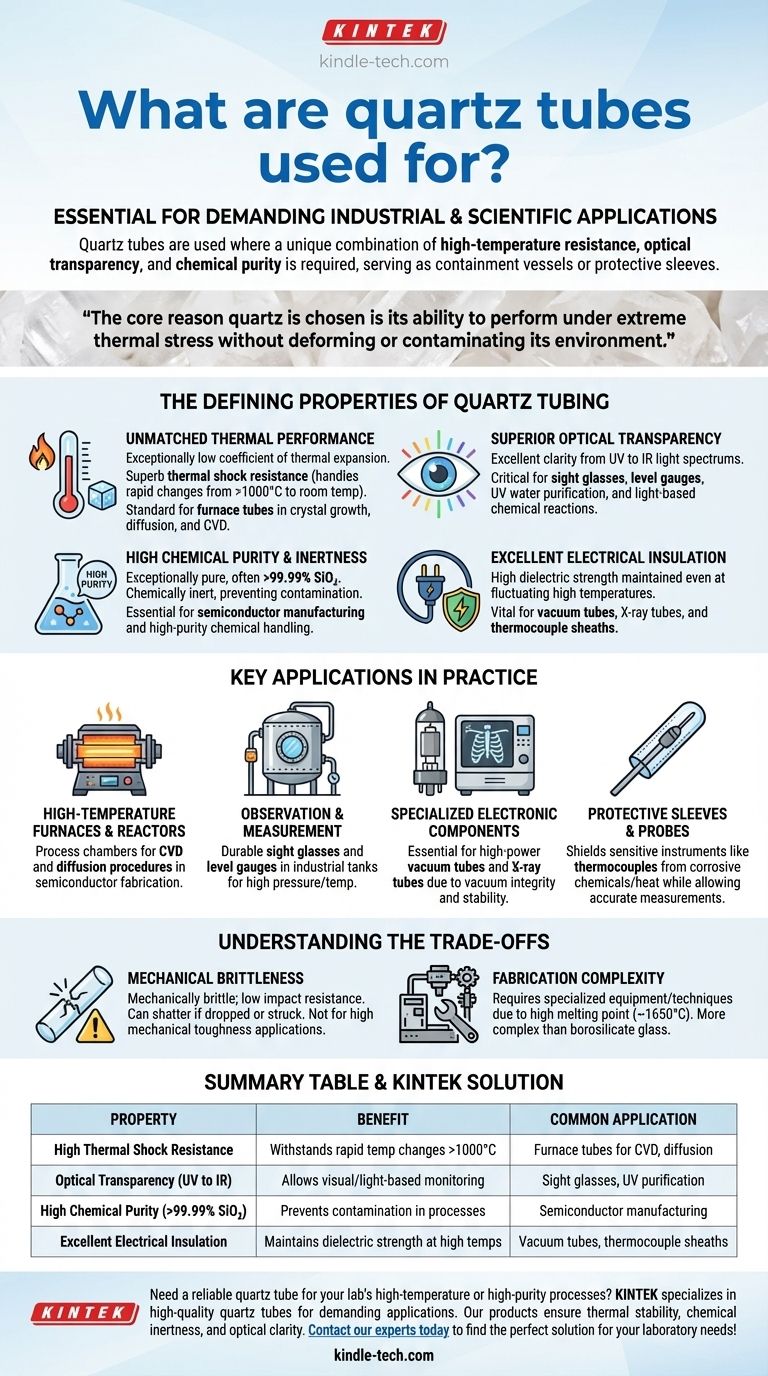
In essence, quartz tubes are used in demanding industrial and scientific applications where a unique combination of high-temperature resistance, optical transparency, and chemical purity is required. They serve as containment vessels or protective sleeves in processes ranging from semiconductor manufacturing and furnace heating to specialized electronic components and fluid level monitoring.
The core reason quartz is chosen over other materials is its ability to perform under extreme thermal stress without deforming or contaminating its environment, all while allowing for visual or optical monitoring of the process inside.

The Defining Properties of Quartz Tubing
The utility of quartz tubes stems from a set of distinct material properties that make them uniquely suited for environments where glass or metal would fail.
Unmatched Thermal Performance
Quartz, specifically fused quartz, possesses an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This gives it exceptional thermal shock resistance, allowing it to endure rapid temperature changes from over 1000°C to room temperature without cracking.
This high-temperature capability makes it the standard material for furnace tubes used in crystal growth, diffusion, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Superior Optical Transparency
Transparent quartz tubes offer excellent clarity across a wide spectrum of light, from ultraviolet (UV) to infrared (IR).
This optical property is critical for applications that require visual monitoring, such as sight glasses and level gauges, or for processes that rely on light energy, such as UV water purification or certain chemical reactions.
High Chemical Purity and Inertness
Industrial quartz tubes are manufactured to be exceptionally pure, often exceeding 99.99% silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
This purity ensures the tube is chemically inert and will not leach contaminants into the process, a non-negotiable requirement in semiconductor manufacturing and high-purity chemical handling.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
Quartz is a superb electrical insulator, maintaining its high dielectric strength even as temperatures fluctuate.
This stability makes it a vital component in creating vacuum tubes, X-ray tubes, and protective sheaths for electrical elements like thermocouples.
Key Applications in Practice
These properties translate directly into specific, high-value industrial uses.
High-Temperature Furnaces and Reactors
The most common application is in horizontal or vertical tube furnaces. Quartz tubes serve as the process chamber for applications like CVD and diffusion procedures in semiconductor fabrication.
Observation and Measurement
Because they are clear and can withstand high pressure and temperature, quartz tubes are used as durable sight glasses and level gauges in industrial tanks and vessels.
Specialized Electronic Components
The combination of vacuum integrity, thermal stability, and electrical insulation makes quartz essential for manufacturing high-power vacuum tubes and X-ray tubes.
Protective Sleeves and Probes
As protective sheaths, quartz tubes shield sensitive instruments like thermocouples from corrosive chemicals or extreme heat while allowing for accurate measurements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its powerful advantages, quartz is not a universally perfect material. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Mechanical Brittleness
The primary drawback of quartz is that it is mechanically brittle. While it is exceptionally resistant to thermal shock, it has low impact resistance and can shatter easily if dropped or struck.
This makes it unsuitable for applications requiring high mechanical toughness or where physical abuse is likely. In such cases, other ceramics might be a better fit.
Fabrication Complexity
Working with quartz requires specialized equipment and techniques due to its extremely high melting point (around 1650°C). This can make custom fabrication more complex and costly compared to standard borosilicate glass.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability and optical clarity: Fused quartz is the definitive choice for furnace tubes, reactors, and sight glasses.
- If your primary focus is process purity in a high-heat environment: The inertness of high-purity quartz is essential for semiconductor and laboratory applications.
- If your primary focus is mechanical toughness and impact resistance: You should consider alternative materials like alumina ceramic, especially if optical transparency is not required.
By understanding its specific strengths and weaknesses, you can effectively leverage quartz tubing in applications where no other material can perform.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| High Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid temp changes >1000°C | Furnace tubes for CVD, diffusion |
| Optical Transparency (UV to IR) | Allows visual/light-based monitoring | Sight glasses, UV purification |
| High Chemical Purity (>99.99% SiO₂) | Prevents contamination in processes | Semiconductor manufacturing |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Maintains dielectric strength at high temps | Vacuum tubes, thermocouple sheaths |
Need a reliable quartz tube for your lab's high-temperature or high-purity processes? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including quartz tubes designed for demanding applications in semiconductor fabrication, research, and industrial heating. Our products ensure the thermal stability, chemical inertness, and optical clarity your work requires. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace required for preparing noble metal catalysts? Unlock Sensor Sensitivity
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum tube furnace for SiCw/2024Al composites? Ensure Pure, High-Strength Results.
- What is the primary purpose of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensure High-Purity Battery Material Synthesis
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What environmental conditions does a vacuum tube furnace provide for copper sintering? Ensure High-Purity Results



















