At its core, induction heating is a highly versatile process used to heat electrically conductive materials in applications ranging from industrial metallurgy and semiconductor fabrication to advanced 3D printing and home cooking. Its primary uses include hardening, brazing, and melting metals, growing high-purity crystals for electronics, and providing rapid, clean heat for induction cooktops.
The true value of induction heating lies not in its applications, but in its fundamental principle: generating rapid, precise, and clean heat directly inside a material using an electromagnetic field, eliminating the inefficiencies and contamination risks of external heat sources.

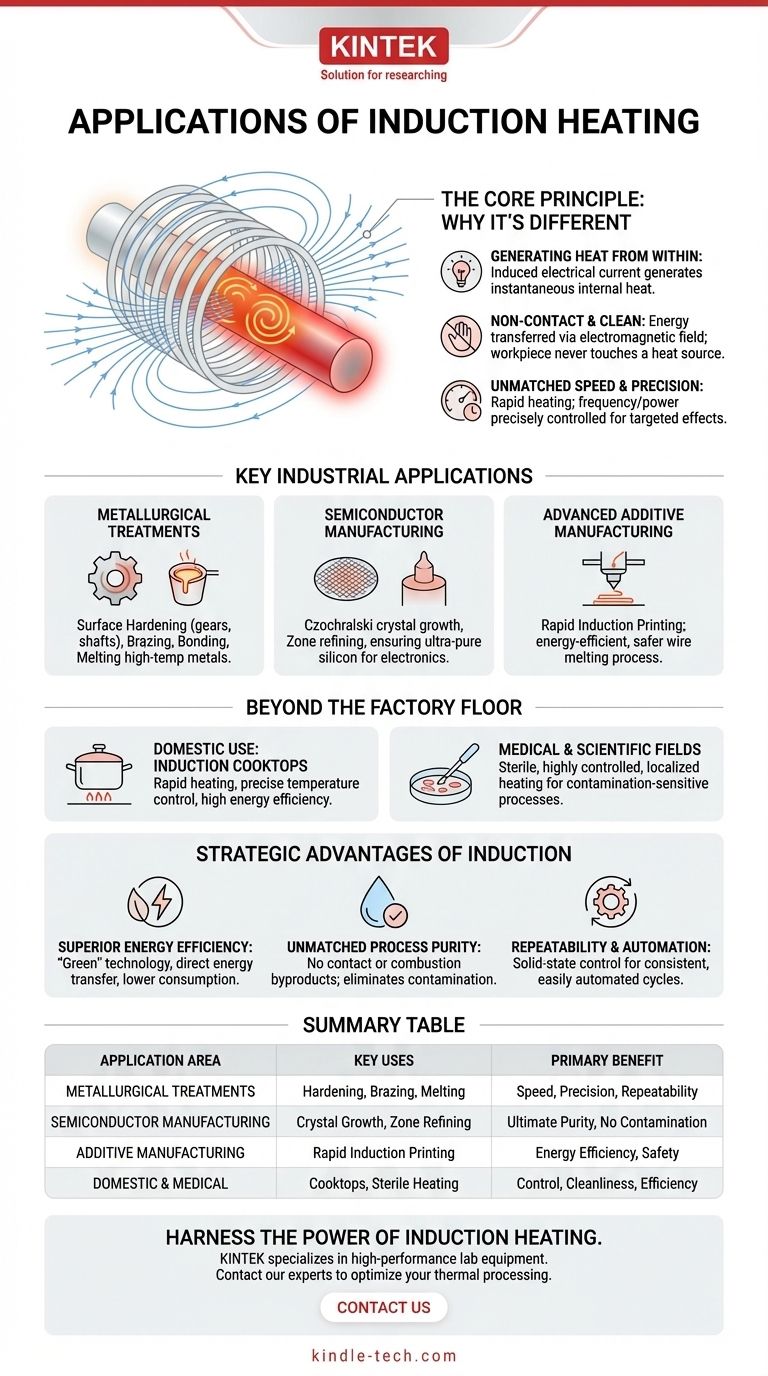
The Core Principle: Why Induction Is Different
Induction heating is fundamentally different from a conventional furnace or an open flame. It does not rely on conduction or radiation from an external heat source to slowly warm an object's surface.
Generating Heat from Within
The process uses an alternating magnetic field to induce an electrical current within the target material. The material's natural resistance to this current flow generates instantaneous, internal heat.
Non-Contact and Clean
Because the energy is transferred via an electromagnetic field, the workpiece never touches a flame or a heating element. This non-contact nature is critical in applications where even microscopic contamination is a problem.
Unmatched Speed and Precision
Since the heat is generated inside the object itself, heating is extremely rapid. Furthermore, the frequency and power of the magnetic field can be precisely controlled to dictate the depth and temperature of the heat, allowing for targeted effects like surface hardening.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique characteristics of induction heating make it indispensable in modern manufacturing processes where speed, control, and purity are paramount.
Metallurgical Treatments
This is the most common industrial application. Induction is used for surface hardening gears and shafts, where only the outer layer is hardened for wear resistance while the core remains tough. It is also used for brazing and bonding metal components, as well as melting even high-temperature refractory metals with incredible speed.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the semiconductor industry, purity is everything. Induction is used for Czochralski crystal growth and zone refining, processes that create the ultra-pure silicon crystals that form the basis of all modern electronics. The non-contact method prevents impurities from being introduced into the melt.
Advanced Additive Manufacturing
Newer techniques like Rapid Induction Printing use induction to melt a metal wire feedstock as it is extruded from a nozzle. This 3D printing process is more energy-efficient and safer than laser-based methods, as it heats only the material being deposited and avoids an open, high-power energy source.
Beyond the Factory Floor
While its roots are industrial, the principles of induction heating have found their way into other critical areas, including the home.
Domestic Use: Induction Cooktops
An induction cooktop is a perfect everyday example of the technology. The electromagnetic field heats the conductive pot or pan directly, while the glass-ceramic surface remains relatively cool. This provides rapid heating, precise temperature control, and high energy efficiency compared to gas or electric coil stoves.
Medical and Scientific Fields
The ability to provide sterile, highly controlled, and localized heating makes induction a valuable tool in medical and scientific applications. It is used in processes where precise thermal management without contamination is essential.
The Strategic Advantages of Induction
Choosing induction heating is a strategic decision driven by several key advantages over traditional heating methods like flames, ovens, and resistance coils.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Induction is a "green" technology. It transfers energy directly into the part being heated, with very little energy wasted heating the surrounding air or furnace components. This results in significantly lower energy consumption and a cooler, more comfortable working environment.
Unmatched Process Purity
The complete absence of direct contact or combustion byproducts means the heated material remains pure. This eliminates product contamination, a non-negotiable requirement for medical-grade materials and semiconductors.
Repeatability and Automation
Induction heating is controlled by solid-state power supplies, making it extremely consistent and repeatable. This level of control allows it to be easily integrated into automated production lines, ensuring every part receives the exact same heat treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the core benefits of induction heating allows you to apply it where it will have the greatest impact on quality, speed, and cost.
- If your primary focus is process speed and consistency: Induction delivers rapid, highly repeatable heating cycles that are ideal for automated, high-volume manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is material purity: The non-contact nature of induction is unrivaled for applications in the semiconductor, medical, or specialty alloy fields where contamination is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and safety: Induction significantly reduces energy waste and creates a safer work environment by eliminating open flames and excess ambient heat.
By leveraging its unique ability to generate heat from within, you can achieve process outcomes that are faster, cleaner, and more precise than ever before.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgical Treatments | Hardening, Brazing, Melting | Speed, Precision, Repeatability |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Crystal Growth, Zone Refining | Ultimate Purity, No Contamination |
| Additive Manufacturing | Rapid Induction Printing | Energy Efficiency, Safety |
| Domestic & Medical | Induction Cooktops, Sterile Heating | Control, Cleanliness, Efficiency |
Ready to harness the power of induction heating in your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced induction heating systems. Whether you are working in R&D, semiconductor fabrication, metallurgy, or advanced manufacturing, our solutions deliver the rapid, precise, and clean heat you need for superior results.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing for greater efficiency, purity, and control.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum required for hot pressing magnesium alloys? Achieve Superior Bonding at 1 x 10^-3 Pa
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- How does the vacuum hot pressing process affect the properties of finished materials? Maximize Density and Performance
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve Nanoscale Hardness in Material Sintering


















