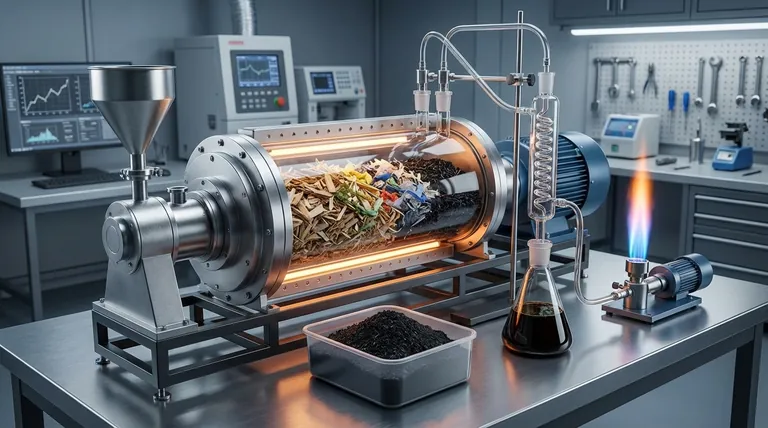
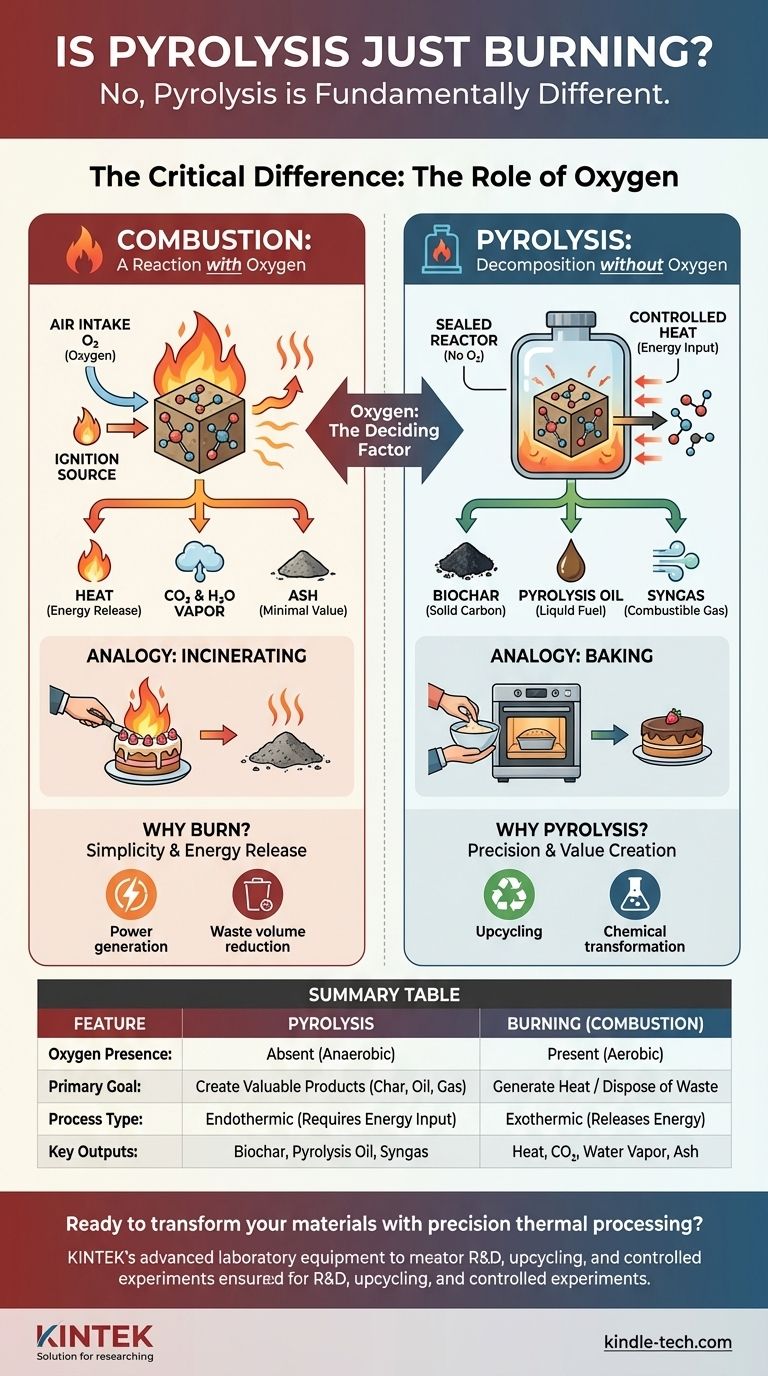
No, pyrolysis is fundamentally different from burning. While both involve high temperatures, burning (combustion) is a chemical reaction with oxygen that destroys a material to release its energy. Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that occurs without oxygen, using heat to deconstruct a material into new, valuable substances.
The critical difference between pyrolysis and burning lies in the presence of oxygen. Burning uses oxygen to break down materials and release energy as heat, while pyrolysis uses heat in an oxygen-free environment to transform materials into valuable char, oil, and gas.

The Role of Oxygen: The Deciding Factor
The presence or absence of oxygen completely changes the chemical pathway and the final outcome of the thermal process. This is the single most important distinction to understand.
Combustion: A Reaction with Oxygen
Burning, or combustion, is a rapid oxidation reaction. A substance combines with oxygen from the air, releasing the stored chemical energy primarily as heat and light.
The original material is consumed and converted into simple, low-energy molecules like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ash.
Pyrolysis: Decomposition without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process. Heat is applied to a material inside a sealed, oxygen-free container.
Instead of reacting with oxygen, the intense heat breaks the complex chemical bonds within the material itself. This deconstructs it into smaller, simpler, but still energy-rich molecules.
An Analogy: Baking vs. Incinerating
Think of "baking" a cake versus setting it on fire.
Baking uses controlled heat in an enclosed oven (low oxygen) to transform ingredients into a new product (a cake). This is analogous to pyrolysis.
Setting the cake on fire uses unlimited oxygen to burn it, releasing heat and leaving behind only ash. This is combustion.
Comparing the Outputs and Energy Flow
The difference in process chemistry leads to drastically different outputs and energy dynamics. One process releases energy, while the other stores it in new products.
Outputs of Burning: Ash and Heat
Combustion is an exothermic process; it generates more energy than it takes to start.
Its primary goal is often energy release for heat or power. The solid byproduct is typically a small amount of mineral ash with no remaining energy value.
Outputs of Pyrolysis: Char, Oil, and Gas
Pyrolysis is primarily an endothermic process; it requires a continuous input of energy to break the chemical bonds.
The goal is not to release energy but to capture it in new forms. The outputs are biochar (a solid carbon material), pyrolysis oil (a liquid fuel), and syngas (a mix of combustible gases). These products retain a high percentage of the original material's energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these processes depends entirely on your objective: are you trying to dispose of something, or create something new?
Why We Burn Things: Simplicity and Energy Release
Combustion is a relatively simple and well-understood process. It is highly effective for immediate heat generation or for drastically reducing the volume of waste material.
The Complexity of Pyrolysis: Precision and Value Creation
Pyrolysis is a more technically complex process that requires specialized equipment like an airtight reactor to control the environment.
Its purpose is not mere disposal but upcycling—transforming low-value feedstocks like plastic waste, tires, or biomass into higher-value chemical products and fuels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the choice between burning and pyrolysis is a choice of intent.
- If your primary focus is immediate heat generation or simple waste disposal: Burning (combustion) is the direct and efficient method.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable products from a feedstock (like turning plastic waste into fuel or biomass into biochar): Pyrolysis is the necessary process for chemical transformation.
Understanding this core distinction empowers you to see one process as energy release and the other as material creation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Burning (Combustion) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Presence | Absent (Anaerobic) | Present (Aerobic) |
| Primary Goal | Create valuable products (char, oil, gas) | Generate heat / Dispose of waste |
| Process Type | Endothermic (requires energy input) | Exothermic (releases energy) |
| Key Outputs | Biochar, Pyrolysis Oil, Syngas | Heat, CO₂, Water Vapor, Ash |
Ready to transform your materials with precision thermal processing?
Whether your goal is efficient waste disposal or creating valuable new products, having the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis reactors, designed for precise control and optimal results.
We help our customers in R&D and industrial labs to:
- Upcycle waste materials like plastics and biomass into valuable resources.
- Conduct controlled thermal decomposition experiments with accuracy and repeatability.
- Achieve their sustainability and material creation goals with reliable, high-performance technology.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















