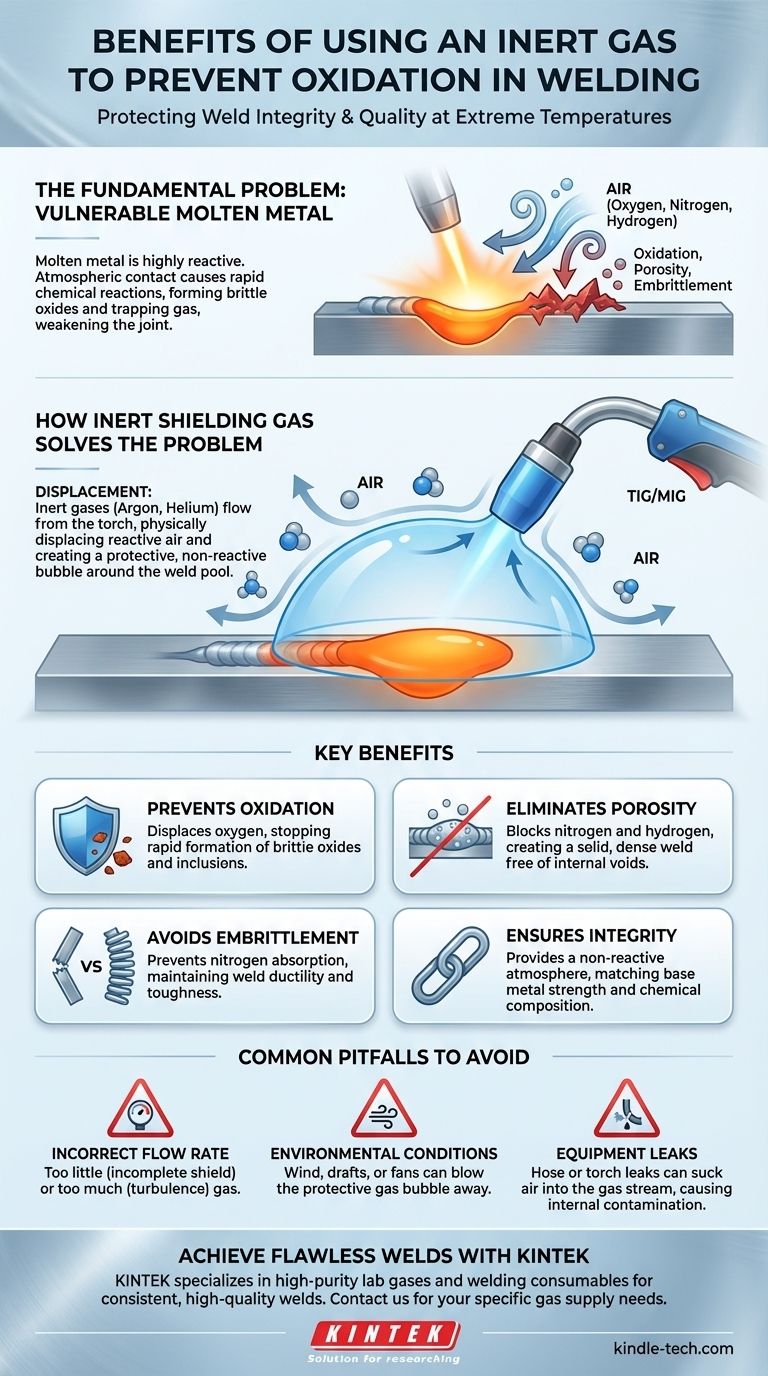
Using an inert gas to shield your weld is the only way to guarantee its strength, integrity, and quality. At the extreme temperatures of a welding arc, molten metal is highly reactive with the surrounding air. An inert gas displaces the air, creating a protective bubble that prevents harmful chemical reactions, primarily oxidation, from compromising the weld pool.
The core purpose of a shielding gas is to protect the molten weld puddle from the damaging effects of oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen in the atmosphere. This protection is not an optional enhancement; it is fundamental to creating a weld that is as strong and reliable as the parent metal itself.

The Fundamental Problem: Why Molten Metal is Vulnerable
To understand the benefit of shielding gas, you must first understand the enemy: the air around us. While harmless in daily life, the atmosphere becomes highly corrosive to molten metal.
The Role of Atmospheric Contamination
The air is composed of approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen, with trace amounts of other gases and water vapor. When a metal is heated to its melting point, its atoms become incredibly active and are primed to react with these elements.
What is Oxidation?
Oxidation is the rapid chemical reaction between the hot metal and oxygen. This process instantly forms metallic oxides, which are essentially a form of rapid, high-temperature rust. These oxides get trapped in the weld as it solidifies.
Unlike the base metal, these oxides are often brittle and weak, creating inclusions that act as internal failure points within the finished joint.
The Impact of Nitrogen and Hydrogen
Oxygen isn't the only threat. Nitrogen from the air can dissolve into some molten metals, like stainless steel and aluminum, causing a significant loss of ductility and making the weld brittle.
Moisture (water vapor) in the air introduces hydrogen, which is a primary cause of porosity (small gas bubbles trapped in the weld) and can lead to delayed hydrogen-induced cracking, a catastrophic form of weld failure.
How Inert Shielding Gas Solves the Problem
Shielding gas directly counteracts this atmospheric threat through a simple but highly effective principle: displacement.
Creating a Protective Barrier
In processes like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, the gas flows from the torch and physically pushes the surrounding air away from the immediate weld zone. This creates a localized, pure, and non-reactive atmosphere precisely where it's needed most.
The Meaning of "Inert"
Gases like Argon and Helium are called inert because they are chemically stable and will not react with the molten weld pool, even at extreme temperatures. They serve as a perfect, invisible shield, allowing the metal to melt, fuse, and solidify without any chemical alteration.
Preventing Porosity and Embrittlement
By keeping nitrogen and hydrogen out of the weld pool, a proper gas shield is the primary defense against porosity. The result is a solid, dense weld free of the pinholes and internal voids that severely weaken the joint. It also prevents the metallurgical changes that cause embrittlement.
Ensuring Metallurgical Integrity
Ultimately, shielding gas ensures that the chemical composition of the finished weld matches the intended properties of the filler and base metals. The weld remains as strong, ductile, and corrosion-resistant as the engineer designed it to be.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While the principle is simple, its application requires precision. Several common errors can negate the benefits of using a shielding gas.
Incorrect Flow Rate
Setting the correct gas flow rate is critical. Too little gas will provide an incomplete shield, allowing contamination. Too much gas can create turbulence, which actually pulls surrounding air into the arc, defeating the entire purpose.
Environmental Conditions
Shielding gas is easily disturbed. Even a light breeze or a shop fan can blow the protective bubble away from the weld pool, leading to sudden and severe oxidation. Welding outdoors often requires windscreens or switching to a process with a more robust shield, like flux-cored or stick welding.
Equipment Leaks
A small leak in a gas hose, fitting, or torch assembly can suck air into the gas stream. This contaminates the shield from the inside and will introduce defects into every weld you produce until it is found and fixed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the atmosphere is a fundamental aspect of welding. Your approach should align directly with the required outcome of the finished product.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and safety: Proper gas shielding is non-negotiable. It is the only way to prevent the invisible defects that lead to joint failure under load.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic appearance: A clean, bright, and smooth weld bead is a direct result of an effective gas shield. It dramatically reduces discoloration and eliminates the spatter and porosity associated with contamination.
- If you are working in drafty or outdoor conditions: You must erect barriers to block the wind or switch to a process like Shielded Metal Arc Welding (stick) that uses a solid flux coating for protection instead of a fragile gas envelope.
Ultimately, using a shielding gas isn't about making the weld look better; it's about ensuring the weld is fundamentally sound.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | How Inert Gas Helps | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Displaces oxygen, stopping rapid rust formation | Eliminates brittle oxides and inclusions |
| Eliminates Porosity | Blocks nitrogen and hydrogen from the atmosphere | Creates a solid, dense weld free of gas bubbles |
| Avoids Embrittlement | Prevents nitrogen absorption in metals like stainless steel | Maintains weld ductility and toughness |
| Ensures Metallurgical Integrity | Provides a non-reactive atmosphere for fusion | Weld matches the strength and corrosion resistance of the base metal |
Achieve flawless, high-integrity welds with the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab gases and welding consumables essential for creating the perfect shielding environment. Whether you are a research lab developing new alloys or a manufacturer requiring consistent, high-quality welds, our products ensure your processes are protected from contamination. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific welding and gas supply needs and discover how we can support your quality and safety goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes



















