution annealing to preserve the corrosion-resistant structure of austenitic stainless steels.
Protective Atmosphere Prevents Damage
Many high-quality annealing processes, such as bright annealing, are conducted in a furnace filled with a protective atmosphere (e.g., hydrogen or nitrogen). This controlled atmosphere prevents the hot metal surface from oxidizing or scaling, resulting in a clean, bright finish that requires no subsequent cleaning.
The Risk of Incorrect Temperature
Heating the material for too long or at a temperature that is too high can cause excessive grain growth. While the material will be very soft, this overly large grain structure can significantly reduce its strength and toughness, which is often an undesirable trade-off.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific annealing cycle you use must be tailored to your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximizing softness and ductility: Use a traditional annealing cycle with a slow, controlled cooling rate inside the furnace to allow for grain refinement and growth.
- If your primary focus is restoring corrosion resistance in austenitic stainless steel: Use a solution annealing process, which involves high heat followed by rapid quenching to lock carbides in solution.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace-based annealing process is fundamental to unlocking a material’s full engineering potential.
Summary Table:
| Annealing Stage | Key Process | Furnace Role |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery | Heats material to relieve internal stresses | Provides uniform, gradual heating |
| Recrystallization | Heats above recrystallization temperature | Maintains precise temperature control |
| Grain Growth | Cools material at a controlled rate | Manages cooling rate for desired grain size |
Ready to unlock your material's full potential? KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory furnaces designed for annealing and other critical thermal processes. Whether you need to enhance ductility, restore corrosion resistance, or achieve specific material properties, our equipment ensures the precise thermal control your research demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering



















