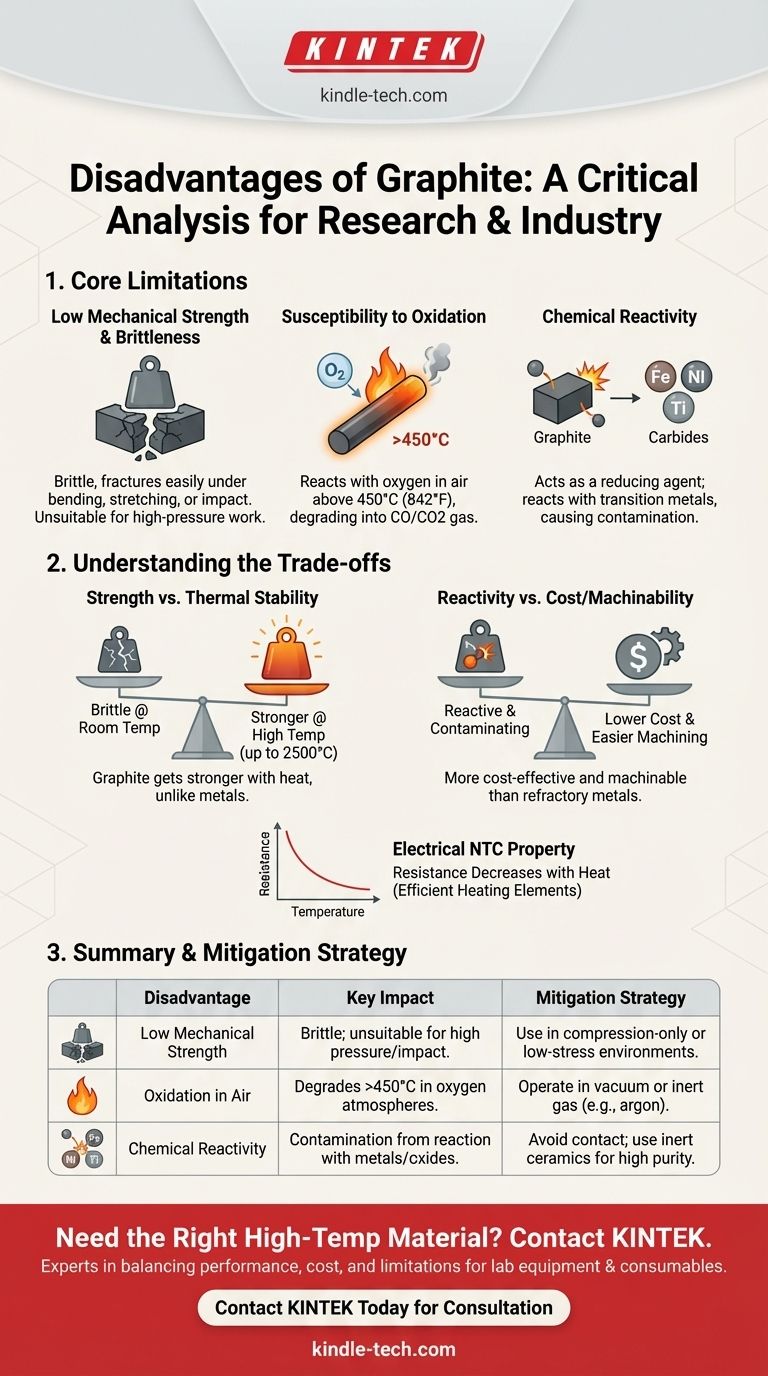
The primary disadvantages of graphite are its low mechanical strength, making it brittle and unsuitable for high-pressure work, and its tendency to react chemically at high temperatures. It is prone to oxidation in air and can react with certain metals and compounds, which can limit its use in specific industrial and metallurgical applications.
While valued for its exceptional thermal and electrical properties, graphite is not a universally ideal material. Its core limitations are physical brittleness and chemical reactivity, which must be carefully managed to prevent catastrophic failure in the wrong environment.

The Core Limitations of Graphite
Understanding where graphite fails is key to using it successfully. Its weaknesses are most apparent under physical stress and in chemically reactive, high-temperature environments.
Low Mechanical Strength and Brittleness
Graphite has very low tensile strength and is a brittle material. This means it cannot withstand bending, stretching, or sudden impacts without fracturing.
While it performs well under compression, its brittleness makes it unsuitable for applications involving high mechanical pressure or where structural integrity under tension is required. This is why graphite dies, for example, cannot be used for high-pressure forming operations.
Susceptibility to Oxidation
One of the most significant practical disadvantages of graphite is its reaction with oxygen at elevated temperatures. Beginning around 450°C (842°F), graphite will begin to oxidize in air.
This reaction consumes the graphite, turning it into carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas, causing the component to degrade and fail. This is why graphite heating elements must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere, like argon, to prevent them from burning away.
Chemical Reactivity with Other Materials
Graphite is not inert in all situations. At high temperatures, it acts as a reducing agent, meaning it can pull oxygen atoms away from metal oxides.
Furthermore, it can react directly with transition metals (like iron, nickel, and titanium) and their nitrides or silicides. This reaction forms metal carbides, which can contaminate the material being processed or degrade the graphite component itself. This is a critical consideration in high-purity metallurgy and semiconductor manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Graphite's disadvantages must be weighed against its significant benefits. The decision to use it often comes down to a series of engineering trade-offs.
Strength vs. Thermal Stability
While mechanically weak at room temperature, graphite has an unusual property: it gets stronger as it gets hotter, up to around 2500°C. Metals, in contrast, typically weaken and soften when heated.
This makes graphite an excellent choice for applications like furnace linings and crucibles where thermal stability is more important than mechanical toughness, provided it is protected from oxygen.
Reactivity vs. Cost and Machinability
Graphite is significantly less expensive than refractory metals like tungsten or molybdenum, which might be used in similar high-temperature applications.
It is also much easier to machine into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing costs. For many applications, it is more cost-effective to use a graphite component and treat it as a consumable item than to invest in a more durable but expensive alternative.
Electrical Properties
Graphite exhibits a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) of resistance. This means its electrical resistance decreases as it gets hotter.
This property makes it a very efficient material for heating elements. As it heats up, it draws more current and generates more heat, a desirable trait that must be managed by the power supply.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing to use graphite requires matching its unique profile to the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is operating under high mechanical pressure or impact: Avoid graphite due to its low tensile strength and brittleness; consider using a metal alloy instead.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating in an open atmosphere: Graphite is unsuitable due to rapid oxidation; use a material like Kanthal (an iron-chromium-aluminium alloy) or operate the graphite in a vacuum or inert gas.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective solution for high-temperature processes in a vacuum: Graphite is an excellent choice due to its high thermal stability, low cost, and ease of machining.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals, oxides, or nitrides: Be cautious, as graphite can form carbides and cause contamination; you may need to use a more inert ceramic like boron nitride or alumina.
By balancing its mechanical and chemical vulnerabilities against its exceptional thermal and economic advantages, you can effectively leverage graphite in the right context.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Low Mechanical Strength | Brittle; unsuitable for high-pressure or impact applications. | Use in compression-only or low-stress environments. |
| Oxidation in Air | Degrades above 450°C (842°F) in oxygen-containing atmospheres. | Operate in a vacuum or inert gas (e.g., argon) environment. |
| Chemical Reactivity | Can react with metals, oxides, and nitrides, causing contamination. | Avoid contact with reactive materials; use inert ceramics for high-purity processes. |
Struggling to choose the right high-temperature material for your lab? The experts at KINTEK understand the critical balance between performance, cost, and material limitations. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, helping you select the perfect solution—whether it's graphite components for vacuum furnaces or alternative materials like ceramics for reactive environments.
Let us help you optimize your process for safety, efficiency, and purity. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite so hard to melt? The Secret Lies in Its Atomic Structure
- How does an induction graphitization furnace facilitate the transformation of unburned carbon into synthetic graphite?
- Why is graphite the best conductor of heat? Understanding Its Directional Thermal Superiority
- What are the industrial applications of graphite? From Metallurgy to Semiconductors
- What are the mechanical properties of graphite? Harnessing Rigidity and Managing Brittleness



















