In essence, a continuous furnace is an industrial heating system designed for uninterrupted processing. Unlike a batch furnace where materials are loaded and unloaded in discrete groups, a continuous furnace constantly moves components through a series of controlled temperature zones, from a charging point to a discharging point.
The core principle of a continuous furnace is not just heating, but creating a highly efficient and consistent production line. It transforms heat treatment from a static, one-off event into a dynamic, flowing process optimized for high-volume manufacturing.
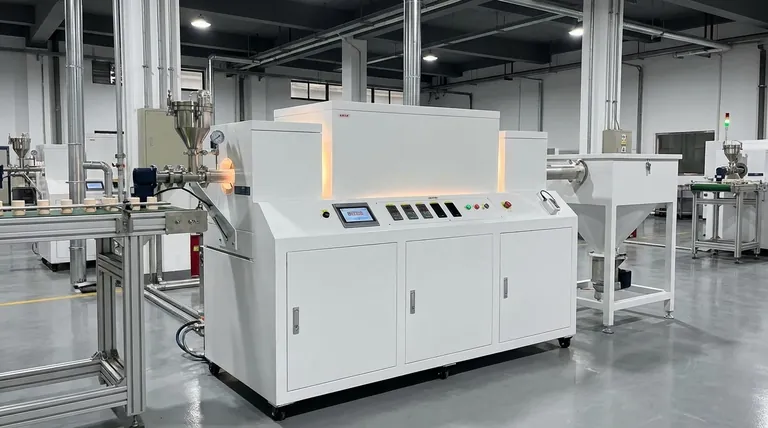

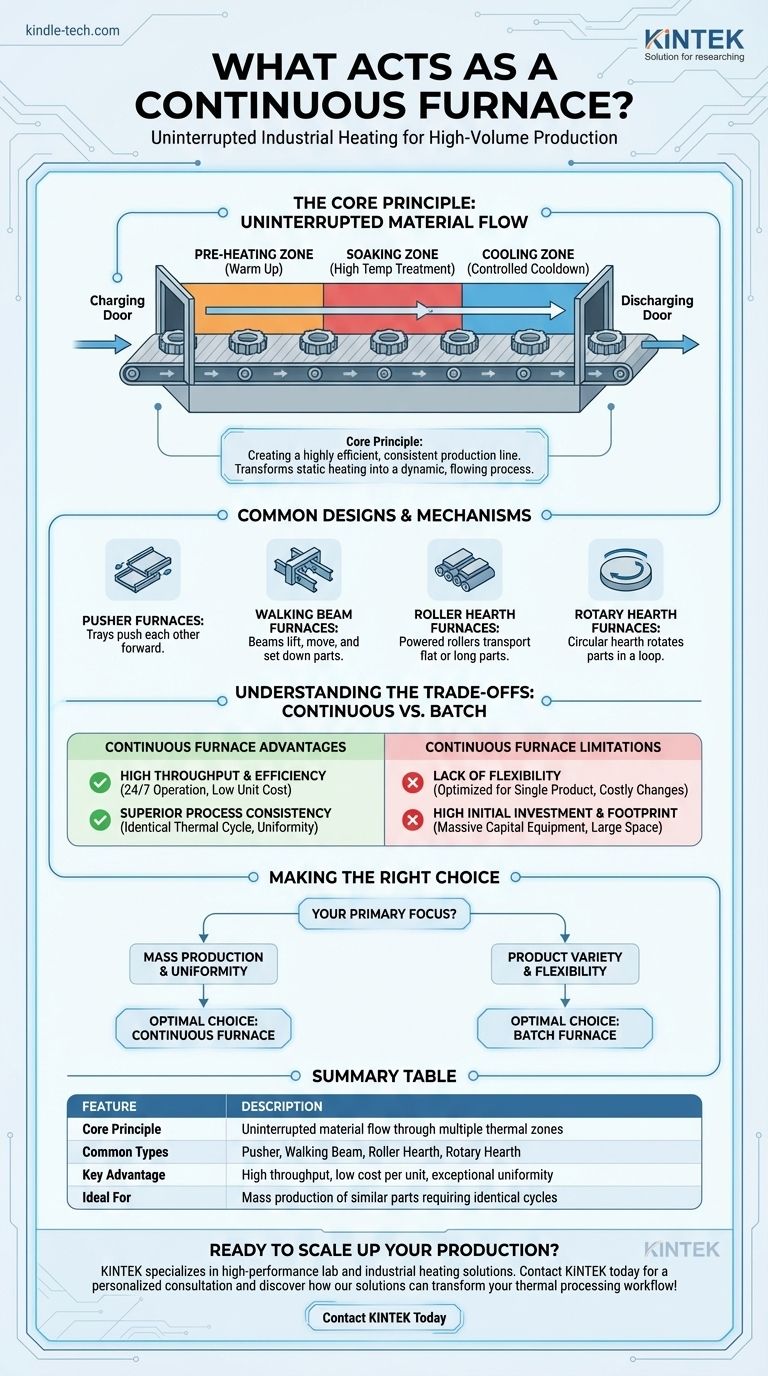
The Core Principle: Uninterrupted Material Flow
The defining feature of a continuous furnace is its ability to process a steady stream of material. This is achieved through a coordinated system of movement and thermal control.
Charging and Discharging
Every continuous furnace has a charging door or entry point where raw or untreated components are fed into the system. They then travel the length of the furnace and exit through a discharging door.
Movement Through Temperature Zones
The journey through the furnace is not uniform. The chamber is typically divided into distinct thermal zones: a pre-heating zone, a high-temperature "soaking" zone where the primary heat treatment occurs, and one or more cooling zones.
This zoned approach ensures each part receives a precise and repeatable thermal profile, which is critical for achieving consistent material properties.
The Goal: Consistent Thermal Processing
By moving every component through the exact same sequence of temperatures for the exact same duration, continuous furnaces eliminate the process variability often found in batch operations. This results in exceptional product uniformity.
Common Designs and Mechanisms
The method used to move components through the furnace defines its specific type and application. The design is chosen based on the size, shape, and fragility of the parts being processed.
Pusher Furnaces
In this design, parts are loaded onto trays. As a new tray is pushed into the charging end, it forces the entire line of trays to advance one position, eventually pushing a finished tray out the discharge end.
Walking Beam or Walking Hearth Furnaces
This mechanism uses a combination of fixed and mobile beams to "walk" products through the furnace. The material is lifted, moved forward, and set down, which is ideal for preventing scratches or damage.
Roller Hearth Furnaces
These furnaces use a series of powered rollers to transport materials. This design is excellent for processing long, flat, or large individual parts like plates, bars, or structural sections.
Rotary Hearth Furnaces
As mentioned in some designs, the furnace chamber is a circular, rotating donut-shaped hearth. Parts are loaded at one point and make a full circle before being unloaded near the starting point, making for a compact footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Continuous vs. Batch
Choosing a continuous furnace involves a clear trade-off between efficiency and flexibility. It is not universally superior to a batch furnace; it is a specialized tool for a specific operational scale.
Advantage: High Throughput and Efficiency
Continuous furnaces are the backbone of mass production. Their ability to run 24/7 with minimal labor intervention results in a very low cost per unit when operated at or near full capacity.
Advantage: Superior Process Consistency
Because the process variables are locked in, the quality of the output is extremely consistent. Every part undergoes the identical thermal cycle, eliminating operator or batch-to-batch variations.
Limitation: Lack of Flexibility
These systems are typically designed and optimized for a single product or a narrow range of similar products. Changing the temperature profile or process is a slow and costly endeavor, making them unsuitable for high-mix, low-volume production.
Limitation: High Initial Investment and Footprint
A continuous furnace is a massive piece of capital equipment. It represents a significant upfront cost and requires substantial floor space compared to the smaller, more modular nature of batch furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision between a continuous or batch furnace hinges entirely on your production goals and operational model.
- If your primary focus is mass production and process uniformity: A continuous furnace is the optimal choice for its unmatched throughput and consistent, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is product variety and operational flexibility: A batch furnace is better suited for smaller, diverse production runs where process parameters must be changed frequently.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating technology requires a clear understanding of whether your priority is industrial-scale efficiency or small-scale adaptability.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uninterrupted material flow through multiple thermal zones for consistent processing. |
| Common Types | Pusher, Walking Beam, Roller Hearth, Rotary Hearth furnaces. |
| Key Advantage | High throughput, low cost per unit, and exceptional process uniformity. |
| Ideal For | Mass production of similar parts requiring identical thermal cycles. |
Ready to scale up your production with a reliable continuous furnace?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and industrial heating solutions tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Whether you're processing metals, ceramics, or other materials, our continuous furnaces are designed for maximum efficiency, durability, and consistent results.
Let our experts help you select the perfect system to boost your throughput and quality.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our solutions can transform your thermal processing workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product



















