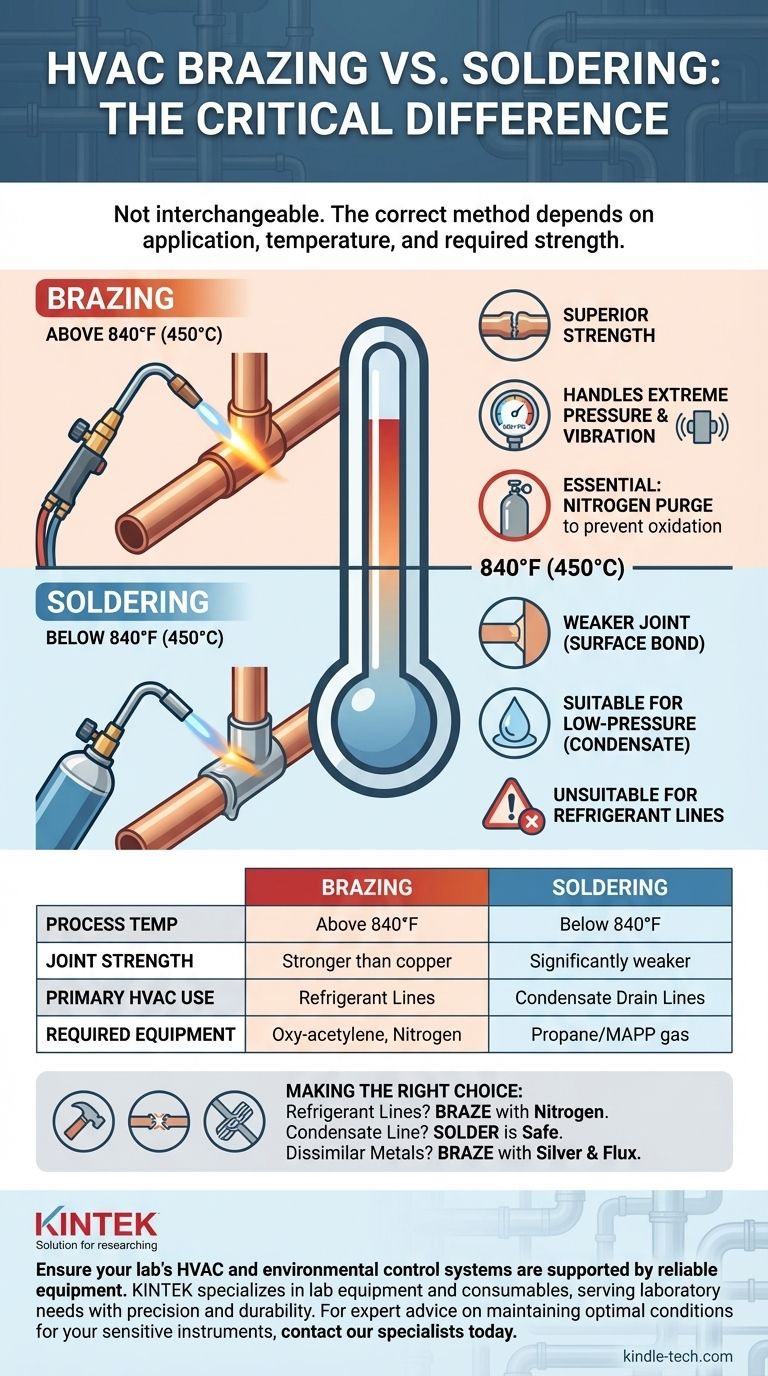
In HVAC, both brazing and soldering are used, but they are not interchangeable. The correct method depends entirely on the application. Brazing is the required standard for joining copper refrigerant lines due to its superior strength, while soldering is reserved for low-pressure applications like condensate drain lines.
The core distinction comes down to temperature and the resulting strength of the joint. Brazing occurs at temperatures above 840°F (450°C), creating a bond that is stronger than the copper pipe itself. Soldering, which happens below this temperature, creates a much weaker joint unsuitable for the high pressures of modern refrigerants.
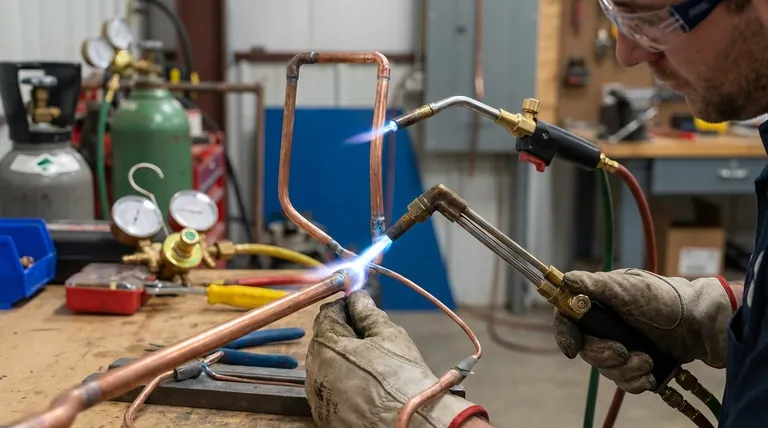

The Fundamental Difference: Temperature and Strength
The terms "brazing" and "soldering" are often confused, but in a technical context, they describe two distinct processes defined by the temperature at which they are performed and the type of filler metal used.
What is Brazing?
Brazing is a metal-joining process where a filler metal with a melting point above 840°F (450°C) is melted and drawn into a tight-fitting joint by capillary action.
In HVAC, this typically involves an oxy-acetylene torch to heat the copper tubing. The filler metal (often a copper-phosphorus or silver alloy) melts, flows into the gap, and forms an exceptionally strong, permanent bond upon cooling.
This high-strength connection is why brazing is the mandatory process for all high-pressure refrigerant lines.
What is Soldering?
Soldering is a similar process but uses a filler metal (solder) with a melting point below 840°F (450°C). The heat source is often a simpler propane or MAPP gas torch.
While the capillary action is the same, the resulting bond is significantly weaker than a brazed joint. It's more of a surface bond, like a strong glue, rather than a metallurgical bond that fuses the materials.
For this reason, soldering is only acceptable for low-pressure applications, such as plumbing for potable water or, in HVAC, for condensate drain lines.
Why Brazing is the Standard for Refrigerant Lines
Using solder on a refrigerant line is a critical mistake that will lead to system failure. Brazing is essential for three primary reasons.
Handling Extreme Pressures
Modern refrigerants like R-410A operate at very high pressures, often exceeding 600 PSI on the high side. A soldered joint simply lacks the mechanical strength to contain these forces and will inevitably leak.
Resisting Vibration
An HVAC system is a dynamic environment. The compressor and fans create constant, subtle vibrations that travel through the copper lines. A brazed joint is ductile and can absorb these vibrations without failing, whereas a soldered joint is more brittle and prone to cracking under long-term stress.
Preventing Oxidation with Nitrogen
A critical, non-negotiable step in HVAC brazing is purging the lines with dry nitrogen during the heating process.
When copper is heated in the presence of oxygen, a black, flaky scale called cupric oxide forms on the inside of the pipe. This scale can break loose, travel through the system, and clog the tiny, precise openings in components like the filter-drier or TXV (Thermostatic Expansion Valve), leading to a complete system blockage and failure.
Flowing a low-pressure stream of nitrogen through the pipe displaces the oxygen, preventing any oxidation from forming and ensuring the inside of the system remains perfectly clean.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While brazing is superior in strength, it requires more skill and specialized equipment than soldering, leading some to cut corners.
Skill and Equipment Requirements
Brazing demands a higher level of skill. The technician must heat the joint evenly to the correct temperature without overheating and damaging the pipe or a nearby valve. It also requires an oxy-acetylene torch setup, which is more complex and expensive than a simple propane torch.
Filler Metal Selection
The choice of brazing alloy is critical. For copper-to-copper joints, a copper-phosphorus alloy (like 15% silver) is common, as the phosphorus acts as a fluxing agent.
However, when brazing copper to a different metal, such as the brass or steel of a service valve, you must use a separate flux and a high-silver-content brazing alloy. Using the wrong rod will result in a weak joint or no bond at all.
The Temptation of "Soft Solder"
Soldering is faster, cheaper, and easier. This makes it tempting for untrained individuals to use it incorrectly on refrigerant lines. This is a severe malpractice that guarantees a future leak, loss of expensive refrigerant, and potential equipment damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice is dictated entirely by the part of the system you are working on.
- If your primary focus is joining refrigerant lines (suction, liquid, or discharge): You must braze with a nitrogen purge to create a strong, clean, and permanent joint.
- If your primary focus is connecting a condensate drain line: Soldering is the correct, safe, and cost-effective method for this low-pressure application.
- If your primary focus is joining copper to a dissimilar metal (like a valve): You must braze using a high-silver alloy and apply flux to ensure a proper bond.
Mastering the correct joining method is a non-negotiable aspect of safe and reliable HVAC work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 840°F (450°C) | Below 840°F (450°C) |
| Joint Strength | Stronger than the base copper pipe | Significantly weaker |
| Primary HVAC Use | High-pressure refrigerant lines | Low-pressure condensate drain lines |
| Required Equipment | Oxy-acetylene torch, nitrogen purge | Propane or MAPP gas torch |
Ensure your lab's HVAC and environmental control systems are supported by reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and durability. For expert advice on maintaining optimal conditions for your sensitive instruments, contact our specialists today and discover the right solutions for your facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Vacuum Cold Mounting Machine for Sample Preparation
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and limitations of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Ultimate Material Integrity
- What is the temperature of a warm isostatic press? Achieve Optimal Densification for Your Materials
- What is the temperature of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Full Density for Critical Components
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- How big is the hot isostatic pressing market? Growth Drivers in Aerospace, Medical & 3D Printing



















