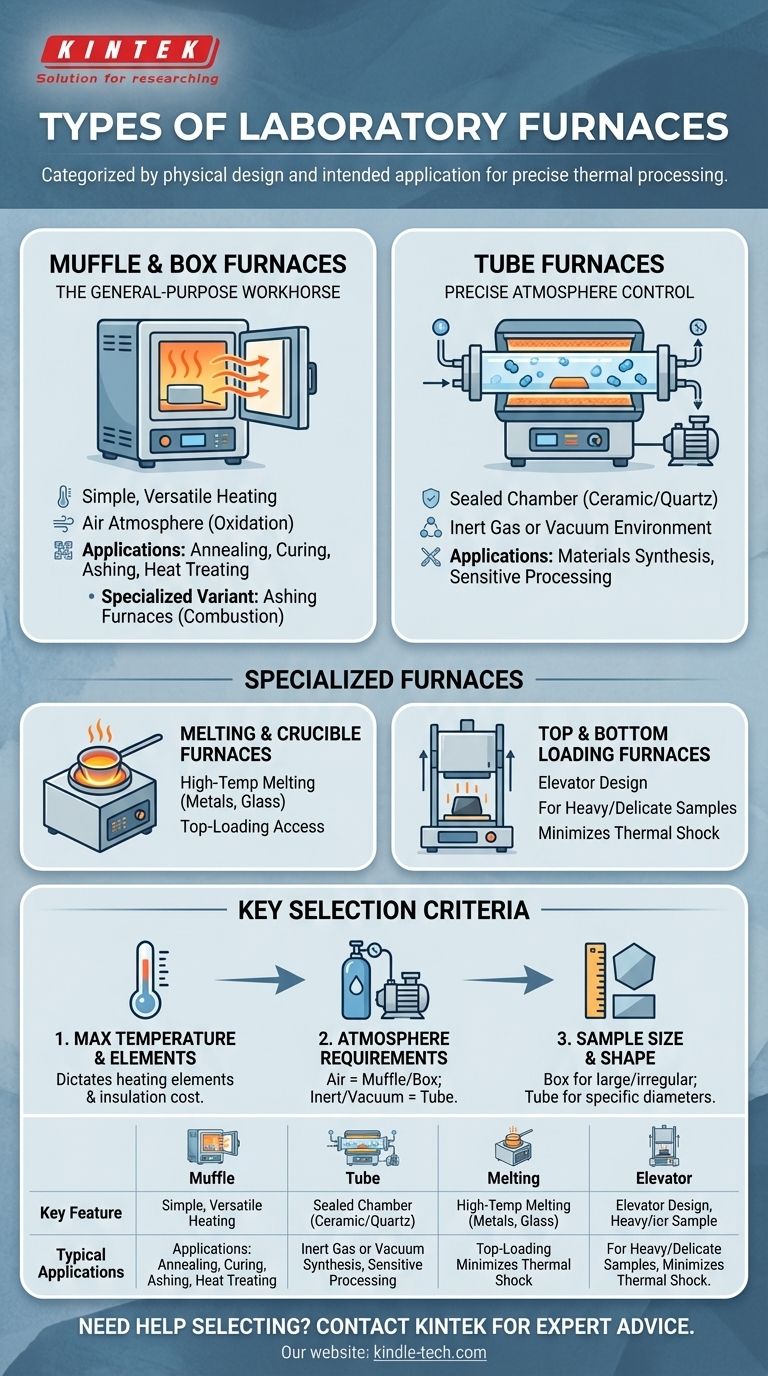
At its core, a laboratory furnace is categorized by its physical design and intended application. The most common types you will encounter are Muffle (or Box) Furnaces for general-purpose heating, Tube Furnaces for processes requiring atmosphere control, and specialized variants like Ashing or Melting furnaces designed for specific material transformations. These furnaces achieve temperatures from 1100°C to over 3000°C, with the design complexity scaling alongside the thermal requirements.
The optimal furnace is not determined by its maximum temperature alone, but by a combination of your sample's form, the necessary processing atmosphere, and the specific thermal application you need to perform.

The General-Purpose Workhorse: Muffle & Box Furnaces
Muffle furnaces, often called box or chamber furnaces, are the most common type found in laboratories. They are valued for their simplicity and versatility in a wide range of heating applications.
How They Work
A muffle furnace is essentially an insulated box with internal heating elements. These elements radiate heat into the central chamber, uniformly heating the sample placed inside. The term "muffle" historically refers to the inner ceramic container that separated the sample from the direct flames or combustion byproducts in older furnace designs.
Key Applications
These furnaces are ideal for general-purpose tasks that occur in an air atmosphere. Common uses include annealing, curing ceramics, chemical synthesis, and material heat-treating.
A Specialized Variant: Ashing Furnaces
Ashing furnaces are a subtype of muffle furnace specifically designed for combustion. Their primary goal is to completely burn off organic material to determine the inorganic content, or "ash," of a sample. They are critical in food science, materials science, and geological analysis.
For Precise Atmosphere Control: Tube Furnaces
When a process cannot be exposed to air, a tube furnace is the definitive choice. Its design is fundamentally different from a box furnace, enabling precise environmental control.
How They Work
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical chamber, typically made of ceramic or quartz, that passes through the insulated, heated section. The sample is placed inside this tube, which can then be sealed at both ends.
The Critical Advantage: Atmosphere Control
By sealing the tube, operators can either pull a vacuum or introduce a continuous flow of a specific gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This creates an inert atmosphere, preventing oxidation or unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Key Applications
Tube furnaces are essential for advanced materials synthesis, processing sensitive components, and any research where the gaseous environment must be strictly managed.
Specialized Furnaces for Specific Tasks
Beyond the two primary categories, several furnace designs exist to solve very specific problems related to sample type, material state, or accessibility.
Melting & Crucible Furnaces
As the name implies, these are high-temperature furnaces designed to melt materials like metals or glass. They are built to safely contain a crucible, the vessel holding the molten material, and often feature a top-loading design for easy crucible access.
Top & Bottom Loading Furnaces
Also known as elevator furnaces, these designs allow the heating chamber to move vertically away from a stationary hearth. This is incredibly useful for loading heavy samples or for delicate materials that could be damaged by thermal shock if placed directly into a hot chamber.
Key Selection Criteria
Choosing the correct furnace requires balancing three primary factors. An error in judgment here can lead to failed experiments or damaged equipment.
Maximum Temperature and Elements
The single most important factor is the maximum temperature you need to achieve. This dictates the type of heating elements (e.g., Kanthal vs. silicon carbide) and the composition of the thermal insulation required, which are major cost drivers.
Atmosphere Requirements
Your second question must be: can my sample be exposed to air? If the answer is no, you are immediately guided toward a tube furnace. If air is acceptable, a muffle or box furnace is the more economical and straightforward solution.
Sample Size and Shape
The physical dimensions of your sample matter. A box furnace offers a large, open volume for multiple or irregularly shaped items. A tube furnace is inherently limited to samples that can fit within the tube's diameter, making it ideal for wafers, rods, or powders in crucibles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is general heating, ashing, or annealing in an air environment: A muffle or box furnace provides the best combination of versatility and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is materials synthesis or processing that requires a vacuum or inert gas: A tube furnace is the only suitable choice to ensure precise atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or handling very heavy or delicate samples: A specialized crucible furnace or a top/bottom loading furnace will provide the safety and accessibility you need.
Ultimately, understanding your process requirements is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Feature | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle / Box Furnace | Simple, versatile heating in air | Annealing, curing, ashing, general heat treatment |
| Tube Furnace | Precise atmosphere control (vacuum/inert gas) | Materials synthesis, sensitive processing |
| Melting / Crucible Furnace | High-temperature melting, top-loading design | Melting metals, glass |
| Top / Bottom Loading Furnace | Easy access for heavy/delicate samples | Handling large or thermally sensitive materials |
Need help selecting the right laboratory furnace for your specific process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your unique research and production needs. Our experts can help you navigate the selection criteria—from temperature range and atmosphere control to sample size—ensuring you get a furnace that delivers precise, reliable results.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK be your partner in achieving your laboratory goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the heat transfer of a muffle furnace? Understanding Indirect Heating for Purity
- How do you run a muffle furnace? Master the Step-by-Step Process for Safe, Precise Results
- What is the melting temperature of ceramics? Understanding High-Temperature Material Performance
- What are the precautions of muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- What is the inside material of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lining for Your Application



















