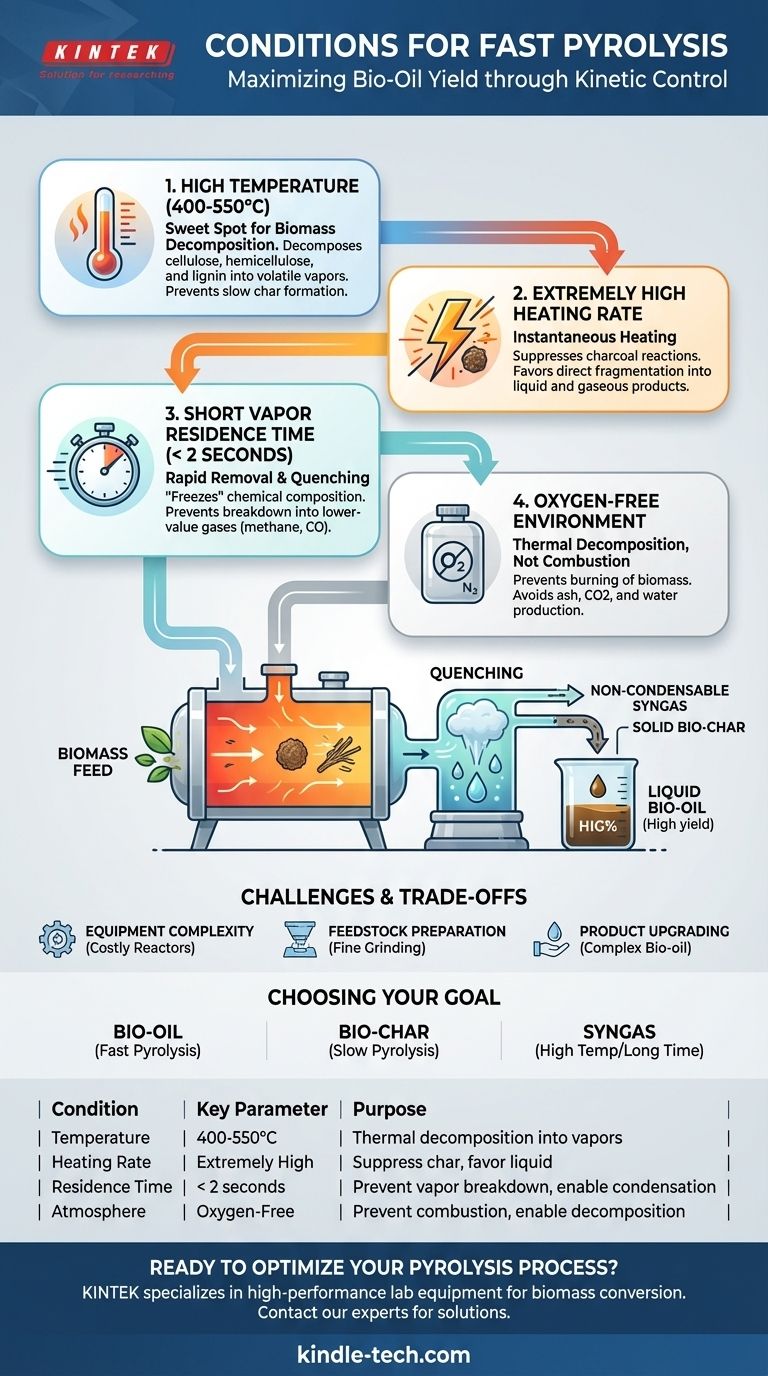
Fast pyrolysis is achieved by meeting four specific operational conditions: a high temperature (typically 400-550°C), an extremely high heating rate, a very short vapor residence time (less than two seconds), and the complete absence of oxygen. These parameters are precisely controlled to rapidly decompose biomass and immediately capture the resulting vapors as a liquid bio-oil, maximizing its yield.
The core principle of fast pyrolysis is kinetic control. The conditions are engineered to thermally crack biomass into valuable vapors and then quench them into a liquid fuel before they have time to break down further into less desirable gases or solids.

The Four Core Conditions of Fast pyrolysis
To understand why fast pyrolysis is effective, we must examine each of its defining conditions. Each parameter plays a critical role in steering the chemical reactions toward the desired liquid product.
High Temperature (400-550°C)
This temperature range is the "sweet spot" for thermally decomposing the primary components of biomass—cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—into smaller, volatile molecules that form vapors.
Temperatures below this range are too slow for rapid conversion, favoring solid char formation. Temperatures significantly above this range tend to promote secondary cracking of the vapors into permanent, non-condensable gases.
Extremely High Heating Rate
This is perhaps the most defining characteristic of fast pyrolysis. The biomass particles must be heated to the target temperature almost instantaneously.
This rapid energy transfer suppresses the reactions that lead to charcoal formation and instead favors the fragmentation of biomass directly into liquid and gaseous products. This stands in sharp contrast to slow pyrolysis, which uses very low heating rates to maximize char yield.
Short Vapor Residence Time (< 2 seconds)
Once the biomass breaks down into hot vapors, those vapors must be removed from the hot reactor zone immediately. A residence time of less than two seconds is crucial.
This rapid removal and subsequent cooling (quenching) "freezes" the chemical composition of the vapors, condensing them into a liquid bio-oil. If left in the hot zone, these vapors would continue to react and decompose into lower-value products like methane and carbon monoxide.
Oxygen-Free Environment
Fast pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition, not combustion. The entire process must be carried out in an inert atmosphere, completely free of oxygen.
Introducing oxygen would cause the biomass to burn, releasing its energy as heat and producing ash, carbon dioxide, and water instead of the desired bio-oil, bio-char, and syngas.
How These Conditions Dictate the Outcome
The interplay between these four conditions is what allows operators to precisely control the final product distribution.
Maximizing Bio-Oil Yield
The combination of a high heating rate and short residence time is specifically engineered to maximize the production of condensable vapors, which form the liquid bio-oil. This process can convert a significant portion of the initial biomass into a liquid fuel product.
Minimizing Char and Gas
By heating the material so quickly, the process bypasses the slower reactions that form a stable char structure. Similarly, by removing the vapors immediately, secondary reactions that would generate excess gas are prevented.
The Role of Secondary Products
While bio-oil is the primary target, the co-products are not wasted. The non-condensable syngas (containing methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide) is often combusted on-site to provide the intense energy required to heat the reactor, making the process more self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While effective, achieving the precise conditions for fast pyrolysis presents several practical challenges.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Maintaining extremely high heating rates and short residence times requires sophisticated and often expensive reactors, such as fluidized bed or ablative pyrolyzers. Simple batch reactors used for slow pyrolysis are insufficient.
Feedstock Preparation
To ensure rapid heat transfer, the biomass feedstock must be dried and ground into very fine particles. This pre-processing step adds energy consumption and cost to the overall operation.
Product Separation and Upgrading
The raw bio-oil produced is a complex mixture that is acidic, unstable, and requires further upgrading before it can be used as a conventional transportation fuel. Efficient separation and purification of the end products is a significant challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis conditions depend entirely on the desired end product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil: You must use high heating rates, moderate temperatures (400-550°C), and a very short vapor residence time.
- If your primary focus is maximizing solid bio-char: You should use low temperatures and slow heating rates, characteristic of slow pyrolysis.
- If your primary focus is maximizing flammable syngas: You would typically use very high temperatures and a longer gas residence time to encourage the complete breakdown of vapors.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis is about precisely controlling heat, time, and atmosphere to dictate the final chemical outcome.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Key Parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 400-550°C | Thermal decomposition of biomass into vapors |
| Heating Rate | Extremely High | Suppress char formation, favor liquid products |
| Vapor Residence Time | < 2 seconds | Prevent vapor breakdown, enable condensation to bio-oil |
| Atmosphere | Oxygen-Free | Prevent combustion, enable thermal decomposition |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Mastering the precise conditions for fast pyrolysis is key to maximizing your bio-oil yield. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for biomass conversion research and development. Our reactors and temperature control systems are designed to help you achieve the exact parameters needed for efficient pyrolysis.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment to control temperature, heating rate, and residence time for your specific biomass feedstock and product goals.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your lab's pyrolysis needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your research efficiency and product yield.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is magnetron sputtering target? The Core Material for High-Performance Thin Film Coatings
- Can you reheat a brazed joint? A guide to repair, disassembly, and post-braze processes
- Does the brazing rod have a higher or lower melting-temperature than the steel being brazed? Lower Melting Point is Key to Strong Joints
- What is the end product of plastic waste? The Alarming Truth About Its Final Destination
- What is the effect of heating rate in heat treatment? Control Hardness, Microstructure, and Distortion
- Why is a drying oven used for low-temperature treatment of Ti/Al2O3? Ensure Powder Purity and Flowability
- What is the advantage of sputtering? Achieve Superior, High-Purity Thin Films from Any Material
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product



















