In short, steel is hardened to dramatically increase its hardness and wear resistance for demanding applications. Common uses include cutting tools, gears, bearings, axles, and structural components where the material must withstand significant stress, abrasion, or deformation without failing. The specific application determines which hardening method is most appropriate.
The decision to harden steel is not simply about making it "stronger." It is a strategic engineering choice to create a material with a precise balance of properties—typically a hard, wear-resistant surface and a tough, shock-absorbing core—tailored to a specific operational environment.
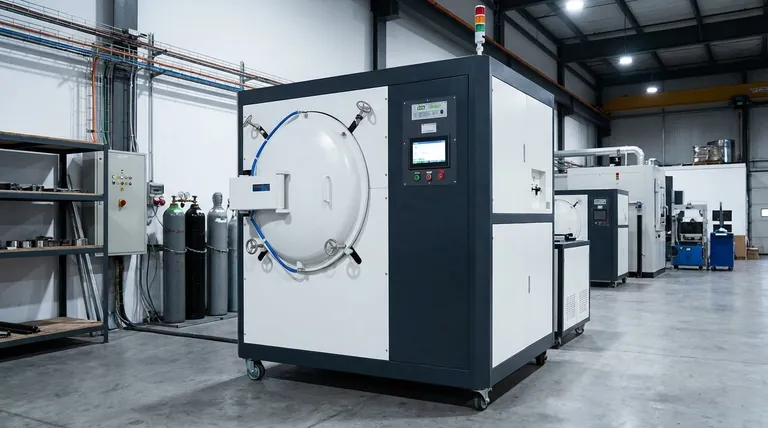

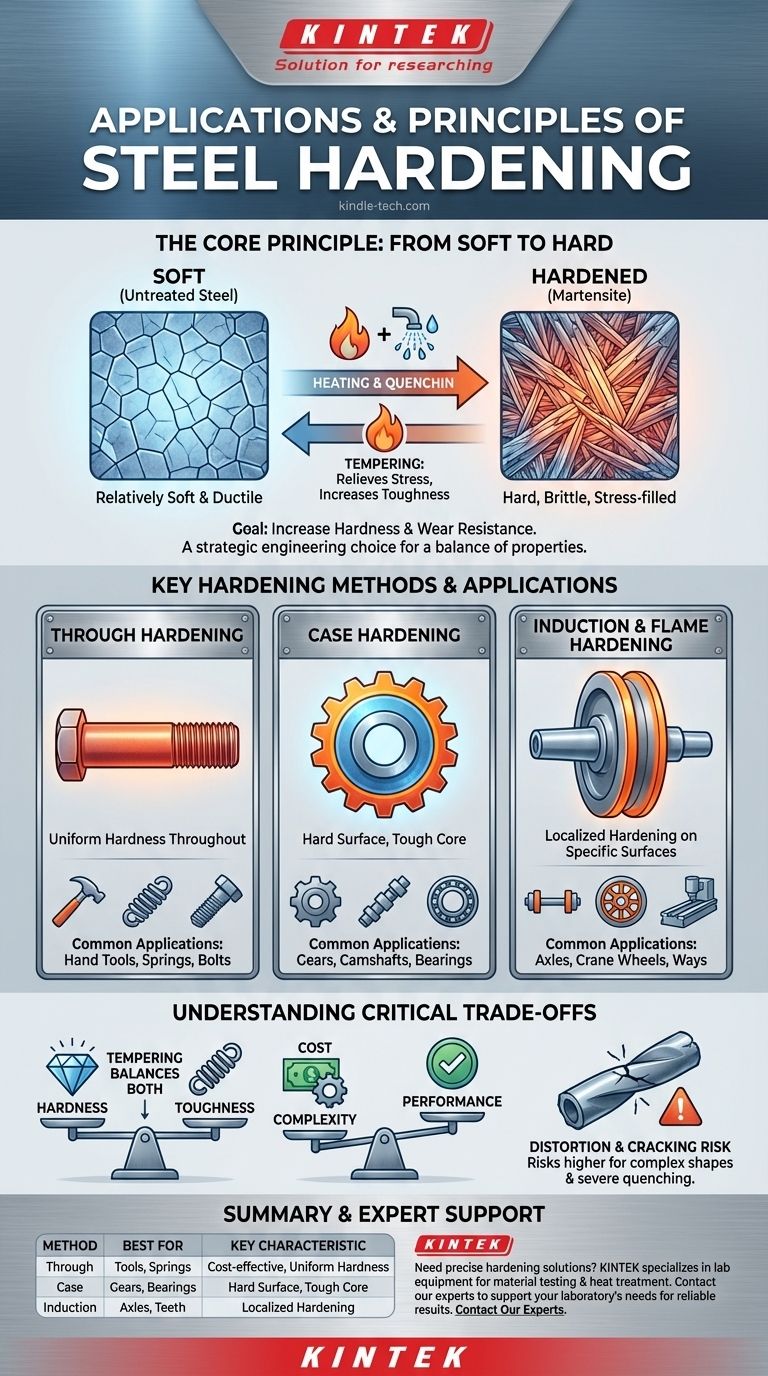
The Core Principle: Why We Harden Steel
Understanding the applications of hardened steel begins with understanding the fundamental change it undergoes. Hardening is a metallurgical process that alters the microscopic crystal structure of the steel.
From Soft to Hard: The Microscopic Transformation
At its core, hardening involves heating steel to a critical temperature, which changes its internal crystalline structure. This is followed by a rapid cooling process called quenching.
This rapid cooling traps the steel in a very hard, brittle, and stress-filled crystal structure known as martensite. A subsequent, lower-temperature heating process called tempering is almost always performed to relieve some of this stress and reduce brittleness, though at the cost of some hardness.
The Primary Benefits: Hardness and Wear Resistance
The main goal of hardening is to increase the steel's resistance to plastic deformation and abrasion. A hardened steel surface can withstand direct contact, friction, and erosion far better than its untreated counterpart.
This makes it essential for any component that cuts, grinds, rolls, or meshes with another part under load.
Key Hardening Methods and Their Applications
Different applications demand different properties, leading to several distinct hardening methods. The choice depends on the type of steel, the component's geometry, and the specific stresses it will face.
Through Hardening (Quench and Temper)
This is the most common and cost-effective method, where the entire component is heated and quenched to achieve a consistent hardness throughout the part.
It is ideal for medium-to-high carbon steels. As noted, it provides sufficient durability for most general purposes where a balance of hardness, toughness, and cost is key.
Common Applications: Hand tools (hammers, chisels), springs, high-strength structural bolts, shafts, and simple gears.
Case Hardening (Carburizing & Nitriding)
Case hardening creates an extremely hard surface layer (the "case") while leaving the interior core of the metal tough and ductile. This is achieved by diffusing elements like carbon or nitrogen into the surface of low-carbon steel.
This creates the best of both worlds: a surface that resists wear and a core that can absorb shock and impact without fracturing.
Common Applications: High-performance gears, camshafts, bearings (both rolling elements and races), and piston pins.
Induction and Flame Hardening
These methods use localized heating to harden only specific areas of a component. An induction coil or a high-temperature flame rapidly heats a select surface, which is then immediately quenched.
This process is ideal for large parts where through hardening is impractical or for components that only require hardness on a specific wear surface, like the teeth of a gear or the track of a wheel.
Common Applications: Axles, crane wheels, machine tool beds (the "ways"), and the teeth of large sprockets or saw blades.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting a hardening process is an exercise in balancing competing properties and costs. There is no single "best" method, only the most appropriate one for the task.
Hardness vs. Toughness
This is the most fundamental trade-off. As steel becomes harder, it almost always becomes more brittle. Hardness is the resistance to scratching and indentation, while toughness is the ability to absorb energy and deform without breaking.
A metal file is extremely hard but will snap if bent. This is why tempering is a critical step; it sacrifices a small amount of peak hardness to regain essential toughness.
Cost and Complexity
Through hardening is relatively simple and inexpensive. Case hardening and induction hardening are more complex, time-consuming, and costly processes. The improved performance for a specific application must justify the additional expense.
Distortion and Cracking
The extreme temperature changes involved in quenching create significant internal stresses. These stresses can cause parts to warp, distort, or, in worst-case scenarios, crack. This risk is higher for complex shapes and more severe quenching methods.
Matching the Process to Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the operational demands of the component.
- If your primary focus is general durability and cost-effectiveness: Through hardening is the standard choice for tools, fasteners, and general machine parts.
- If your primary focus is extreme surface wear with a tough, impact-resistant core: Case hardening is the definitive solution for high-load gears and bearings.
- If your primary focus is hardening a specific area on a large or complex part: Induction or flame hardening offers precise control and efficiency.
Choosing the right hardening process is a foundational decision in mechanical design, directly translating metallurgical principles into real-world performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Hardening Method | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Through Hardening | Hand tools, springs, bolts | Cost-effective, uniform hardness throughout |
| Case Hardening | Gears, camshafts, bearings | Hard surface, tough core for extreme wear |
| Induction Hardening | Axles, gear teeth, large parts | Localized hardening for specific wear surfaces |
Need precise hardening solutions for your lab or production equipment? The right hardening process is critical for performance and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables needed to support your material testing and heat treatment workflows. Our expertise ensures you can achieve the perfect balance of hardness and toughness for your specific application. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's needs for reliable, high-performance results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















