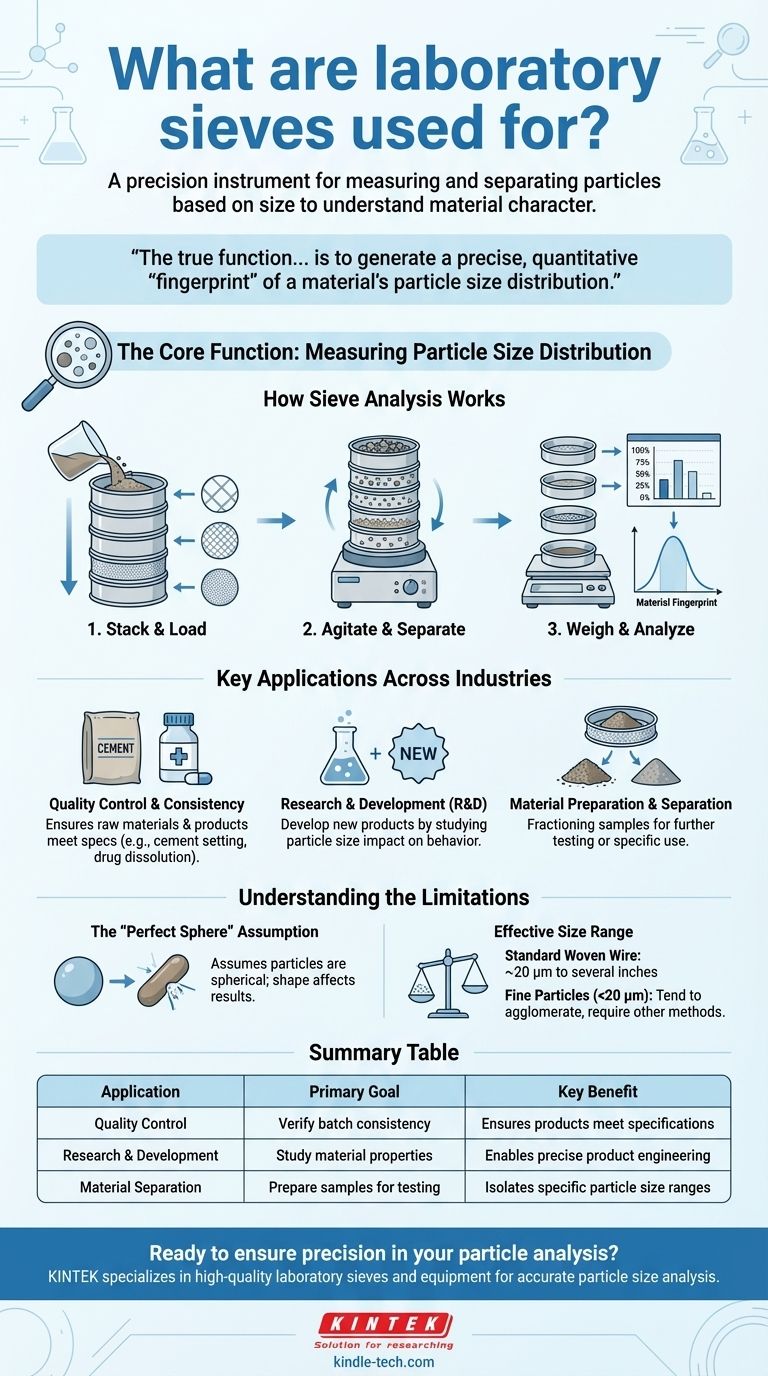
At its core, a laboratory sieve is a precision instrument used for one primary purpose: to measure and separate particles based on their size. This process, known as sieve analysis, is fundamental for understanding the physical character of granular materials, from fine powders to coarse aggregates.
The true function of a laboratory sieve isn't just to sort materials. It's to generate a precise, quantitative "fingerprint" of a material's particle size distribution, which is a critical predictor of its performance, quality, and consistency.

The Core Function: Measuring Particle Size Distribution
The most critical application of laboratory sieves is determining the particle size distribution of a sample. This is not simply finding the average size, but understanding the full range of sizes present and their relative proportions.
How Sieve Analysis Works
The principle is straightforward. A sample is placed on the top sieve in a stacked column, with each sieve below having a progressively smaller mesh opening.
The stack is agitated, causing particles to fall through the apertures until they are retained by a sieve mesh that is smaller than their diameter.
After agitation, the material retained on each sieve is weighed, providing a clear picture of the mass of particles within each size range.
From Raw Data to Actionable Insight
The weight data from each sieve allows you to calculate the percentage of material within specific size fractions.
This data is then often plotted to create a distribution curve, a visual representation of the material's character. This "fingerprint" is essential for comparing batches, ensuring consistency, and meeting specifications.
Key Applications Across Industries
The data generated from sieve analysis is vital for process control and material validation in countless fields, including pharmaceuticals, construction, food science, and chemical manufacturing.
Quality Control and Product Consistency
Sieve analysis is a cornerstone of quality control. It ensures that raw materials and finished products meet precise particle size specifications.
For example, the particle size of cement directly impacts its setting time and strength, while the granule size in pharmaceuticals affects dissolution rates and dosage. Consistent particle size ensures a consistent final product.
Research and Development (R&D)
In R&D, sieves are used to develop new products with desired physical properties. By fractioning materials into narrow size ranges, researchers can study the impact of particle size on a product's behavior.
This allows for the precise engineering of materials, from the texture of a food product to the performance of an industrial abrasive.
Material Preparation and Separation
Beyond analysis, sieves are also used for simple fractioning, or preparing a sample for further testing.
This involves separating a bulk material into specific size ranges. This is often a preliminary step before other forms of chemical or physical analysis where a specific particle size is required.
Understanding the Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis operates on a key assumption and has practical limits. Understanding these is crucial for interpreting results correctly.
The "Perfect Sphere" Assumption
The methodology inherently assumes particles are spherical, measuring the second-smallest dimension that allows them to pass through the square mesh.
Elongated or flat particles may pass through apertures that do not reflect their true volume or longest dimension, a factor that must be considered during analysis.
Effective Size Range
Standard woven wire sieves are highly effective for particles from several inches down to approximately 20 micrometers (μm).
For particles smaller than this, other methods like laser diffraction or air jet sieving are required, as fine particles tend to agglomerate and resist passing through the mesh.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using a laboratory sieve is about more than just the equipment; it's about defining your analytical objective clearly.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Your goal is batch-to-batch consistency, using a standardized procedure to verify that products fall within an established size distribution.
- If your primary focus is material development: You will use sieves to isolate specific particle sizes to test how they influence the bulk properties of your new material.
- If your primary focus is sample preparation: You are simply using the sieve as a tool to separate a bulk sample into the required size fraction for a different analytical test.
Ultimately, laboratory sieves provide a reliable and fundamental method for turning an unknown granular material into a set of known, actionable data points.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | Verify batch consistency | Ensures products meet specifications |
| Research & Development | Study material properties | Enables precise product engineering |
| Material Separation | Prepare samples for testing | Isolates specific particle size ranges |
Ready to ensure precision and consistency in your particle analysis?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory sieves and equipment designed for accurate particle size distribution analysis. Whether your focus is on rigorous quality control, innovative R&D, or precise sample preparation, our solutions deliver the reliable data you need to optimize your processes and products.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieve solution for your laboratory's unique requirements and achieve superior material characterization.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is a sieve used for in construction? Ensure Material Quality and Project Success
- Why is it necessary to process dried SiC mixed powders through sieving equipment? Ensure Uniform Powder Quality
- Why is a 200-mesh sieve required for LCFA ceramic membrane precursor powders? Ensure Defect-Free Membrane Fabrication
- What are the advantages of using a sieve? Achieve Reliable, Low-Cost Particle Analysis
- What problem is solved by installing a Tyler standard sieve mesh at the end of a pyrolysis reactor? Prevent Blockage!
- What is the order of sieves in sieving? Master the Coarse-to-Fine Stack for Accurate Results
- What is the basis of selecting the size of the sieves for the sieve analysis of the given aggregates? Follow the Standard for Accurate Gradation
- How do you calculate sieve mesh size? Use Official Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis



















