In modern dentistry, ceramics are a cornerstone material used for a wide range of restorative applications. They are found in fixed prostheses like crowns and bridges, serve as critical strengthening fillers in resin-composite materials, and are key components in the dental cements used to bond restorations to teeth.
The core reason for the widespread use of ceramics is their unique ability to mimic the appearance and function of natural teeth. They offer a superior combination of aesthetics, biocompatibility, and durability that metals and polymers alone cannot match.
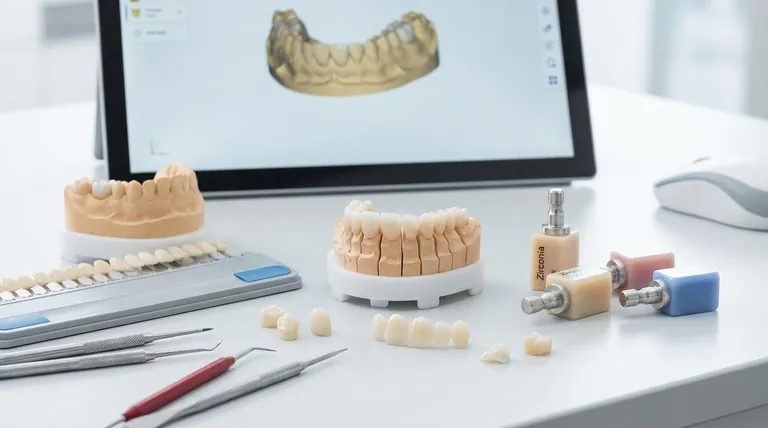
Why Ceramics are Central to Restorative Dentistry
The dominance of ceramics stems from a set of highly desirable physical and biological properties. These characteristics solve the fundamental challenges of replacing tooth structure.
Unmatched Aesthetics
Ceramics can be manufactured with varying levels of translucency, opacity, and color, allowing for a near-perfect match to a patient's natural dentition. This capability is essential for restorations, especially in the anterior (front) of the mouth. They are also highly resistant to staining.
Superior Biocompatibility
Dental ceramics are biologically inert, meaning they do not trigger immune or allergic responses in the body. This is a significant advantage over some metal alloys, which can cause reactions in sensitive patients.
High Compressive Strength
Ceramics exhibit exceptional compressive strength, enabling them to withstand the powerful chewing forces exerted in the mouth, particularly in the posterior (back) region.
Chemical and Thermal Stability
These materials are chemically stable and do not corrode over time. They are also poor thermal conductors, which helps insulate the underlying tooth pulp from sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.
Key Ceramic Systems and Their Applications
Not all ceramics are the same. Different formulations are used to optimize for either strength or aesthetics, dictating their clinical application.
Feldspathic Ceramics
This is the traditional dental porcelain, known for its outstanding optical properties. Due to its lower strength, it is primarily used for aesthetic veneers and some low-stress anterior crowns where appearance is the highest priority.
Glass-Ceramics
Materials like lithium disilicate represent a major advancement, offering an excellent balance of strength and beauty. They are strong enough for single crowns in any part of the mouth, as well as for inlays, onlays, and short-span bridges.
Polycrystalline Ceramics
Zirconia is the strongest ceramic available in dentistry. It lacks the natural translucency of glass-ceramics but provides exceptional fracture resistance, making it the material of choice for posterior crowns, long-span bridges, and implant abutments.
Ceramic-Filled Composites and Cements
Ceramic particles are added as fillers to resin-composite filling materials to improve their wear resistance and strength. Similarly, they are used in modern luting cements to enhance the mechanical properties of the bond between the restoration and the tooth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, ceramics are not without their limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for successful long-term outcomes.
Brittleness and Fracture Risk
The primary weakness of ceramics is their brittleness. While strong under compression, they can fracture under tension or if subjected to a sharp impact. This requires precise preparation design and careful handling by the dentist and laboratory.
Potential for Abrasiveness
Some high-strength ceramics, particularly older formulations of zirconia, can be more abrasive than natural enamel. This can cause wear on the opposing natural teeth over time, a factor that must be considered in material selection.
Fabrication Complexity
Creating a high-quality ceramic restoration is a technically demanding process. Whether layered by hand or milled with CAD/CAM technology, it requires a high degree of skill and precision to achieve proper fit, form, and function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a ceramic material is always dictated by the specific clinical need, balancing the demands of strength and aesthetics.
- If your primary focus is anterior aesthetics: Glass-ceramics (lithium disilicate) or traditional feldspathic porcelain offer the most lifelike results for veneers and front crowns.
- If your primary focus is posterior strength: Zirconia is the definitive choice for crowns and bridges in high-stress areas due to its superior fracture resistance.
- If your primary focus is a single-unit restoration anywhere in the mouth: Lithium disilicate provides an exceptional balance of proven strength and high-end aesthetics.
- If your primary focus is a direct filling: Resin composites with ceramic fillers provide a durable and aesthetic solution for repairing small to moderate cavities.
Ultimately, the versatility of ceramics empowers dental professionals to restore both function and beauty with remarkable predictability.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Ceramic Type | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Crowns & Bridges | Zirconia, Lithium Disilicate | High Strength & Durability |
| Veneers | Feldspathic Porcelain | Superior Aesthetics |
| Inlays/Onlays | Lithium Disilicate | Balance of Strength & Beauty |
| Resin Composites | Ceramic Fillers | Enhanced Wear Resistance |
| Dental Cements | Ceramic Particles | Improved Bond Strength |
Achieve superior dental restorations with KINTEK's advanced ceramic solutions.
Whether you are fabricating crowns, bridges, veneers, or composites, the right ceramic material is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support the precise fabrication of dental ceramics, ensuring optimal strength, aesthetics, and biocompatibility for your patients.
Let us help you enhance your practice’s capabilities—contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What would be an advantage of biomass over the use of coal? A Cleaner, Carbon-Neutral Energy Source
- What function does a high-temperature sintering furnace serve in biomass carbonization? Unlock Superior MFC Performance
- What are the key differences between incineration and gasification? Explore Waste Management Solutions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs












