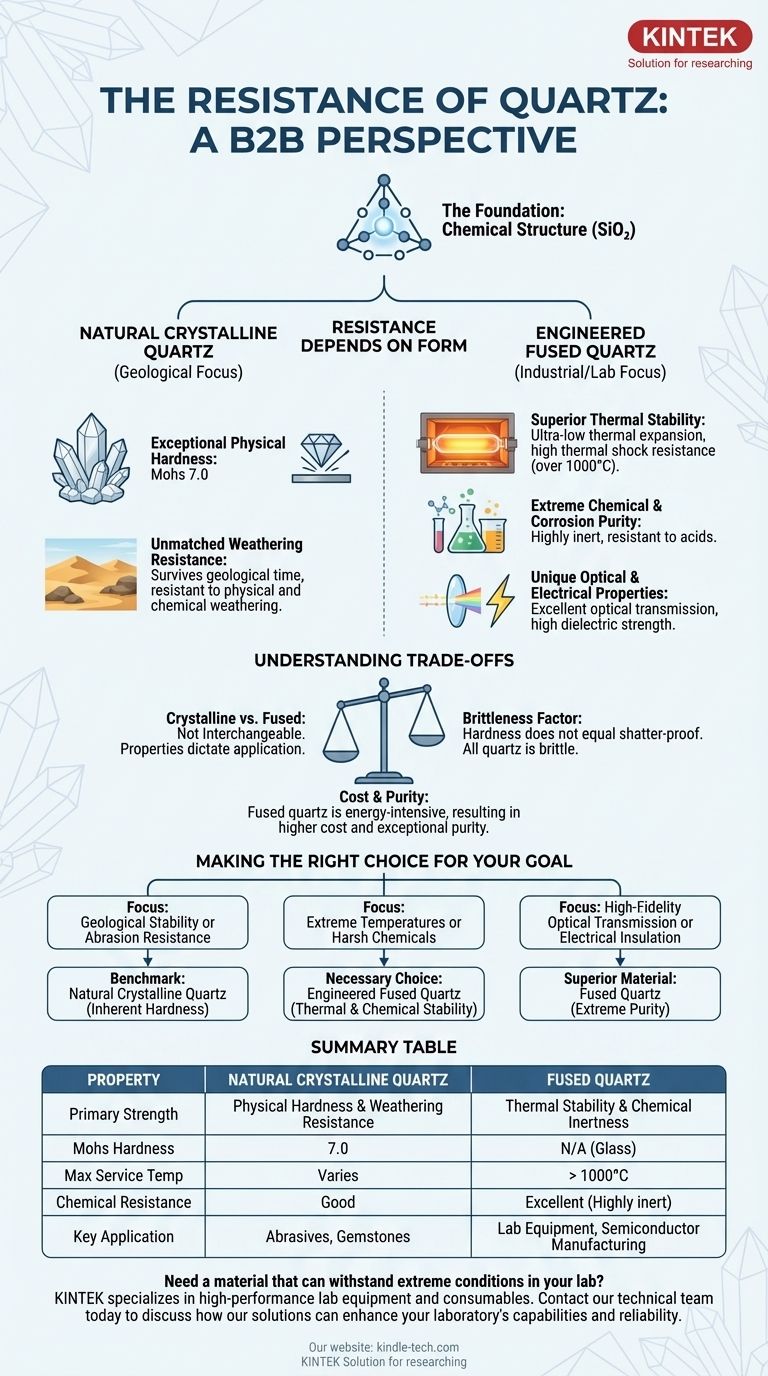
Yes, quartz is an exceptionally resistant material, but its specific resistive properties depend entirely on its form. Natural crystalline quartz is famous for its physical hardness and resistance to weathering, while its manufactured counterpart, fused quartz, offers an extraordinary range of thermal, chemical, and optical resistances.
Quartz's fundamental strength comes from its stable chemical structure. However, its practical application splits into two paths: natural crystalline quartz, which excels in physical durability, and engineered fused quartz, which is designed for extreme thermal and chemical environments.
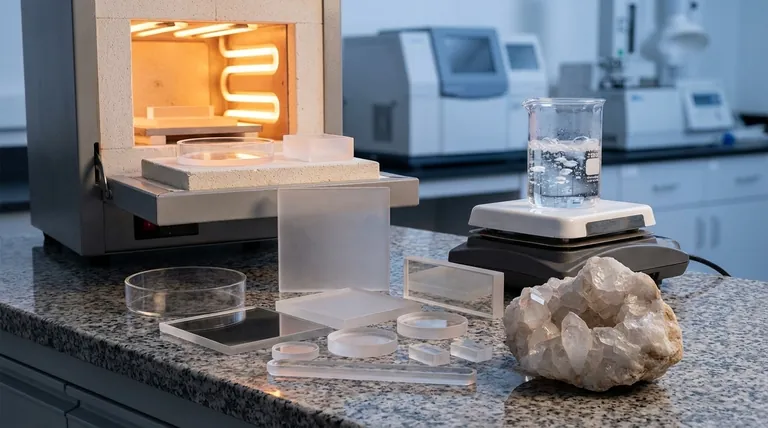

The Foundation of Resistance: Chemical Structure
A Network of Silicon-Oxygen Bonds
At its core, quartz is silicon dioxide (SiO₂). Its atoms are linked in a continuous, strong framework of silicon-oxygen tetrahedra.
This tight, stable covalent bonding is the source of its inherent resistance to being broken down by either physical force or chemical attack.
Resistance in Natural Crystalline Quartz
Exceptional Physical Hardness
Crystalline quartz scores a 7.0 on the Mohs hardness scale.
This makes it harder than steel and highly resistant to scratching and abrasion. It is this property that makes it a durable gemstone and a common abrasive.
Unmatched Weathering Resistance
In nature, quartz is one of the most resistant common minerals to both physical and chemical weathering.
Over geological time, as other minerals in rocks like granite break down and wash away, the durable quartz grains remain. This is why sand on beaches and in deserts is composed primarily of quartz.
Engineered Resistance: The Case of Fused Quartz
What is Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is not a crystal; it is a high-purity industrial glass. It is manufactured by melting down natural quartz crystals and cooling them rapidly enough that they cannot reform a crystalline structure.
This amorphous, non-crystalline structure, combined with extreme purity, gives fused quartz properties far superior to natural quartz or any other type of glass.
Superior Thermal Stability
Fused quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion and elevated resistance to thermal shock.
You could heat it to over 1000°C and plunge it into cold water without it cracking. This makes it essential for applications like semiconductor manufacturing and high-temperature lab equipment.
Extreme Chemical and Corrosion Purity
Due to its high purity and stable structure, fused quartz is highly inert and resistant to corrosion.
It will not react with the vast majority of chemicals, including nearly all acids, making it a critical material for chemical reactors and high-purity fluid handling.
Unique Optical and Electrical Properties
The purity of fused quartz allows it to transmit light across a wide spectrum, from the ultraviolet to the infrared, with minimal distortion.
Furthermore, it is an exceptional electrical insulator with high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand strong electric fields without breaking down.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Crystalline vs. Fused: Not Interchangeable
The properties that make crystalline quartz a great gemstone are completely different from those that make fused quartz ideal for a telescope mirror or a furnace tube.
Choosing between them is not a matter of which is "better," but which is correct for the specific thermal, chemical, or physical stress it will face.
The Brittleness Factor
Despite its hardness, all forms of quartz are brittle. Hardness refers to resistance to scratching, not resistance to shattering.
A sharp, heavy impact can fracture or shatter both natural quartz crystals and fused quartz components.
Cost and Purity
The exceptional properties of fused quartz come from an energy-intensive manufacturing process required to achieve its high purity.
This makes it significantly more expensive than common glass and most other industrial ceramics, restricting its use to applications where its performance is mission-critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the two primary forms of quartz is the key to leveraging its resistance.
- If your primary focus is geological stability or abrasion resistance: Natural crystalline quartz is the benchmark due to its inherent hardness and exceptional resistance to weathering.
- If your primary focus is performance under extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals: Engineered fused quartz is the necessary choice for its unparalleled thermal stability and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is high-fidelity optical transmission or electrical insulation: The extreme purity of fused quartz makes it the superior material for demanding optical and electronic applications.
Ultimately, knowing which type of resistance you need allows you to select the correct form of this remarkable material.
Summary Table:
| Property | Natural Crystalline Quartz | Fused Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Physical Hardness & Weathering Resistance | Thermal Stability & Chemical Inertness |
| Mohs Hardness | 7.0 | N/A (Glass) |
| Max Service Temperature | Varies | > 1000°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent (Highly inert) |
| Key Application | Abrasives, Gemstones | Lab Equipment, Semiconductor Manufacturing |
Need a material that can withstand extreme conditions in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Whether your application requires the thermal stability of fused quartz or the durability of other advanced materials, our experts can help you select the right components for your specific thermal, chemical, and physical challenges.
Contact our technical team today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- 400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
- Zinc Selenide ZnSe Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer and Lens
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the post-annealing treatment of MoS2 photoanodes? Optimize Stability
- What is the role of a high-vacuum high-temperature tube furnace in grain boundary engineering? Enhance Material Strength
- What are the three types of pyrolysis? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process for Your Output
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in pre-oxidation? Master Surface Engineering of Steels
- Why Is Argon Purging Required for FeCrAl Oxidation? Ensure High-Purity Results in Materials Testing
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the CVD synthesis of Fe-C@C nanoparticles? Key Insights
- Where are horizontal furnaces used? Achieve Superior Thermal Processing for Your Materials


















