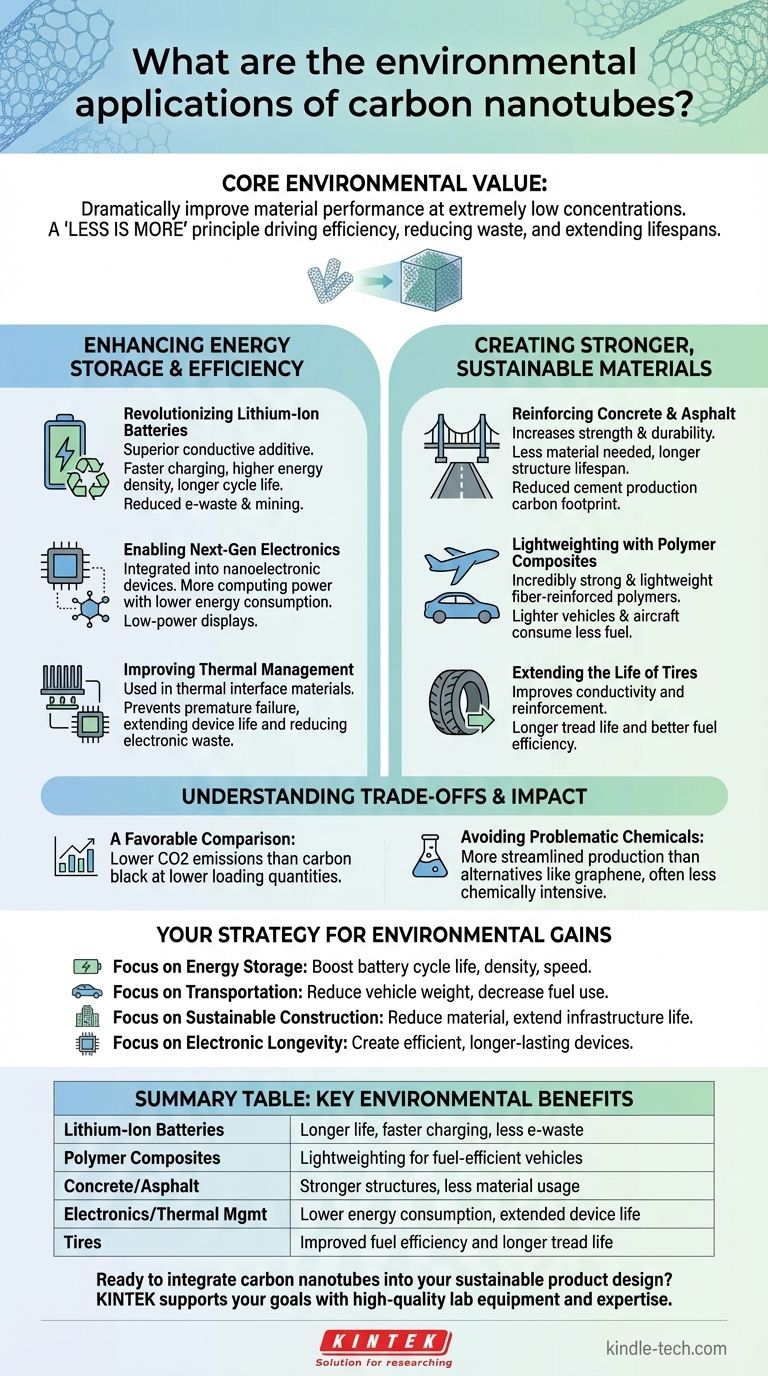
In the field of green technology, the primary environmental applications of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are to enhance the performance and efficiency of other materials. Their most significant use is as a conductive additive in lithium-ion batteries, but they are also used to create stronger and more durable composites for industries like construction and transportation, and to enable more efficient electronics.
The core environmental value of carbon nanotubes is not in a single application, but in their ability to dramatically improve material performance at extremely low concentrations. This principle of "less is more" drives efficiency, reduces waste, and extends product lifespans across multiple critical sectors.

Enhancing Energy Storage and Efficiency
The unique electrical and thermal properties of CNTs make them ideal for improving how we store and use energy. This is their most mature and impactful environmental application area.
Revolutionizing Lithium-Ion Batteries
CNTs act as a superior conductive additive in both the cathode and anode of lithium-ion batteries. This creates a highly efficient electrical network within the battery.
This network allows for faster charging, higher energy density, and a significantly longer cycle life. Longer-lasting batteries directly translate to less electronic waste and a reduced need for mining raw materials.
Enabling Next-Generation Electronics
By depositing CNTs using methods like plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), they can be integrated into nanoelectronic devices.
This enables the creation of ultra-large-scale integrated circuits that deliver more computing power with lower energy consumption. It also allows for applications like low-power field emission displays.
Improving Thermal Management
CNTs are used in thermal interface materials to dissipate heat more effectively from electronic components.
Better heat management allows electronics to run more efficiently and prevents premature failure, extending the usable life of devices and further reducing waste.
Creating Stronger, More Sustainable Materials
The exceptional strength-to-weight ratio of CNTs allows them to act as a powerful reinforcement agent, making traditional materials more durable and resource-efficient.
Reinforcing Concrete and Asphalt
When added to concrete or asphalt in very small quantities, CNTs significantly increase their mechanical strength and durability.
This means structures require less material to achieve the same strength, or they can last much longer before needing repair or replacement. This reduces the immense carbon footprint associated with cement production and road maintenance.
Lightweighting with Polymer Composites
CNTs are incorporated into fiber-reinforced polymers and other composites to create materials that are both incredibly strong and lightweight.
These materials are critical for the automotive and aerospace industries. Lighter vehicles and aircraft consume less fuel, directly reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Extending the Life of Tires
In tires, CNTs can improve both conductivity and reinforcement. This can lead to longer tread life and better fuel efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Production Impact
No material is perfect, and a clear-eyed assessment requires understanding the full lifecycle. While the application of CNTs provides clear environmental benefits, their production is an energy-intensive process.
A Favorable Comparison to Alternatives
The key is comparing CNTs to incumbent materials. When measured per kilogram, CNT production generally results in lower CO2 emissions than traditional additives like carbon black.
Furthermore, carbon black often requires much higher loading quantities to achieve a similar effect, amplifying its negative environmental impact.
Avoiding Problematic Chemicals
Other advanced materials, such as graphene, often face significant production hurdles. These can include high energy and water usage, as well as the need for harsh chemicals that create disposal challenges.
The production of CNTs, while not impact-free, often presents a more streamlined and less chemically intensive pathway to achieving high-performance material properties.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your strategy for using carbon nanotubes should be guided by the specific environmental outcome you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is energy storage: Use CNTs as a conductive additive to boost battery cycle life, energy density, and charging speed.
- If your primary focus is transportation efficiency: Incorporate CNTs into polymer composites to reduce vehicle weight and decrease fuel consumption.
- If your primary focus is sustainable construction: Add CNTs to concrete to reduce the total material required and extend the lifespan of infrastructure.
- If your primary focus is electronic longevity: Leverage CNTs in thermal interface materials and integrated circuits to create more efficient, longer-lasting devices.
Ultimately, carbon nanotubes provide a powerful tool for achieving significant environmental gains by fundamentally improving the efficiency of the materials we already use.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Longer life, faster charging, less e-waste |
| Polymer Composites | Lightweighting for fuel-efficient vehicles |
| Concrete/Asphalt | Stronger structures, less material usage |
| Electronics/Thermal Mgmt | Lower energy consumption, extended device life |
| Tires | Improved fuel efficiency and longer tread life |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your sustainable product design?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced material research and development. Whether you are developing next-generation batteries, lightweight composites, or durable construction materials, our expertise can support your goals for enhanced performance and environmental sustainability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve your efficiency and sustainability targets.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- Are semiconductors thin or thick? Discover the Power of Microscopic Thinness in Modern Electronics
- What are the natural sources of graphene? Unlocking the Power of Graphite, the True Precursor
- How were the first gem-quality synthetic diamonds produced? Discover the 1970 GE Breakthrough
- What is the thickness of CVD graphene? From Single-Atom Layers to Precise Multi-Layer Control
- How is thin film used as coating material? A Guide to Enhancing Material Performance
- What is the process of ion sputtering? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the purpose of ITO coating? Enabling Transparent Electronics for Modern Devices
- What are the factors affecting optical properties? Master the Atomic and Microstructural Influences



















