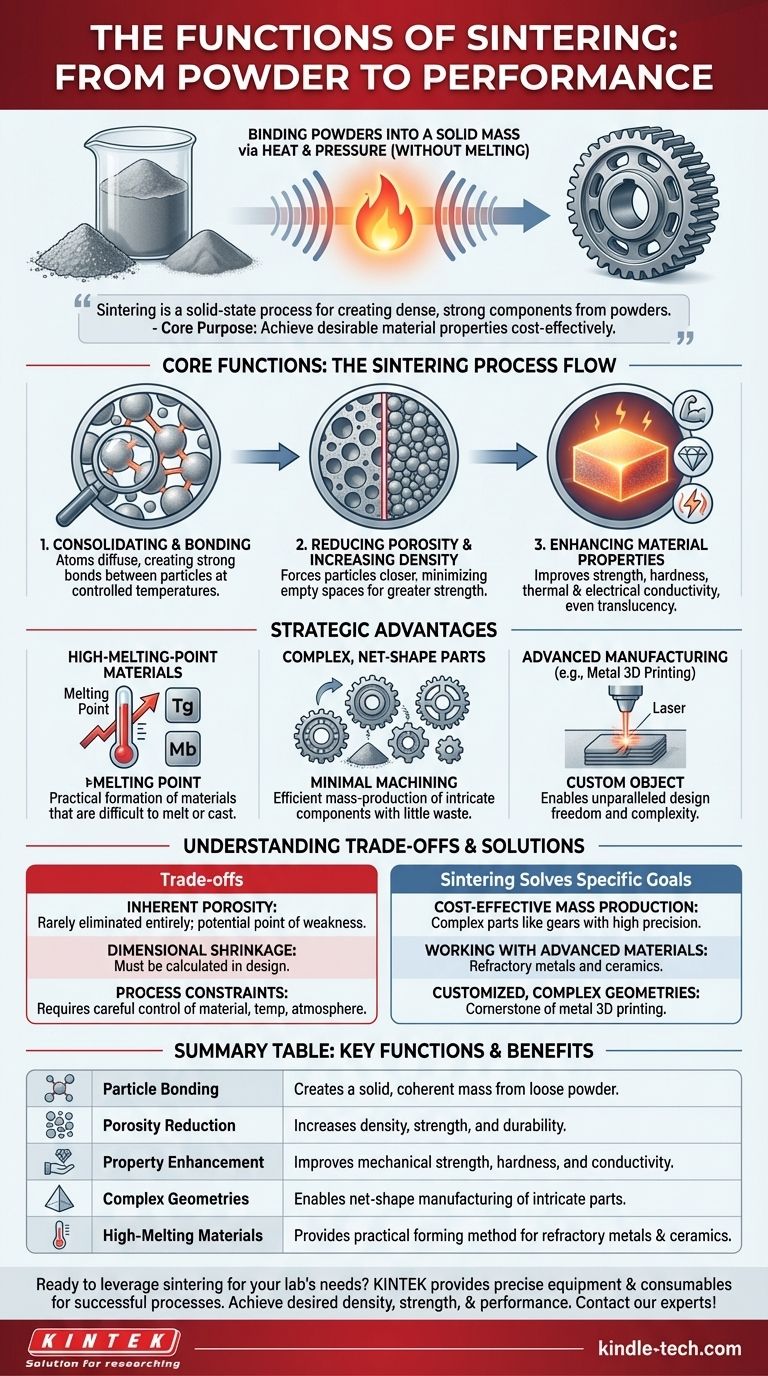
The primary function of the sintering process is to bind powdered materials into a solid, dense mass using heat and pressure without reaching the material's melting point. This transforms loose particles into a strong, unified object by encouraging atoms to form tighter bonds, which significantly enhances the material's physical properties like strength and durability.
Sintering is not about melting; it's a solid-state process for creating dense, strong components from powders. Its core purpose is to achieve desirable material properties in a cost-effective way, especially for materials with extremely high melting points.

The Core Functions: From Powder to Performance
Sintering is a foundational process in fields like powder metallurgy and ceramics manufacturing. It accomplishes several critical functions simultaneously by carefully controlling heat and pressure.
Function 1: Consolidating and Bonding Particles
The most fundamental function of sintering is to transform a loose collection of particles into a coherent, solid mass.
This is achieved by heating the material to a temperature where the atoms become mobile enough to diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles, creating strong bonds between them. The material never becomes a liquid, making the process highly controlled.
Function 2: Reducing Porosity and Increasing Density
A pressed, unsintered part (often called a "green part") contains significant empty space, or porosity, between its particles.
Sintering forces these particles closer together, systematically minimizing these porous spaces. This densification process is critical for increasing the overall strength and durability of the final component.
Function 3: Enhancing Material Properties
By increasing density and creating a unified structure, sintering directly enhances a wide range of a material's characteristics.
This includes improvements in mechanical strength, hardness, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity. For some ceramics, it can even increase translucency.
Key Applications and Strategic Advantages
The functions of sintering translate into significant advantages that make it the process of choice across many industries, from automotive parts to advanced electronics.
Enabling the Use of High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering provides a practical way to form parts from materials like tungsten or molybdenum, which have melting points so high that melting and casting them would be extremely energy-intensive and difficult.
Because sintering operates below the melting point, it offers a more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing route for these advanced materials.
Creating Complex, Net-Shape Parts
In powder metallurgy, powders are first pressed into a desired shape before being sintered. This is a highly efficient way to mass-produce complex components like gears, bearings, sprockets, and cams.
The resulting parts are "net-shape" or "near-net-shape," meaning they require little to no subsequent machining, which saves time and reduces material waste.
Facilitating Advanced Manufacturing
Sintering is a key step in many forms of metal 3D printing. A laser selectively sinters layers of metal powder to build a custom object, allowing for unparalleled design freedom and complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Porosity
Although sintering significantly reduces porosity, it rarely eliminates it entirely. The remaining microporosity can sometimes be a point of weakness compared to a component made from fully melted and cast metal.
Dimensional Control and Shrinkage
The process of densification causes the component to shrink. This shrinkage must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial design of the mold or part to achieve the final desired dimensions.
Material and Process Constraints
The success of sintering depends on careful control of the material's particle size, pressure, temperature, and furnace atmosphere. Not all materials are suitable for sintering, and the process requires specialized equipment and expertise.
How Sintering Solves Specific Manufacturing Goals
Your choice of manufacturing process depends on your ultimate goal. Sintering is the optimal solution in several key scenarios.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Sintering is ideal for creating complex parts like gears and bearings with high precision and minimal need for finishing work.
- If your primary focus is working with advanced materials: It provides the most practical method for forming components from metals and ceramics with extremely high melting points.
- If your primary focus is customized, complex geometries: Sintering is a cornerstone of metal 3D printing, enabling the creation of intricate parts that are impossible to produce with traditional methods.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful and versatile method for engineering materials with specific properties that casting or machining alone cannot achieve.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Particle Bonding | Creates a solid, coherent mass from loose powder. |
| Porosity Reduction | Increases density, strength, and durability. |
| Property Enhancement | Improves mechanical strength, hardness, and conductivity. |
| Complex Geometries | Enables net-shape manufacturing of intricate parts. |
| High-Melting Materials | Provides a practical forming method for refractory metals and ceramics. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material or component needs? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables required for successful sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials or manufacturing complex parts, our expertise ensures you achieve the desired density, strength, and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results



















