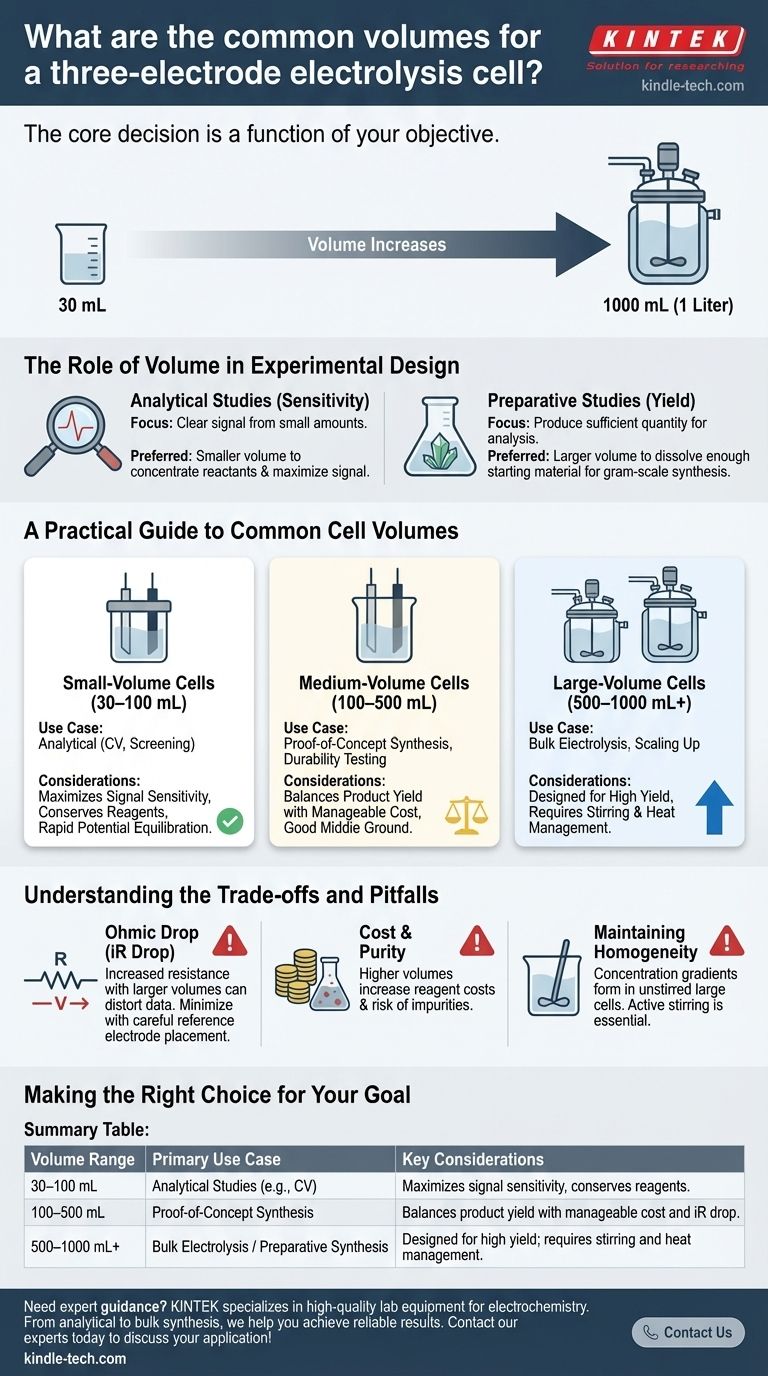
When selecting a three-electrode cell, the most common working volumes range from 30 mL to 1000 mL (1 liter). While this is a wide spectrum, the specific volume chosen is not arbitrary. It is a critical experimental parameter determined entirely by the goal of your electrochemical study.
The core decision is a function of your objective. Small volumes (~30-100 mL) are standard for analytical measurements where sensitivity is key, while larger volumes (200-1000 mL) are necessary for bulk electrolysis and preparative synthesis where yield is the primary concern.

The Role of Volume in Experimental Design
The volume of an electrolysis cell directly influences factors like analyte concentration, mass transport, and the total amount of product you can generate. Understanding this link is the first step toward designing a successful experiment.
The Link Between Volume and Goal
Electrochemical experiments typically fall into two categories: analytical or preparative.
Analytical studies, such as cyclic voltammetry (CV), aim to measure properties like redox potentials or reaction kinetics. Here, the focus is on generating a clear, measurable signal from a small amount of material.
Preparative studies, or bulk electrolysis, aim to synthesize a new material or transform a starting material into a product. The primary objective is to produce a sufficient quantity of the substance for isolation and further analysis.
Impact on Analytical Sensitivity
For analytical measurements, a smaller cell volume is almost always preferred. A smaller volume concentrates the reactants, maximizing the current response relative to the background signal.
This approach also conserves expensive or rare materials, such as the analyte, solvent, and supporting electrolyte.
Scaling for Electrosynthesis
For electrosynthesis, a larger cell volume is required. The goal is to dissolve enough starting material to produce a tangible, weighable amount of product.
A larger volume provides the necessary capacity to scale the reaction up from a small analytical test to a preparative run capable of generating gram-scale quantities.
A Practical Guide to Common Cell Volumes
Choosing the right volume means matching the hardware to the experimental objective. Cells are generally optimized for a specific type of work.
Small-Volume Cells (30–100 mL)
These are the workhorses of analytical electrochemistry. They are ideal for initial screening experiments, mechanistic investigations, and standard cyclic voltammetry. Their compact geometry ensures rapid potential equilibration across the working electrode.
Medium-Volume Cells (100–500 mL)
This range represents a common middle ground. These cells are often used for small-scale preparative work, testing the durability of electrode materials over time, or developing proof-of-concept synthetic routes before scaling up.
Large-Volume Cells (500–1000 mL+)
These cells are explicitly designed for bulk electrolysis and scaling up chemical production. They can accommodate larger electrodes to drive higher currents and often include features like ports for mechanical stirrers or cooling jackets to manage the heat generated during long experiments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While a larger volume is necessary for synthesis, it introduces complexities that can compromise the quality of electrochemical data if not properly managed.
The Problem of Ohmic Drop
Ohmic drop, or iR drop, is the voltage loss caused by the resistance of the electrolyte solution. In larger cells, the distance between the reference and working electrodes is often greater, increasing this resistance.
This effect can distort the shape and shift the position of peaks in a voltammogram, leading to inaccurate measurements. Careful placement of the reference electrode's Luggin capillary is critical to minimize this error.
The Cost and Purity Factor
Larger volumes demand significantly more solvent, supporting electrolyte, and active species. This not only increases the cost per experiment but also raises the risk of introducing impurities that can interfere with the reaction.
Maintaining Homogeneity
In large, unstirred cells, concentration gradients can easily form around the electrodes. This means the concentration of the reactant at the electrode surface is different from the bulk solution, affecting reaction rates. For this reason, large-volume cells almost always require active stirring to ensure efficient mass transport.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the correct cell volume is the one that best serves your primary experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is analytical measurement: Opt for a smaller volume (30-100 mL) to maximize signal sensitivity and minimize the consumption of reagents.
- If your primary focus is proof-of-concept synthesis: A medium-volume cell (100-500 mL) offers a practical balance for producing usable amounts of product without excessive cost.
- If your primary focus is bulk production: You will require a large-volume cell (500 mL+) designed for high-throughput synthesis with features for managing mass transport and heat.
Matching the cell volume to your objective is a foundational step toward achieving reliable and reproducible electrochemical results.
Summary Table:
| Volume Range | Primary Use Case | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 30–100 mL | Analytical Studies (e.g., CV) | Maximizes signal sensitivity, conserves reagents. |
| 100–500 mL | Proof-of-Concept Synthesis | Balances product yield with manageable cost and iR drop. |
| 500–1000 mL+ | Bulk Electrolysis / Preparative Synthesis | Designed for high yield; requires stirring and heat management. |
Need expert guidance to select the perfect electrolysis cell for your lab's specific needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for electrochemistry. Whether you are conducting sensitive analytical measurements or scaling up your synthesis, we can help you choose the right cell to achieve reliable and reproducible results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
People Also Ask
- How is a high-precision electrolytic cell used to evaluate metal corrosion resistance? Validate DCT Results Accurately
- What role does a water-jacketed electrolytic cell play in variable-temperature electrochemical corrosion measurements?
- How is a three-electrode electrochemical electrolytic cell utilized to evaluate Zr-Nb alloy corrosion resistance?
- What is the difference between electrolytic corrosion cell and electrochemical corrosion cell? Understand the Driving Force Behind Corrosion
- How does an electrochemical cell system ensure measurement precision during DL-EPR? | Expert Testing Guide