Crucible furnaces are primarily used for melting and holding small to medium batches of non-ferrous metals. Their applications range from artisan jewelry making and small-scale foundry work to laboratory research and development. They are valued for their flexibility, allowing for quick changes between different metals with minimal contamination.
A crucible furnace's key advantage is its versatility—the ability to melt diverse, small batches of metal cleanly. This flexibility, however, often comes at the cost of lower energy efficiency and limited capacity compared to large-scale industrial furnaces.
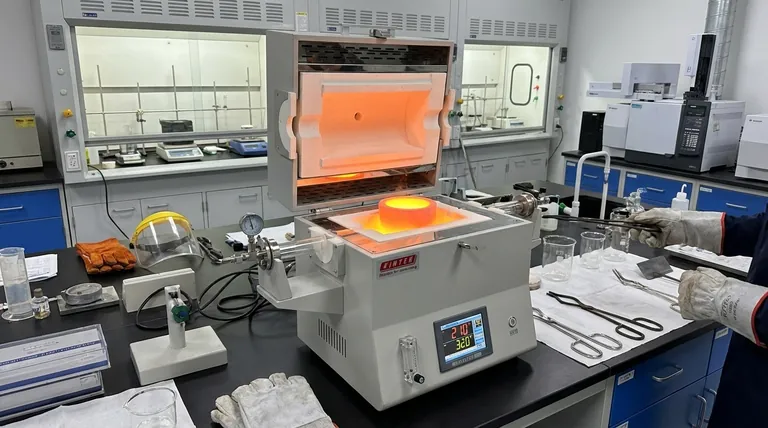

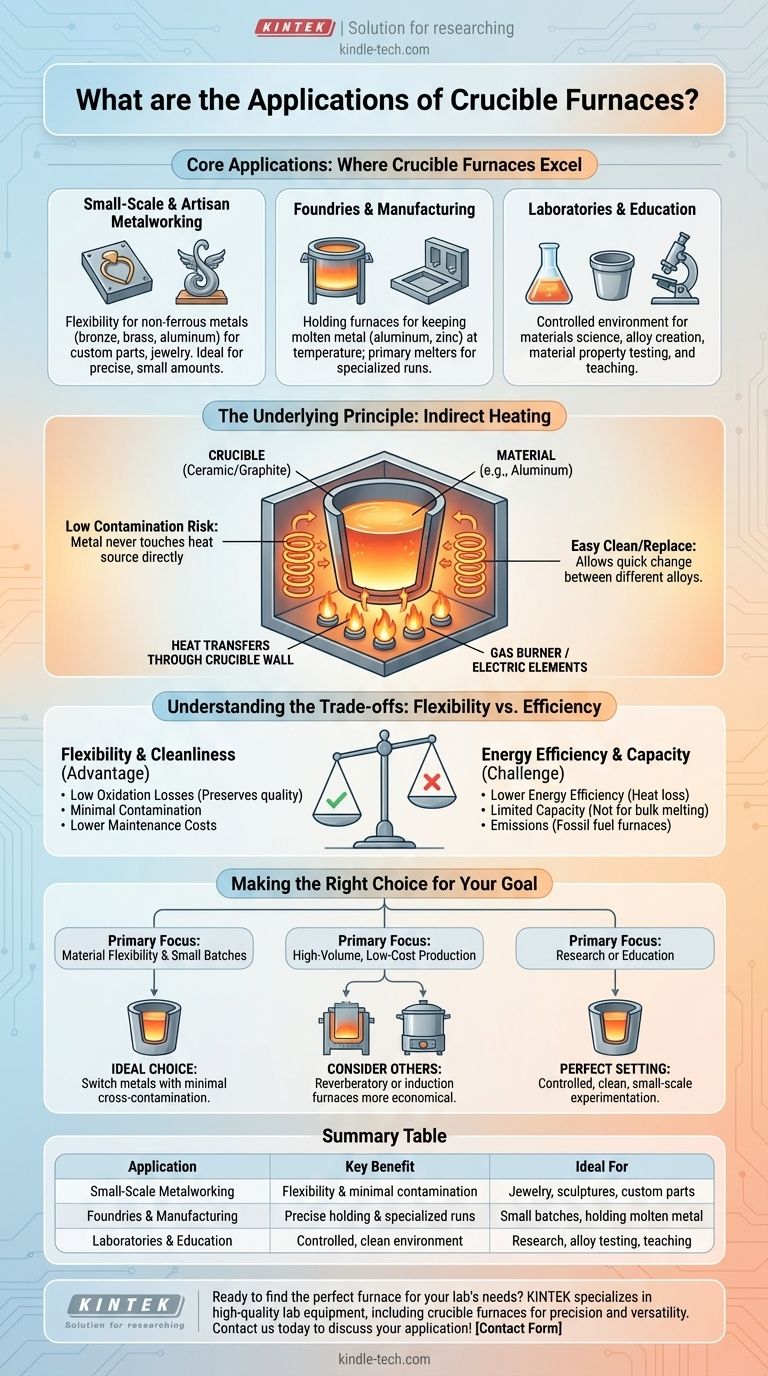
Core Applications: Where Crucible Furnaces Excel
A crucible furnace is chosen when the ability to handle different materials in small quantities is more important than raw production volume.
Small-Scale and Artisan Metalworking
Crucible furnaces are a cornerstone for craftspeople and small businesses. They are ideal for melting metals like bronze, brass, and aluminum for custom parts, sculptures, and jewelry. The ability to melt a small, precise amount for a single project is invaluable.
Foundries and Manufacturing
In larger industrial settings, crucible furnaces serve specialized roles. They are often used as holding furnaces, keeping a batch of molten metal like aluminum or zinc at the correct temperature before it's used for casting. They also serve as primary melters for small, specialized production runs.
Laboratories and Education
For materials science, chemistry, and engineering research, crucible furnaces provide a controlled environment. They allow for the creation of specific alloys and the testing of material properties on a manageable scale. Their simplicity also makes them excellent teaching tools in vocational schools and universities.
The Underlying Principle: Indirect Heating
The function of a crucible furnace dictates both its strengths and its weaknesses.
How It Works
The material to be melted (e.g., aluminum) is placed inside a container called a crucible, which is typically made of ceramic or graphite. This crucible is then heated from the outside by a gas burner or electric elements. The heat transfers through the crucible wall to melt the contents.
Why This Matters for Versatility
Because the metal never touches the heat source directly, the risk of contamination is extremely low. After a melt, the crucible can be cleaned or replaced, allowing a completely different alloy or metal to be melted next. This is a significant advantage over furnaces where the metal is in direct contact with the furnace lining.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Flexibility vs. Efficiency
No single tool is perfect for every job. The primary trade-off for a crucible furnace is its operational efficiency.
The Advantage of Cleanliness and Control
Indirect heating results in low oxidation losses, as the metal is not exposed to the direct flame of combustion. This preserves the quality of the melt. Maintenance costs are also often lower because the furnace's structural components are not in direct contact with corrosive molten metal.
The Challenge of Energy Efficiency
Transferring heat indirectly is fundamentally less efficient than direct heating methods. A significant amount of energy is lost heating the air around the crucible and the crucible itself. While modern designs with high-quality refractory and insulation have vastly improved performance, many traditional crucible furnaces can have very low energy efficiency, some as low as 12%.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
Furnaces powered by fossil fuels produce emissions that may require separate pollution control measures. Due to their lower efficiency, crucible furnaces can consume a lot of power, making them less economical for large-scale, continuous operations compared to other furnace types.
Capacity and Scale Limitations
By their nature, crucible furnaces are limited in size. They are simply not designed for the bulk melting required in major industrial foundries. Their strength lies in batches, not continuous, high-volume throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace requires aligning the technology with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is material flexibility and small batches: A crucible furnace is an ideal choice, offering the ability to switch between different non-ferrous metals with minimal cross-contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: The energy inefficiency and capacity limits of a crucible furnace make other options, like reverberatory or induction furnaces, more economical.
- If your primary focus is research or education: The controlled, clean, small-scale melting environment of a crucible furnace provides the perfect setting for experimentation and teaching fundamental principles.
Ultimately, choosing a crucible furnace is a strategic decision that prioritizes versatility and melt quality for small-scale operations.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Small-Scale Metalworking | Flexibility & minimal contamination | Jewelry, sculptures, custom parts |
| Foundries & Manufacturing | Precise holding & specialized runs | Small batches, holding molten metal |
| Laboratories & Education | Controlled, clean environment | Research, alloy testing, teaching |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including crucible furnaces designed for precision, cleanliness, and versatility in research and small-scale production. Let our experts help you select the right solution to enhance your efficiency and achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- Why Use a Quartz Tube Reactor for Y-Ti-O Phase Transformations? Achieve Absolute Purity and Precision Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















