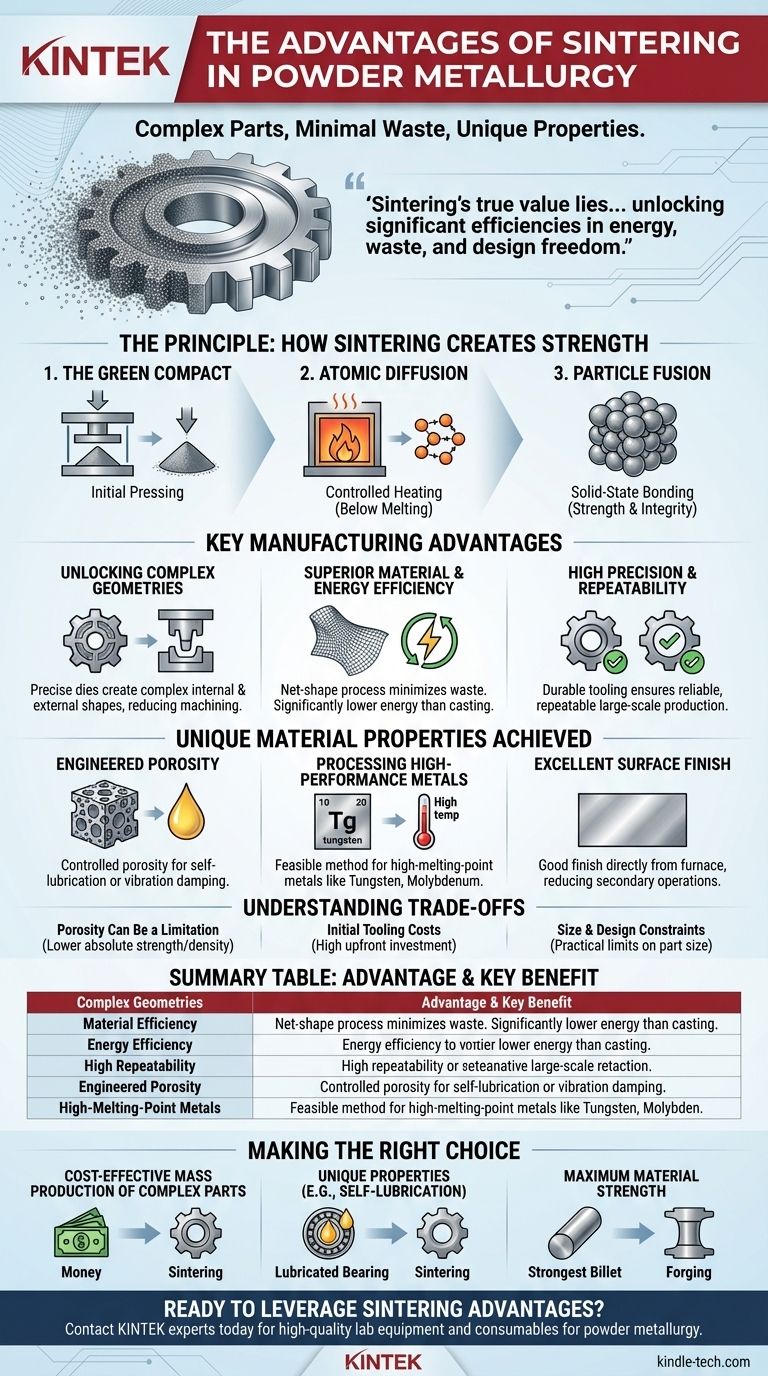
The primary advantages of sintering in powder metallurgy are its ability to create complex, high-precision parts with minimal material waste and its capacity to work with high-melting-point metals that are difficult to process by other means. This heat-based bonding process is highly repeatable, making it ideal for large-scale production, and it allows for the engineering of unique material properties like controlled porosity for self-lubrication.
Sintering's true value lies not just in shaping metal, but in fundamentally changing the manufacturing equation. It decouples the creation of a strong, complex part from the need to melt the material, unlocking significant efficiencies in energy, waste, and design freedom.
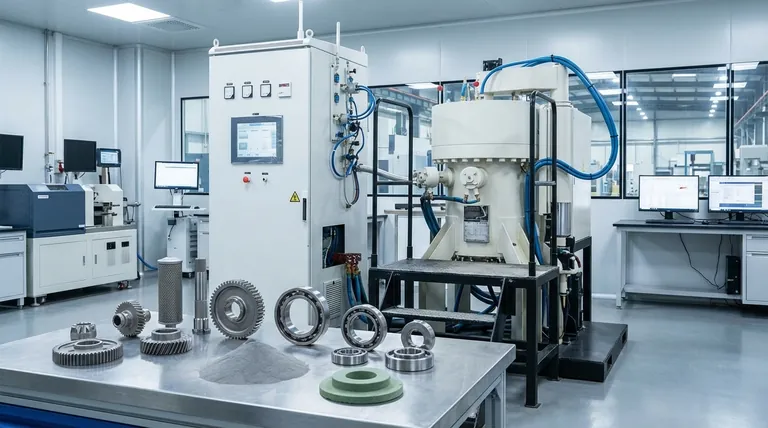

The Principle: How Sintering Creates Strength
Sintering is a heat treatment process that gives a metal part its final strength and integrity. Understanding how it works is key to appreciating its advantages.
The "Green Compact"
The process begins with powdered metal that is pressed into a desired shape using a high-precision mold, or die. This initial, fragile piece is known as a green compact.
The Role of Atomic Diffusion
The green compact is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below the metal's melting point. This heat provides the energy needed to initiate atomic diffusion.
Particle Fusion
At this elevated temperature, the metal particles bond at their contact points, much like ice cubes in a glass of water will fuse together over time. This process of solid-state bonding closes many of the porous spaces between particles, creating a solid, cohesive final part.
Key Manufacturing Advantages
Sintering offers distinct benefits that make it a highly reliable and efficient method for modern manufacturing.
Unlocking Complex Geometries
Because the initial shape is formed by precise dies, sintering can produce parts with very complex external and internal shapes that would be difficult or costly to achieve through traditional machining.
Superior Material and Energy Efficiency
Sintering is a net-shape process, meaning the final part is very close to its final dimensions with minimal material waste. Since the metal is never fully melted, the energy consumption is significantly lower than in casting or forging processes.
High Precision and Repeatability
The use of durable, high-precision tooling ensures that every part is virtually identical. This makes sintering an exceptionally reliable and repeatable method for producing large series of components with tight tolerances.
Unique Material Properties Achieved Through Sintering
Beyond manufacturing efficiency, the sintering process can impart unique and valuable properties to the final product.
Engineered Porosity
Unlike fully dense materials, sintered parts retain a certain level of porosity. This can be a significant advantage, allowing parts to be impregnated with lubricants for self-lubricating bearings or designed to dampen vibrations.
Processing High-Performance Metals
Sintering is one of the few viable methods for manufacturing parts from metals with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum. The process provides a way to consolidate them into a strong, solid form without the extreme energy required for melting.
Excellent Surface Finish
The process typically results in a good surface finish directly from the furnace, reducing the need for extensive secondary finishing operations.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
No process is perfect, and being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the limitations.
Porosity Can Be a Limitation
While controlled porosity is an advantage for some applications, it also means that sintered parts may not achieve the same absolute strength or density as a part forged or machined from a solid billet.
Initial Tooling Costs
The precision molds and dies required for the initial pressing stage represent a significant upfront investment. This makes sintering most cost-effective for high-volume production runs where the cost can be amortized over many thousands of parts.
Size and Design Constraints
There are practical limits to the size of parts that can be produced via powder metallurgy. Furthermore, uniform density can be challenging to achieve in very large or unusually complex parts during the initial pressing phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex parts: Sintering is an ideal choice due to its high repeatability and minimal material waste.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with unique properties like self-lubrication: Sintering is often the only practical method to achieve controlled porosity.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum material strength and impact resistance: You should consider processes like forging, which produce a fully dense and work-hardened material.
Ultimately, sintering empowers engineers to design and manufacture parts based on the unique advantages of solid-state bonding, moving beyond the limitations of traditional casting and machining.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Complex Geometries | Produces intricate shapes difficult with other methods |
| Material Efficiency | Net-shape process with minimal waste |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy use than melting-based processes |
| High Repeatability | Ideal for large-scale, high-precision production |
| Engineered Porosity | Enables self-lubrication and vibration damping |
| High-Melting-Point Metals | Processes metals like tungsten and molybdenum |
Ready to leverage the advantages of sintering for your laboratory or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for precise and efficient powder metallurgy processes. Whether you are researching new materials or scaling up production, our solutions can help you achieve superior results with complex parts, minimal waste, and unique material properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your sintering and powder metallurgy needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the key functions of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Produce High-Density UN Ceramic Pellets
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context



















