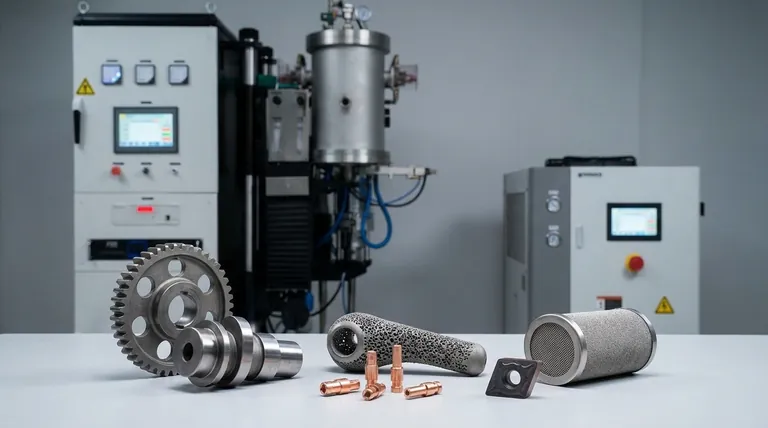
In short, sintered products are used across a vast range of industries to create strong, complex, and specialized components. You will find them in applications from structural automotive parts and self-lubricating bearings to medical implants, electrical contacts, and industrial cutting tools. The process is chosen for its unique ability to work with high-melting-point metals and create intricate shapes with minimal waste.
The core reason for sintering's widespread use is not just the products it creates, but its fundamental ability to control a material's final properties—such as density, porosity, and hardness—in ways that traditional melting and casting cannot.

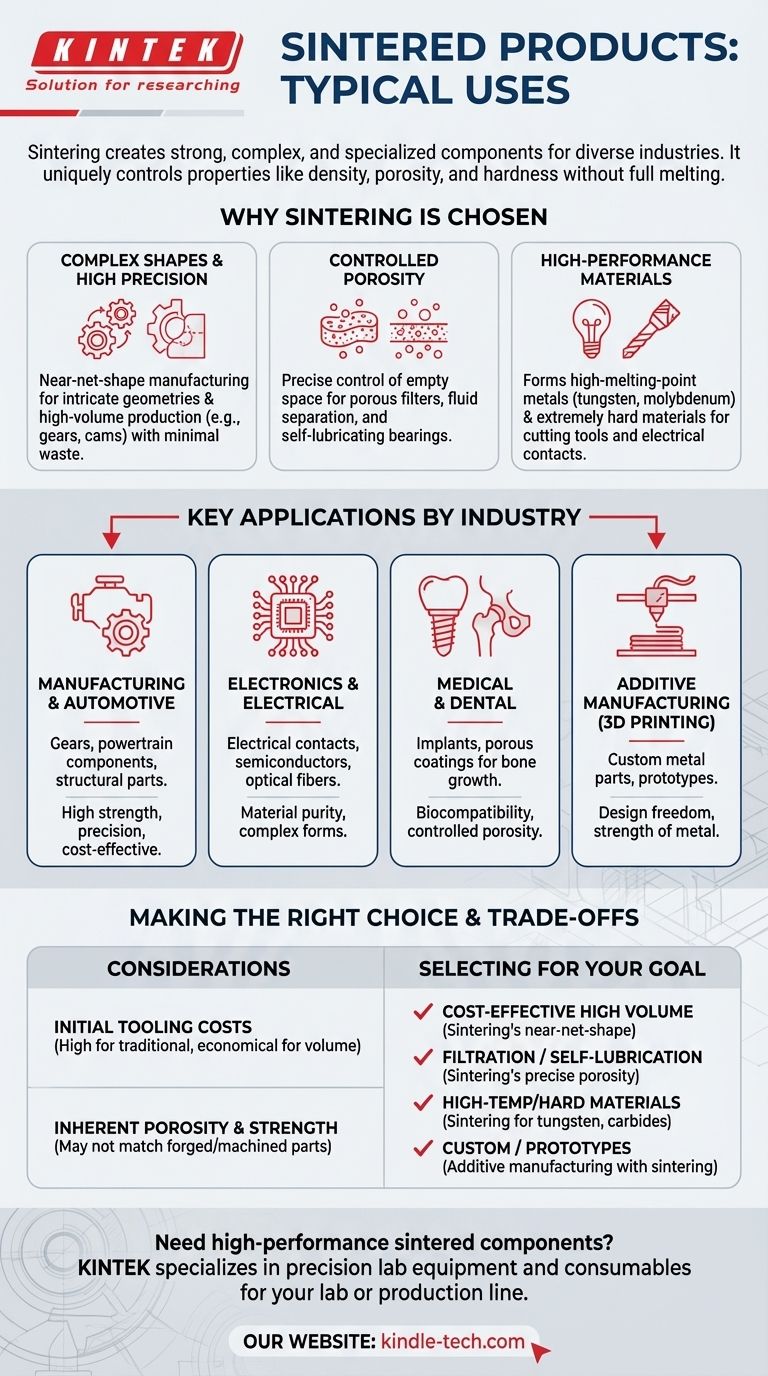
Why Sintering is the Chosen Method
Sintering is a thermal process that uses pressure and heat—below the material's melting point—to bond powder particles together. This fundamental difference from melting is what gives rise to its unique advantages and drives its use in specific, high-value applications.
For Complex Shapes and High Precision
Sintering excels at producing parts that are close to their final dimensions, often called near-net-shape manufacturing.
This process starts with metal or ceramic powder pressed into a mold, allowing for the creation of highly complex geometries that would be difficult or costly to machine from a solid block.
Because very little material is wasted, powder metallurgy is an efficient and cost-effective choice for high-volume production of parts like gears, cams, and structural components.
To Control Porosity for Unique Functions
Unlike melting, which creates a solid, non-porous object, sintering can precisely control the amount of empty space, or porosity, in the final part.
This capability is essential for creating porous metal or plastic filters used in fluid and gas separation. The interconnected pore structure allows fluids to pass through while trapping contaminants.
It is also the principle behind self-lubricating bearings. These components are created with a specific level of porosity and then impregnated with oil, which is released during operation to provide continuous lubrication.
For High-Performance and Specialized Materials
Many advanced materials, like tungsten or molybdenum, have extremely high melting points, making them impractical to shape using traditional casting.
Sintering allows these metals to be formed into useful products, such as tungsten wiring for lightbulb filaments or heating elements, without ever reaching their liquid state.
The process is also used to create extremely hard materials for cutting tools and to manufacture specialized components like electrical contacts and magnetic materials by blending different types of powders.
Key Applications by Industry
The principles above translate into tangible products used every day across critical sectors.
Manufacturing and Automotive
The bulk of sintered parts are structural components for machinery and vehicles. This includes gears, powertrain components, and other complex steel parts where strength and precision are vital.
Electronics and Electrical
Sintering is used to produce electrical components and contacts. It is also a key process in fabricating certain semiconductors and even optical fibers, where material purity and form are critical.
Medical and Dental
The ability to create parts with controlled porosity and from biocompatible materials makes sintering ideal for medical and dental products. This includes porous coatings on implants that encourage bone growth.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Modern metal 3D printing often relies on sintering. A laser selectively sinters layers of metal powder to build a custom object, combining the design freedom of 3D printing with the strength of metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not the ideal solution for every problem.
Initial Tooling Costs
For traditional press-and-sinter powder metallurgy, the cost of creating the initial molds and tooling can be high. This makes it most economical for medium- to high-volume production runs.
Inherent Porosity and Strength
While porosity can be an advantage, any residual porosity in a structural part can be a point of weakness. Sintered parts may not achieve the same ultimate tensile strength as a component forged or machined from a solid billet of the same alloy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of complex metal parts: Sintering is an exceptional choice due to its near-net-shape capability and low material waste.
- If your primary focus is filtration or self-lubrication: Sintering is the definitive method for creating components with precise, controlled porosity.
- If your primary focus is creating parts from high-temperature or extremely hard materials: Sintering provides a practical path to manufacture components from materials like tungsten and carbides that are difficult to melt.
- If your primary focus is custom, one-off metal prototypes or parts: Additive manufacturing techniques that utilize sintering are the clear solution for this need.
Ultimately, sintering is a foundational manufacturing technology that enables the creation of high-performance components that would otherwise be impractical or impossible to produce.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Sintered Products | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Gears, powertrain components | High strength, precision, cost-effective for high volume |
| Medical/Dental | Implants, porous coatings | Biocompatibility, controlled porosity for bone growth |
| Electronics | Electrical contacts, semiconductors | Material purity, complex shapes |
| Industrial | Cutting tools, filters, bearings | Hardness, controlled porosity for self-lubrication |
| Additive Manufacturing | Custom 3D-printed metal parts | Design freedom, strength of metal |
Need high-performance sintered components for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. Whether you require custom sintered parts or reliable sintering equipment, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for materials with high melting points or complex geometries. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your manufacturing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Acid and Alkali Resistant Chemical Powder Material Scoops
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Custom Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
People Also Ask
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?



















