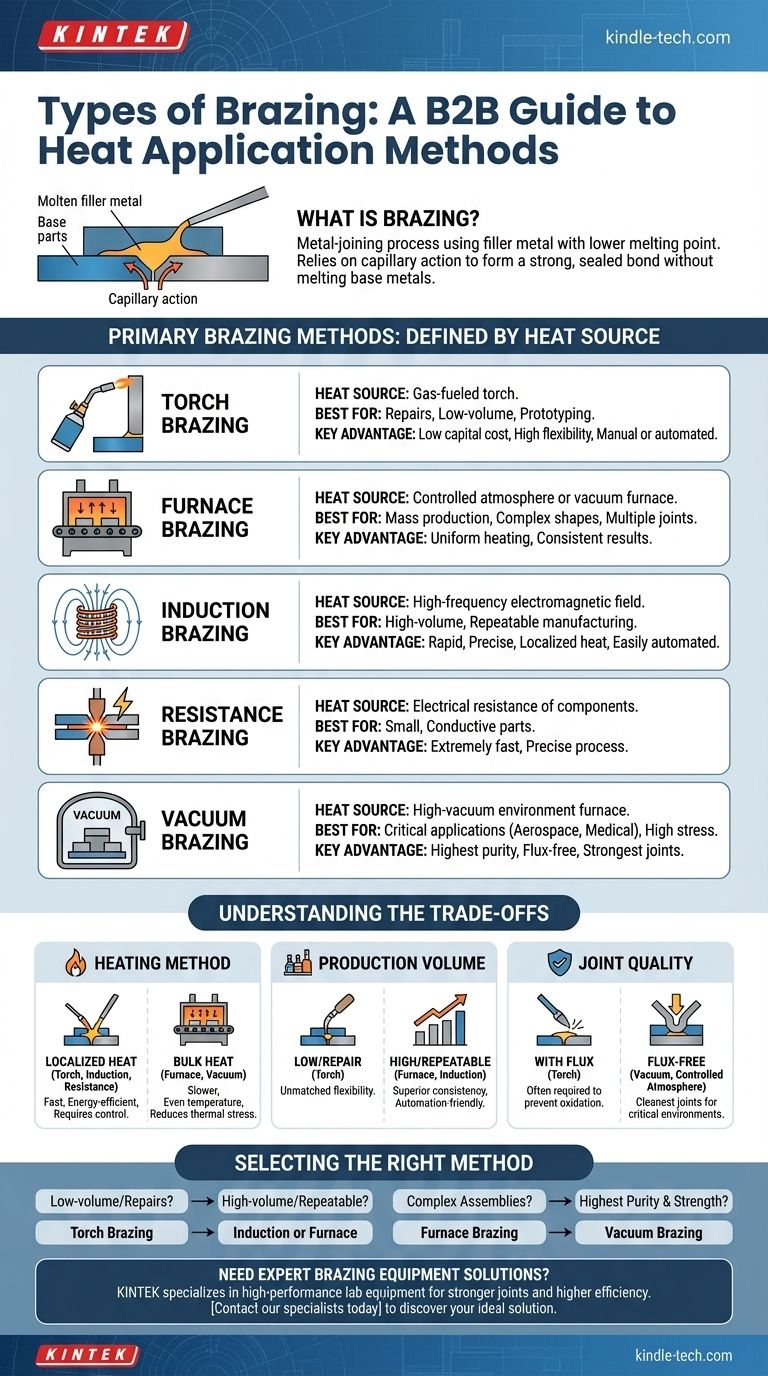
Brazing is not a one-size-fits-all process. The different types of brazing are defined by the method used to apply heat to the workpiece. The primary methods include torch, furnace, induction, resistance, and vacuum brazing, each suited for different materials, production volumes, and joint quality requirements.
The core principle to understand is that the "type" of brazing refers to its heat source. Your choice of method will directly impact production speed, joint quality, and overall cost, making it a critical decision based on your specific application.

How Brazing Works: The Core Principle
What Defines a Brazed Joint?
Brazing is a metal-joining process where two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint.
The filler metal has a lower melting point than the adjoining base metals. The base metals are heated, but they are not melted.
The Role of Capillary Action
The process relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the narrow gap between the parts. This creates a strong, sealed, and often permanent metallurgical bond as the filler metal cools and solidifies.
The Primary Methods of Heat Application
The key differentiator between brazing types is the technique used to heat the assembly to the filler metal's melting temperature.
Torch Brazing
This is one of the most common and versatile methods. Heat is applied using a gas-fueled torch, which can be operated manually for repairs and low-volume work or automated for production lines. It is valued for its low capital cost and flexibility.
Furnace Brazing
In this method, the parts (with the filler metal pre-placed) are loaded into a furnace and heated in a controlled atmosphere or vacuum. This process heats the entire assembly uniformly, making it ideal for joining complex shapes or parts with multiple joints. It is highly suitable for mass production.
Induction Brazing
Induction brazing uses a high-frequency electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the parts. The heat is rapid, precise, and localized to the joint area, which minimizes distortion and protects the surrounding material. This method is easily automated and excellent for high-volume, repeatable manufacturing.
Resistance Brazing
This method uses the electrical resistance of the components to generate heat. Electrodes pass a high current through the parts, and the resistance at the joint interface creates the heat necessary to melt the filler metal. It is an extremely fast and precise process, typically used for smaller, electrically conductive components.
Vacuum Brazing
A specialized type of furnace brazing, this is performed in a high-vacuum environment. The vacuum prevents oxidation and eliminates the need for flux, resulting in exceptionally clean, strong, and high-purity joints. It is the preferred method for aerospace, medical, and other critical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right method requires balancing speed, cost, and quality requirements.
Localized vs. Bulk Heating
Torch, induction, and resistance brazing apply localized heat. This is fast and energy-efficient but requires careful control to avoid overheating.
Furnace and vacuum brazing apply bulk heat. This is slower but ensures even temperature distribution, reducing thermal stress on complex parts.
Production Volume and Automation
For one-off repairs or prototyping, the flexibility of manual torch brazing is unmatched.
For high-volume, repeatable production, the consistency of furnace and induction brazing is superior. These methods are easily integrated into automated production lines.
Joint Quality and Cleanliness
Open-air methods like torch brazing often require a chemical flux to prevent oxidation.
Controlled atmosphere and vacuum brazing produce the cleanest, flux-free joints, which is essential for parts that must withstand high stress or operate in critical environments.
Selecting the Right Brazing Method for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or repairs: Torch brazing offers the most flexibility and lowest initial investment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable manufacturing: Automated induction or furnace brazing will provide the necessary speed and consistency.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies with multiple joints: Furnace brazing ensures uniform heating and consistent results across the entire part.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible joint purity and strength: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for critical applications in demanding industries.
Understanding these core heating methods allows you to match the process precisely to your material, design, and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Heat Source | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Gas Torch | Repairs, Low-Volume | Low cost, High flexibility |
| Furnace Brazing | Controlled Furnace | High-Volume, Complex Parts | Uniform heating, Mass production |
| Induction Brazing | Electromagnetic Field | High-Volume, Repeatable | Fast, Precise, Localized heat |
| Resistance Brazing | Electrical Current | Small, Conductive Parts | Extremely fast, Precise |
| Vacuum Brazing | Vacuum Furnace | Critical Applications (Aerospace, Medical) | Highest purity, No flux required |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right brazing equipment for your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Whether you're scaling up production or require precise, reliable brazing solutions, our expertise can help you achieve stronger joints and higher efficiency.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your specific application and discover the ideal brazing solution for your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















