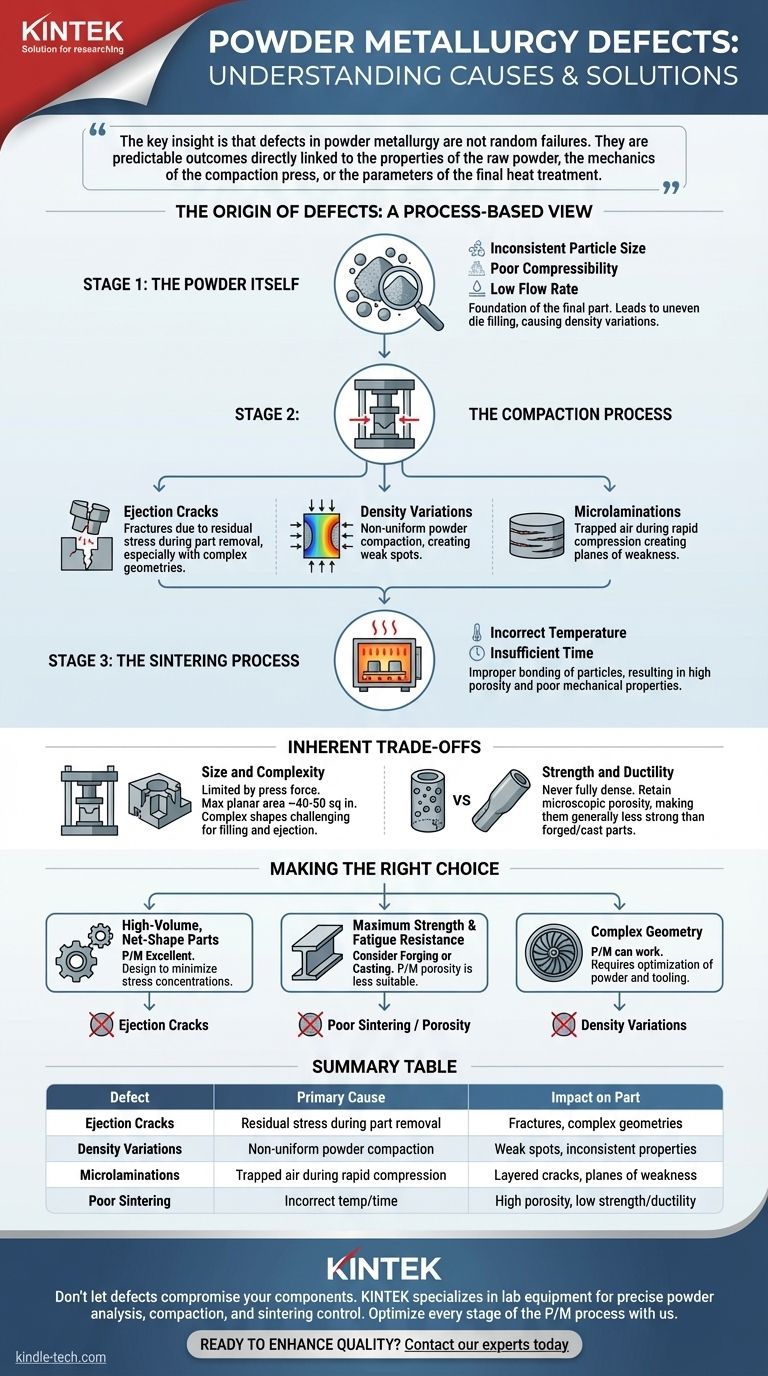
The most common defects in powder metallurgy are ejection cracks, density variations, microlaminations, and poor sintering. These issues arise from the unique three-stage process of P/M: preparing the powder, compacting it under immense pressure, and heating it to bond the particles together.
The key insight is that defects in powder metallurgy are not random failures. They are predictable outcomes directly linked to the properties of the raw powder, the mechanics of the compaction press, or the parameters of the final heat treatment.
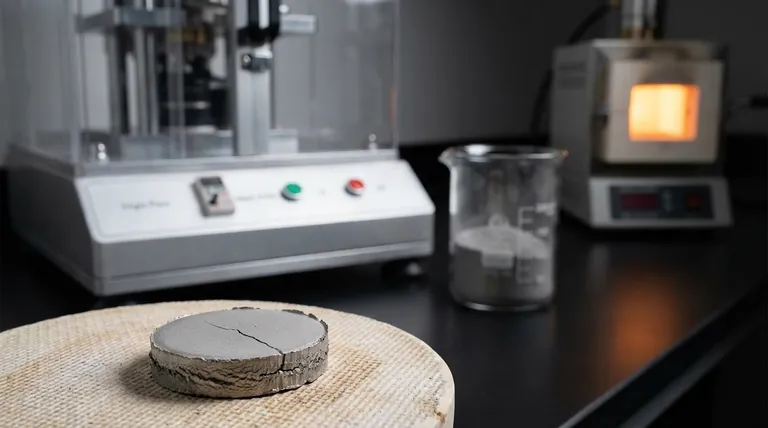

The Origin of Defects: A Process-Based View
Understanding where defects come from requires looking at the fundamental stages of the powder metallurgy process. An issue in any one stage will inevitably impact the quality of the final component.
Stage 1: The Powder Itself
The characteristics of the metal powder are the foundation of the final part. Poor quality powder makes a high-quality part impossible.
Factors like inconsistent particle size, poor compressibility, or a low flow rate can lead to uneven filling of the die cavity. This is a primary cause of density variations before the press even begins its cycle.
Stage 2: The Compaction Process
This is where the loose powder is pressed into a solid, but fragile, "green" compact. The immense forces and mechanical movements involved are a common source of defects.
Ejection Cracks
These are fractures that occur as the green compact is pushed out of the die. They are often caused by residual stress from the compaction phase, especially in parts with complex geometries or sharp changes in cross-section.
Density Variations
Because pressure is applied from the top and bottom, it's difficult to achieve perfectly uniform density throughout the part. Powder doesn't flow like a liquid, so areas farther from the punches may be less compacted, creating weak spots.
Microlaminations
These are fine, layered cracks that form perpendicular to the pressing direction. They are often caused by air being trapped within the powder during rapid compression, creating planes of weakness within the compact.
Stage 3: The Sintering Process
Sintering is a heat treatment below the material's melting point that bonds the metal particles, giving the part its final strength.
Improper sintering is a critical defect. If the temperature is too low or the time is too short, the metallurgical bonds between particles will be weak. This results in a part with high porosity and poor mechanical properties, such as low strength and ductility.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
Beyond specific defects, it's crucial to understand the fundamental limitations of the P/M process itself. These are not failures but inherent trade-offs you must consider during the design phase.
Size and Complexity
The P/M process is limited by the force of the compaction press. The largest industrial presses can only produce parts up to about 40-50 square inches in planar area. Extremely complex shapes can also be challenging, as they make uniform powder filling and safe part ejection difficult.
Strength and Ductility
P/M parts are almost never fully dense. They retain some level of microscopic porosity even after sintering. Because of this, they are generally not as strong or ductile as components produced by forging or casting, which result in fully dense materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these potential defects and limitations allows you to use powder metallurgy effectively for the right applications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, net-shape parts with moderate complexity: P/M is an excellent choice, but you must design the component to minimize stress concentrations that can lead to ejection cracks.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue resistance: You should consider forging or casting, as the inherent porosity of P/M parts makes them less suitable for the most demanding structural applications.
- If your primary focus is a complex geometry: P/M can work, but success requires close collaboration with a skilled manufacturer to optimize powder selection and tooling design to avoid density variations.
By anticipating these potential issues, you can effectively leverage powder metallurgy's advantages in creating complex parts with minimal machining.
Summary Table:
| Defect | Primary Cause | Impact on Part |
|---|---|---|
| Ejection Cracks | Residual stress during part removal from die | Fractures, especially in complex geometries |
| Density Variations | Non-uniform powder compaction in the die | Weak spots, inconsistent mechanical properties |
| Microlaminations | Trapped air during rapid compression | Layered cracks, planes of weakness |
| Poor Sintering | Incorrect temperature/time during heat treatment | High porosity, low strength and ductility |
Don't let defects compromise your components.
Understanding the root causes of powder metallurgy defects is the first step to prevention. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise powder analysis, compaction, and sintering control. Our expertise helps you optimize every stage of the P/M process, from powder selection to final heat treatment, ensuring you achieve the desired density, strength, and complex geometries for your laboratory's specific needs.
Ready to enhance the quality and reliability of your powder metallurgy parts? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of an agitated thin film evaporator? Master Heat-Sensitive & Viscous Liquids
- What is the primary function of a laboratory drying oven? Ensure Purity in Ni-Al2O3-TiO2 Composite Pretreatment
- What are the most efficient and environment-friendly refrigerant fluids used in Ultra Freezers? Choose Natural Hydrocarbons for a Greener Lab
- What is the process of calcination? A Guide to Purification & Thermal Transformation
- What affects the pressure of an object? Master the Force and Area Relationship for Better Engineering
- What materials are hot isostatically pressed? Achieve Full Density in Critical Components
- What are the disadvantages of biomass to the environment? Debunking the 'Green' Myth
- What is the primary function of a high-speed magnetic stirrer in the synthesis of Pd-on-Au NPs? Ensure Uniform Diffusion



















