At its core, brazing is a highly versatile metal-joining process used across a vast range of industries. It is commonly applied to create strong, leak-proof joints in automotive components, HVAC systems, electromechanical housings, aerospace hardware, and medical equipment.
Brazing is selected not just for the products it creates, but for the engineering challenges it solves. Its true value lies in its ability to join complex assemblies, dissimilar metals, and parts with thin cross-sections where other methods would fail.
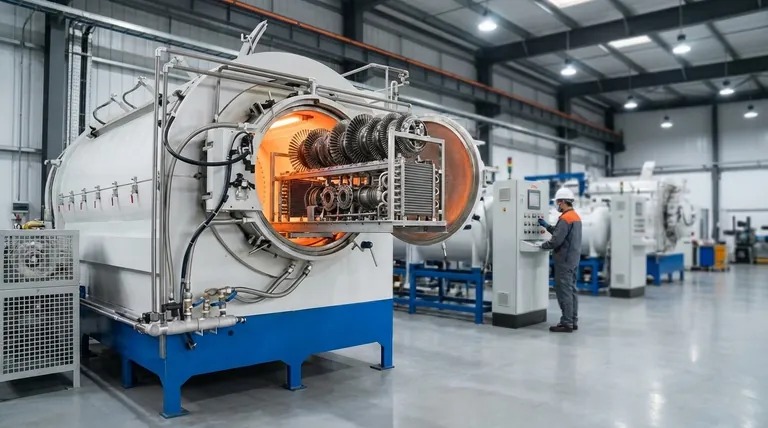

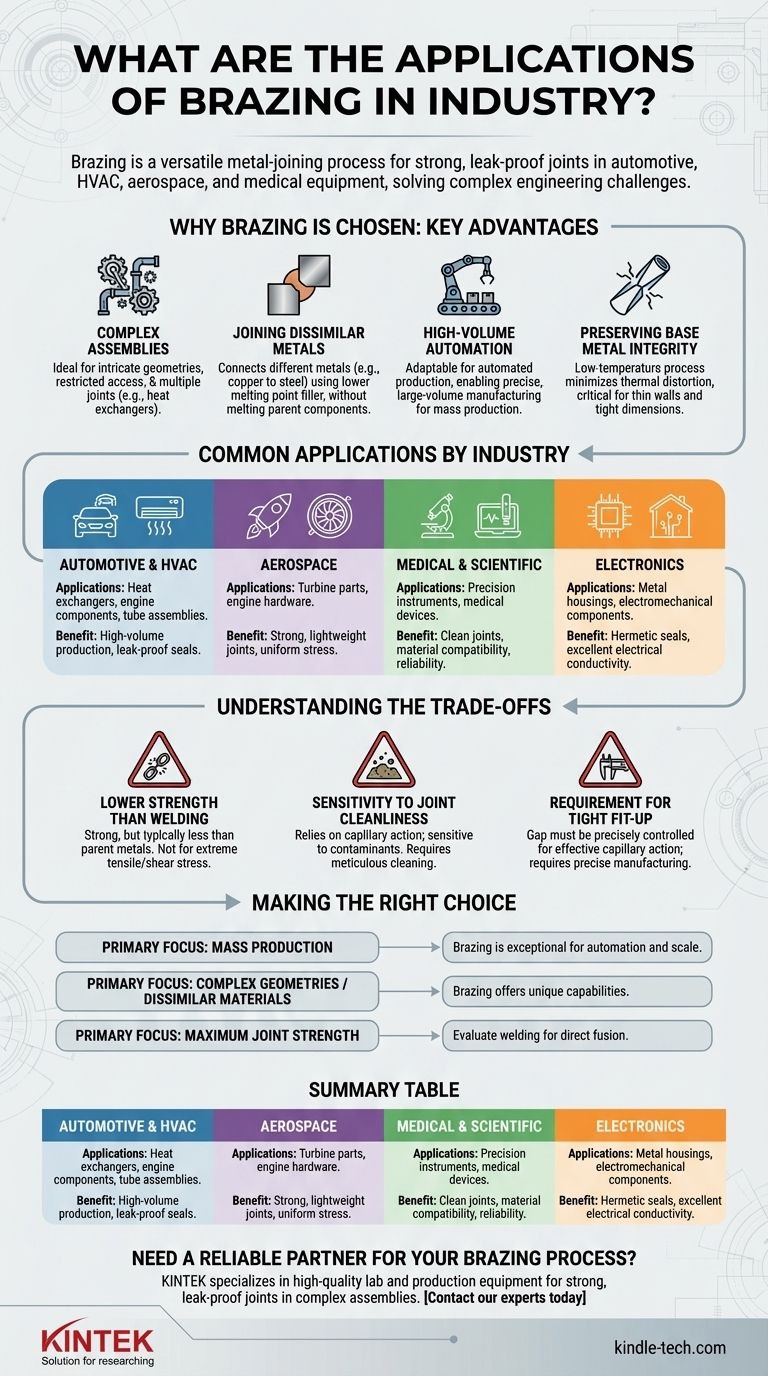
Why Brazing is Chosen: Key Advantages
To understand its wide application, we must look at the specific technical problems that brazing solves better than other joining methods.
Creating Complex or Intricate Assemblies
Brazing is exceptionally well-suited for parts with complex geometries. It allows for joining components with restricted access or creating multiple joints on a single assembly simultaneously, as is common with furnace brazing.
This makes it ideal for items like heat exchangers, which have a dense network of tubes and fins.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
The process uses a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base materials being joined. This fundamental characteristic allows for the successful joining of different metals, such as copper to steel or aluminum to copper, without melting the parent components.
High-Volume and Automated Production
Brazing is highly adaptable to automation. Automatic brazing machines can be programmed to produce large volumes of parts quickly and with precise tolerances, making the process cost-effective for mass production.
This is a primary reason for its prevalence in the automotive and HVAC industries.
Preserving Base Metal Integrity
Because brazing occurs at temperatures below the melting point of the base materials, it minimizes the risk of thermal distortion. This is critical when working with thin-walled tubes, machined assemblies, or components requiring tight dimensional control after joining.
Common Applications by Industry
Brazing's unique advantages lead to its adoption in sectors where reliability, precision, and material compatibility are paramount.
Automotive and HVAC
This is a high-volume sector for brazing. Applications include engine components, hydraulic fittings, and air conditioning system components like heat exchangers and tube assemblies. The process provides the necessary strength and leak-proof seals for these fluid- and gas-handling systems.
Aerospace and High-Performance Engineering
In aerospace, brazing is used for critical components like industrial gas turbine parts and other engine hardware. The ability to create strong, lightweight joints with uniform stress distribution is essential for performance and safety in these demanding environments.
Medical and Scientific Equipment
The medical field relies on brazing for manufacturing precision scientific instruments and devices. The clean, strong joints and compatibility with various metals are crucial for applications where reliability and hygiene are non-negotiable.
Electronics and Electromechanical Components
Brazing is used to assemble metal housings and other electromechanical components. It provides excellent electrical conductivity and hermetic seals, protecting sensitive electronics from the environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the limitations of brazing.
Lower Strength Than Welding
While a properly brazed joint is strong—often stronger than the filler metal itself—it typically does not reach the full strength of the parent materials. For applications under extreme tensile or shear stress, a full-penetration weld may be a better choice.
Sensitivity to Joint Cleanliness
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the joint. This action is extremely sensitive to contaminants like oils, oxides, and dirt. A successful brazing operation requires meticulous cleaning and preparation of the joint surfaces.
Requirement for a Tight Fit-Up
For capillary action to work effectively, the gap between the two parts being joined must be precisely controlled. Gaps that are too small or too large will result in a weak or incomplete joint, requiring more precise manufacturing of the individual components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct joining process depends entirely on your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is mass production of reliable components: Brazing is an exceptional choice due to its suitability for automation and its ability to create consistent, high-quality joints at scale.
- If your primary focus is joining complex geometries or dissimilar materials: Brazing offers unique capabilities that are often impossible to achieve with conventional welding.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum joint strength on simple assemblies: You may want to evaluate welding processes that fuse the parent metals directly.
Ultimately, brazing is a powerful and versatile tool chosen when precision, material compatibility, and assembly complexity are the driving engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & HVAC | Heat exchangers, engine components, tube assemblies | High-volume production, leak-proof seals |
| Aerospace | Turbine parts, engine hardware | Strong, lightweight joints, uniform stress |
| Medical & Scientific | Precision instruments, medical devices | Clean joints, material compatibility, reliability |
| Electronics | Metal housings, electromechanical components | Hermetic seals, excellent electrical conductivity |
Need a reliable partner for your brazing process? The right equipment is crucial for achieving strong, leak-proof joints in complex assemblies. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab and production equipment, including brazing solutions, to meet the precise demands of industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your production goals with the right technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer



















