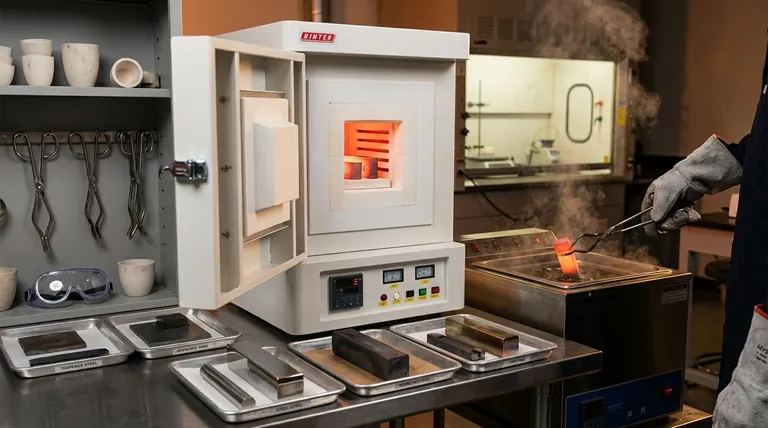
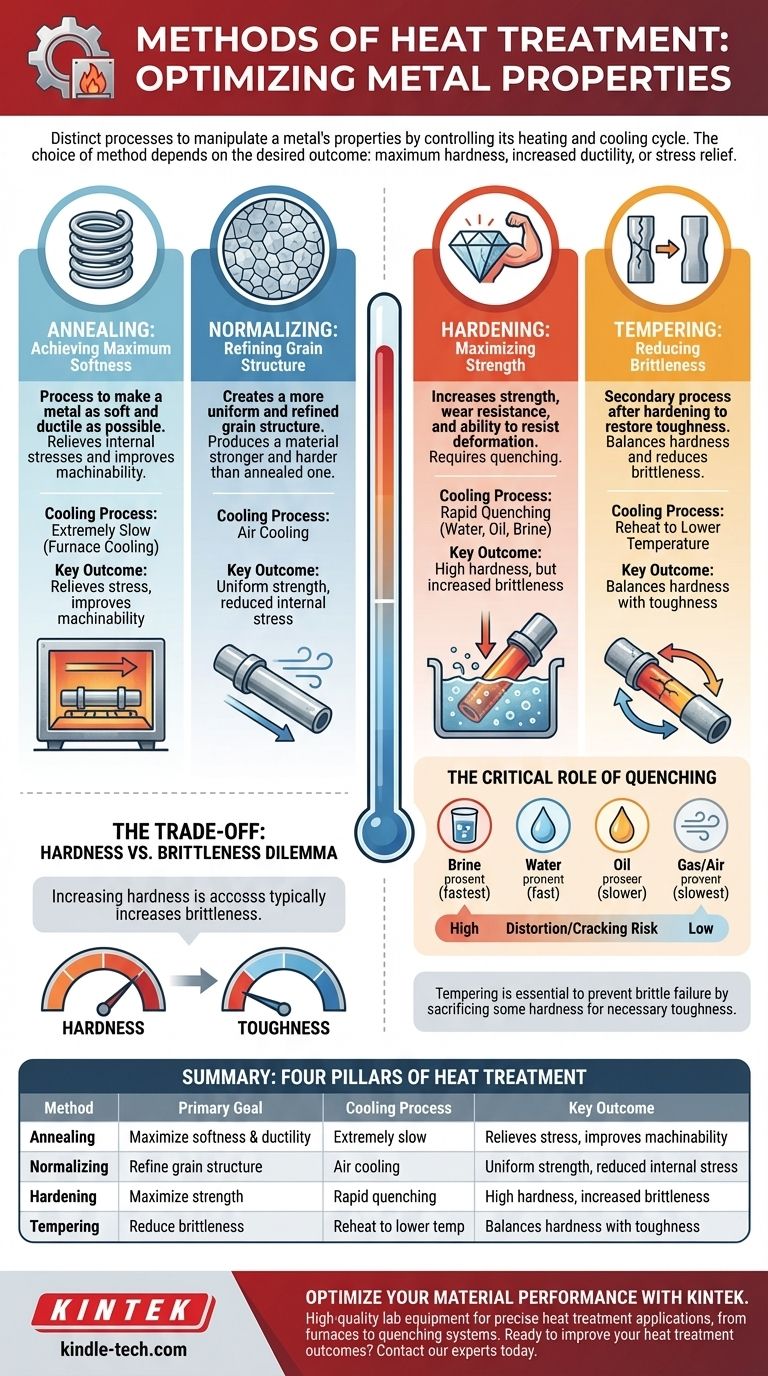
The core methods of heat treatment are distinct processes designed to manipulate a metal’s properties by controlling its heating and cooling cycle. The most common categories include annealing, normalizing, hardening (which relies on quenching), and tempering, with each method producing a different combination of hardness, toughness, and ductility in the final material.
Heat treatment is not a single process, but a set of controlled procedures involving heating and, most importantly, cooling a metal at a specific rate. The choice of method depends entirely on the desired outcome, whether it's achieving maximum hardness, increasing softness and ductility, or relieving internal stress.

The Four Pillars of Heat Treatment
To understand heat treatment, it's best to categorize the methods by their primary objective. Each process alters the metal's internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure, to achieve a specific set of mechanical properties.
Annealing: Achieving Maximum Softness
Annealing is a process used to make a metal as soft and ductile as possible. This is often done to relieve internal stresses from previous work, improve machinability, or prepare the material for further shaping.
The key to annealing is extremely slow cooling. The metal is heated to a specific temperature and then cooled very slowly, often by leaving it inside the furnace as it cools down.
Normalizing: Refining Grain Structure
Normalizing is used to create a more uniform and refined grain structure within the metal. This process removes internal stresses and produces a material that is stronger and harder than an annealed one.
The defining characteristic of normalizing is air cooling. After being heated, the material is removed from the furnace and allowed to cool in the open air, a rate that is faster than annealing but much slower than hardening.
Hardening: Maximizing Strength
Hardening is performed to increase a metal's strength, wear resistance, and ability to resist deformation. This is achieved by heating the metal and then cooling it so rapidly that the internal structure becomes "frozen" in its hardest possible state.
This critical step of rapid cooling is known as quenching. Without a rapid quench, true hardening of most ferrous alloys is impossible.
Tempering: Reducing Brittleness
A metal that has been hardened is often extremely brittle and susceptible to cracking. Tempering is a secondary heat treatment performed after hardening to restore some toughness.
The process involves reheating the hardened part to a much lower temperature and holding it there. This relieves internal stresses and reduces brittleness, though it comes at the cost of some of the hardness gained during quenching.
The Critical Role of Quenching
As the references highlight, quenching is the most decisive step in the hardening process. The choice of quenching medium directly controls the cooling rate and, therefore, the final hardness of the material.
What is Quenching?
Quenching is the act of rapidly cooling a heated metal by immersing it in a liquid or gas. This sudden drop in temperature locks the metal's microstructure in a very hard but brittle state called martensite.
Common Quenching Mediums
The effectiveness and severity of the quench depend on the medium used. Different mediums extract heat at different rates.
- Brine (Salt Water): Provides the fastest and most severe quench, but carries the highest risk of causing distortion or cracking.
- Water: A very fast quench, but less severe than brine. It is widely used but can still cause distortion in complex parts.
- Oil: A slower quench than water, offering a good balance of hardening with a reduced risk of cracking. It is ideal for many alloy steels.
- Gas/Air (Nitrogen): The slowest form of quenching, typically used for high-alloy steels that can harden even with a gentle cooling rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing a heat treatment method is never without consequences. The goals of hardness, toughness, and stability are often in direct opposition to one another.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Dilemma
The central trade-off in heat treatment is between hardness and toughness. As you increase a material's hardness through quenching, you almost always increase its brittleness.
This is why tempering is not optional but essential for most hardened components. It is a controlled sacrifice of some hardness to gain the necessary toughness to prevent the part from shattering in service.
The Danger of Distortion and Cracking
Rapid cooling from a quench creates immense thermal stress within a material. If these stresses exceed the material's strength, the part can warp, distort, or even crack.
The risk is highest with severe quenches (like brine) and on parts with complex geometries, sharp corners, or drastic changes in thickness.
Matching the Method to Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment process requires a clear understanding of your final objective for the component.
- If your primary focus is machinability and stress relief: Annealing is the correct approach due to its slow, controlled cooling process.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform, strong structure before further processing: Normalizing provides a balanced and consistent result through air cooling.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness and wear resistance: Hardening through quenching is necessary, but it must be followed by tempering.
- If your primary focus is increasing toughness in a hardened part: Tempering is the essential final step to prevent catastrophic failure under load.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment means understanding that the speed of cooling is the primary tool for defining a metal's final character.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Goal | Cooling Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Maximize softness & ductility | Extremely slow (furnace cooling) | Relieves stress, improves machinability |
| Normalizing | Refine grain structure | Air cooling | Uniform strength, reduced internal stress |
| Hardening | Maximize strength & wear resistance | Rapid quenching (water, oil, brine) | High hardness, but increased brittleness |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness after hardening | Reheat to lower temperature | Balances hardness with toughness |
Optimize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Choosing the right heat treatment process is critical for achieving the desired balance of hardness, toughness, and durability in your metal components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support precise heat treatment applications—from reliable furnaces for annealing and tempering to quenching systems for effective hardening.
Whether you're in manufacturing, R&D, or quality control, our solutions help you:
- Achieve consistent results with precise temperature control
- Minimize risks of distortion or cracking
- Enhance material properties for your specific needs
Ready to improve your heat treatment outcomes? Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK’s equipment can elevate your laboratory’s capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the hottest temperature a furnace can be? Exploring Limits from 3,000°C+ to Your Application
- What are muffle furnaces used for? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What happens in the muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- How do you cool down a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety with the Correct Procedure
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application



















