At its core, heat treatment is a group of controlled heating and cooling processes used to deliberately change a material's internal microstructure. This fundamental engineering practice is applied to enhance specific properties, making a standard material suitable for a demanding application, such as turning a simple piece of steel into a high-performance cutting tool or a durable structural beam.
Heat treatment is not a single process, but a versatile toolkit. Its primary application is to precisely tailor a material’s properties—like hardness, toughness, and internal stress—to match the specific performance requirements of its final job.

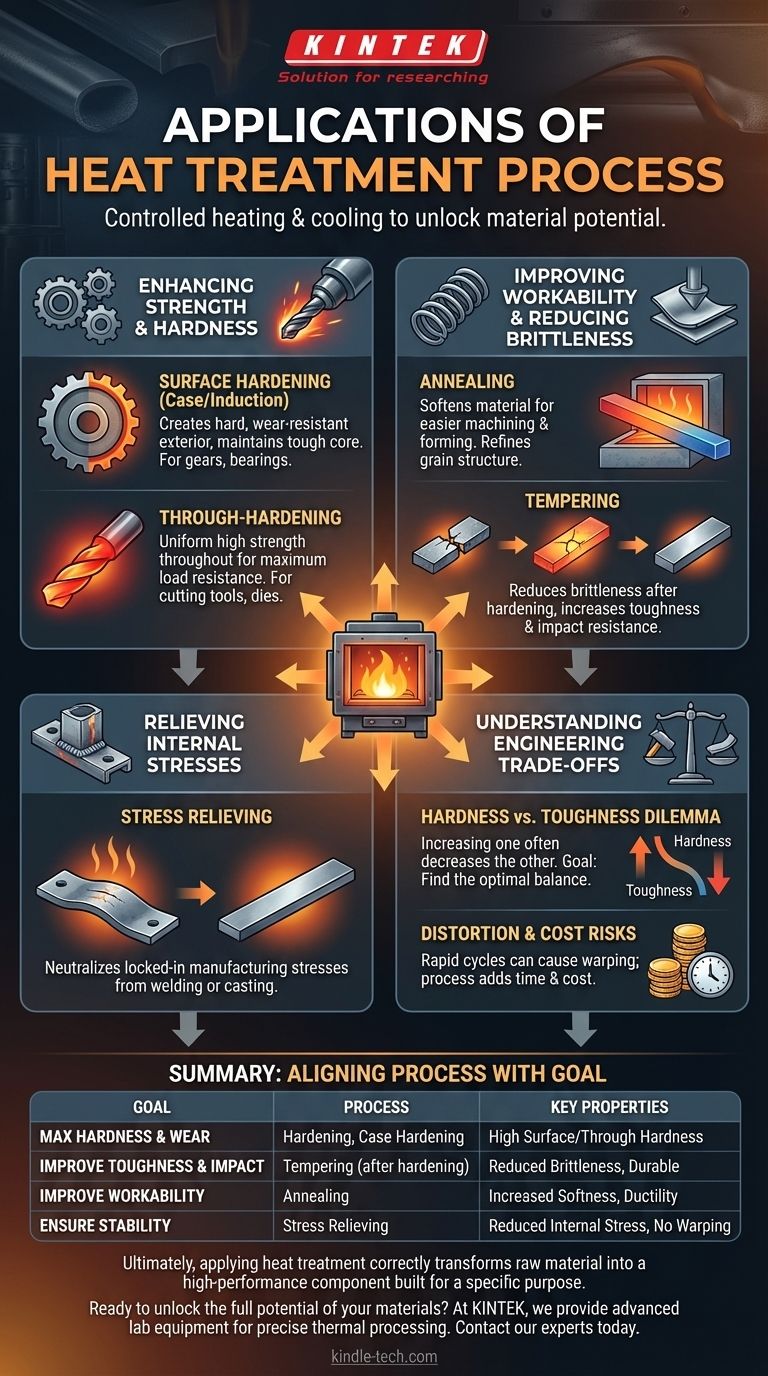
Enhancing Strength and Hardness
One of the most common reasons to apply heat treatment is to make a material, particularly steel, significantly stronger and more resistant to wear and deformation.
Creating Hard, Wear-Resistant Surfaces
For components that experience high friction, like gears, bearings, and camshafts, only the surface needs to be extremely hard. Processes like case hardening or induction hardening create a "case" of high hardness on the exterior while leaving the inner "core" of the part softer and more tough, preventing it from becoming brittle.
Achieving Through-Hardness for Tools and Components
When the entire component needs to be strong, a process called through-hardening is used. This is critical for applications like cutting tools (drills, knives), dies, and high-strength structural parts that must resist bending or breaking under immense load.
Improving Workability and Reducing Brittleness
Counterintuitively, heat treatment is also used to make materials softer and less brittle, which is often a necessary intermediate step in manufacturing.
Softening for Easier Manufacturing (Annealing)
Annealing is a process that involves heating a material and cooling it very slowly. This makes the material softer, more ductile, and much easier to machine, stamp, or form into a complex shape without cracking. It also refines the internal grain structure.
Increasing Toughness (Tempering)
After a part is hardened, it is often extremely strong but also very brittle and can shatter like glass. Tempering is a secondary treatment where the part is reheated to a lower temperature. This process reduces some of the hardness and brittleness, but significantly increases its toughness, which is its ability to absorb impact and resist fracture.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, and heavy machining introduce significant stress into a material's structure. If left untreated, this stress can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack over time.
Stabilizing Parts After Fabrication
A stress-relieving heat treatment gently heats the component to a temperature below its transformation point and holds it there. This allows the internal crystal structure to relax and realign, neutralizing the locked-in stresses without changing the part's core mechanical properties, ensuring its dimensional stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it requires navigating a series of critical engineering trade-offs. The choice of process is always a compromise designed to achieve the best balance of properties for the application.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Increasing a material's hardness almost always decreases its toughness, making it more brittle. The goal of processes like tempering is to find the optimal sweet spot between wear resistance (hardness) and impact resistance (toughness).
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid heating and cooling cycles inherent in many heat treatments can cause parts to warp, change dimensions, or even crack. This is especially true for complex geometries or if the process is not controlled with extreme precision.
Cost and Process Time
Heat treatment is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized equipment, energy, and time. This adds cost to the final product, which must be justified by the required performance improvement.
Aligning the Process with the Engineering Goal
Choosing the correct heat treatment process is entirely dependent on the desired outcome for the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Use hardening (and potentially case hardening) for applications like cutting tools, bearings, or gear teeth.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or formability: Use annealing to make the raw material soft and ductile before shaping it.
- If your primary focus is durability and resistance to impact: Use a hardening process followed by tempering to create a balance of strength and toughness for parts like axles, springs, and structural bolts.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability after welding or machining: Use a stress-relieving process to prevent future warping or cracking in the finished component.
Ultimately, applying heat treatment correctly is what unlocks the full potential of an engineering material, transforming it from a raw commodity into a high-performance component built for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Common Heat Treatment Processes | Key Material Properties Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| Enhance Hardness & Wear Resistance | Hardening, Case Hardening, Induction Hardening | Increased surface/through hardness, wear resistance |
| Improve Toughness & Impact Resistance | Tempering (after hardening) | Reduced brittleness, increased durability |
| Improve Workability & Formability | Annealing | Increased softness, ductility, and machinability |
| Ensure Dimensional Stability | Stress Relieving | Reduced internal stresses, prevention of warping/cracking |
Ready to unlock the full potential of your materials? The right heat treatment process is critical for achieving the perfect balance of hardness, toughness, and stability in your components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for precise thermal processing. Whether you're developing cutting tools, automotive parts, or structural components, our solutions help you achieve superior material performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific heat treatment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between vacuum hardening and normal hardening? Choose the Right Process for Your Application
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in 1200 °C composite heat treatment? Achieve Perfect Layer Bonding
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play in Mn-Al-O catalysts? Expert Guide to Hexaaluminate Phase Transformation
- What is a low temperature vacuum? The Ultimate Tool for Achieving Ultra-High Vacuum
- What is the purpose of utilizing a high-temperature vacuum furnace? Optimize Ti-Cr Coating Adhesion at 1223 K
- How does a vacuum environment facilitate the surface modification of MIL-88B with APTMS? Enhance MOF Coating Uniformity
- What role does a two-stage rotary vane vacuum pump play in a radio frequency (rf) plasma carbonitriding system?
- Why is multi-point temperature monitoring critical in magnesium vacuum distillation? Master Purity & Gradient Control



















