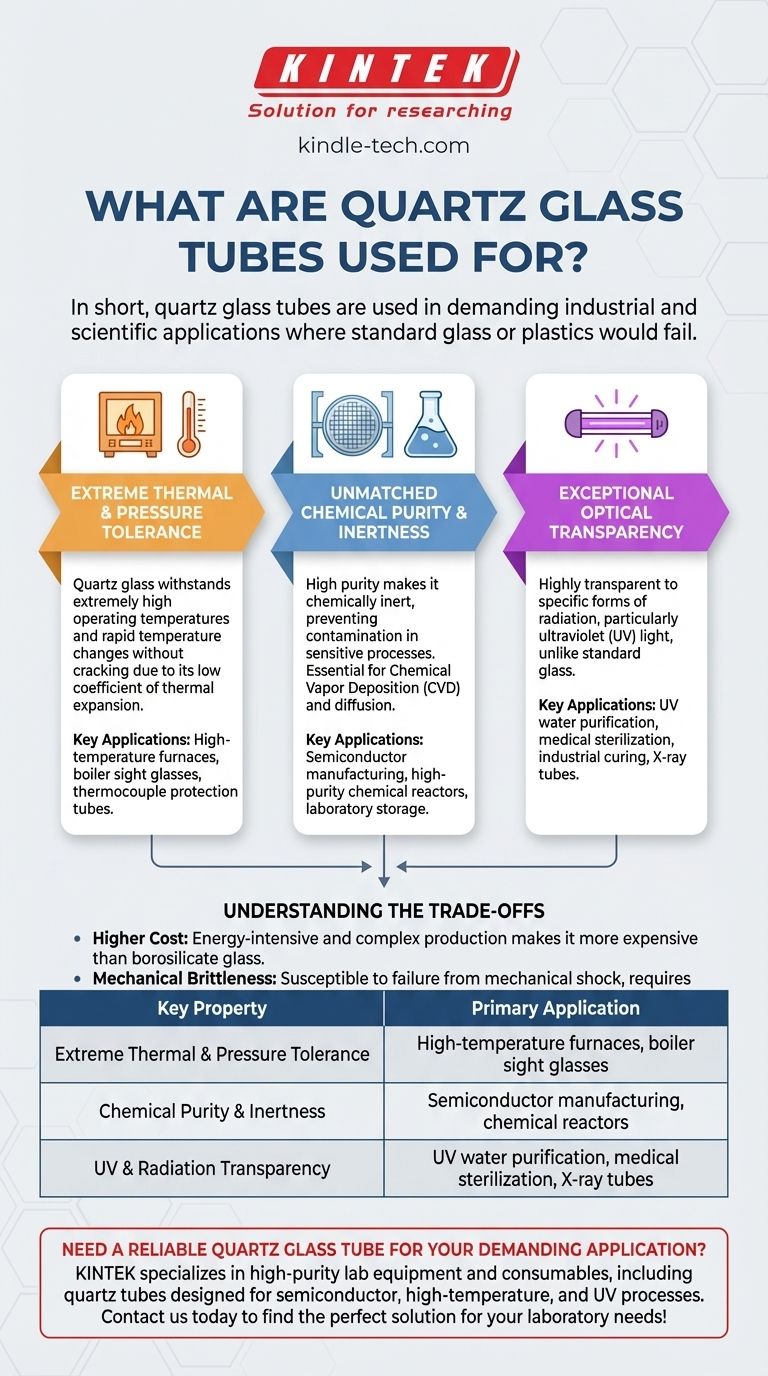
In short, quartz glass tubes are used in demanding industrial and scientific applications where standard glass or plastics would fail. Their use is critical in processes like semiconductor manufacturing (CVD and diffusion), high-temperature furnaces, chemical reactors, and boiler level gauges due to their unique material properties.
The widespread use of quartz glass tubes is not arbitrary; it's a direct result of a powerful combination of three properties: extreme resistance to high temperatures and thermal shock, exceptional chemical purity, and high transparency to specific forms of radiation like ultraviolet light.

The Core Properties Driving Its Use
To understand where quartz tubes are applied, you must first understand the fundamental characteristics that set them apart from common materials like borosilicate (Pyrex) glass.
Extreme Thermal and Pressure Tolerance
Quartz glass is formed from melting extremely pure (99.9%+) natural quartz crystals. This simple, strong structure of silicon dioxide (SiO2) gives it a very low coefficient of thermal expansion.
This means it can withstand extremely high operating temperatures and rapid temperature changes without cracking. It also provides excellent tolerance for high-pressure applications, such as in boiler sight glasses.
Unmatched Chemical Purity and Inertness
The high purity of quartz glass makes it chemically inert, meaning it will not react with or contaminate the vast majority of chemicals.
This property is absolutely critical in semiconductor manufacturing for procedures like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and diffusion, where even trace impurities can ruin silicon wafers. It is also essential for laboratory reactors and high-purity chemical storage.
Exceptional Optical Transparency
Unlike standard glass, which blocks most ultraviolet (UV) light, quartz is highly transparent to it. This makes it the essential material for UV-based applications.
This includes UV water purification systems, medical sterilization devices, and industrial curing processes. It is also transparent to other forms of radiation, leading to its use in components like X-ray tubes.
Key Industrial Applications Explained
These core properties directly translate into specific, high-value industrial uses.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
Quartz tubes act as process chambers or "boats" and carriers for silicon wafers. Their high purity prevents contamination, and their thermal stability is essential for the high-temperature deposition and diffusion steps involved in creating integrated circuits.
High-Temperature Environments
In industrial settings, quartz tubes are used as thermocouple protection tubes, sight glasses for monitoring processes inside furnaces and boilers, and as the core component of furnace heating systems.
Laboratory and Chemical Processing
For scientific research, quartz tubes and vessels serve as reactors for sensitive chemical experiments. Their inertness ensures that the results are not skewed by reactions with the container itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, quartz is not the solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Higher Cost
The process of melting and forming high-purity quartz is energy-intensive and complex. This makes quartz glass tubes significantly more expensive than their borosilicate glass counterparts.
Mechanical Brittleness
Like all ceramics, quartz is brittle. It has excellent thermal and compressive strength but is susceptible to failure from mechanical shock or impact. Careful handling is always required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine if quartz is not only the right choice but the only choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability or thermal shock resistance: Quartz is the ideal material for furnaces, reactors, and sight glasses exposed to rapid temperature cycling.
- If your primary focus is preventing chemical contamination: The extreme purity of quartz makes it non-negotiable for semiconductor fabrication and high-purity chemical analysis.
- If your primary focus is UV light transmission: Quartz is the necessary choice for UV sterilization lamps or curing systems, as standard glass is opaque to UV-C radiation.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a non-demanding application: Standard borosilicate glass is often a more practical and economical alternative for general laboratory use below 500°C.
Ultimately, selecting a quartz glass tube is a decision to prioritize performance, purity, and stability in an environment where other materials would fail.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Application |
|---|---|
| Extreme Thermal & Pressure Tolerance | High-temperature furnaces, boiler sight glasses |
| Chemical Purity & Inertness | Semiconductor manufacturing (CVD, diffusion), chemical reactors |
| UV & Radiation Transparency | UV water purification, medical sterilization, X-ray tubes |
Need a reliable quartz glass tube for your demanding application? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including quartz tubes designed for semiconductor, high-temperature, and UV processes. Our products ensure unmatched thermal stability, chemical inertness, and optical clarity for your critical operations. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is the choice of material for grinding balls and jars critical? Optimize Your Mechanical Alloying Purity
- What are vacuum furnace parts? A Guide to the Core Systems for Precision Heat Treatment
- What is the function of zirconia grinding jars and balls in Li6PS5Cl synthesis? Ensure Purity and High Performance
- What monitoring function do graphite rams perform during vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Eu:Y2O3 Ceramic Densification
- How do oil-free vacuum pumps differ from oil-sealed vacuum pumps in terms of operation? A Guide to Performance vs. Purity
- How does a vacuum drying oven contribute to Ag-SnO2-Y2O3 powder prep? Preserve Purity and Prevent Silver Oxidation
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding
- Why is a K-type thermocouple thermometer necessary for plasma treatment? Ensure Safety in Biological Material Processing



















