Beyond its utility, compressed air introduces a unique and often underestimated set of industrial hazards. The primary dangers are not from breathing the air, but from the immense kinetic energy it carries. These hazards fall into several categories: direct bodily injury from high-pressure injection, eye and face trauma from propelled particles, hearing damage from noise, and violent equipment failure.
The core danger of compressed air stems from a common misconception: treating it like ordinary, harmless air. Its high pressure transforms it into a potent source of kinetic energy capable of causing severe injury through skin penetration, equipment explosion, and the projectile-like force of airborne debris.

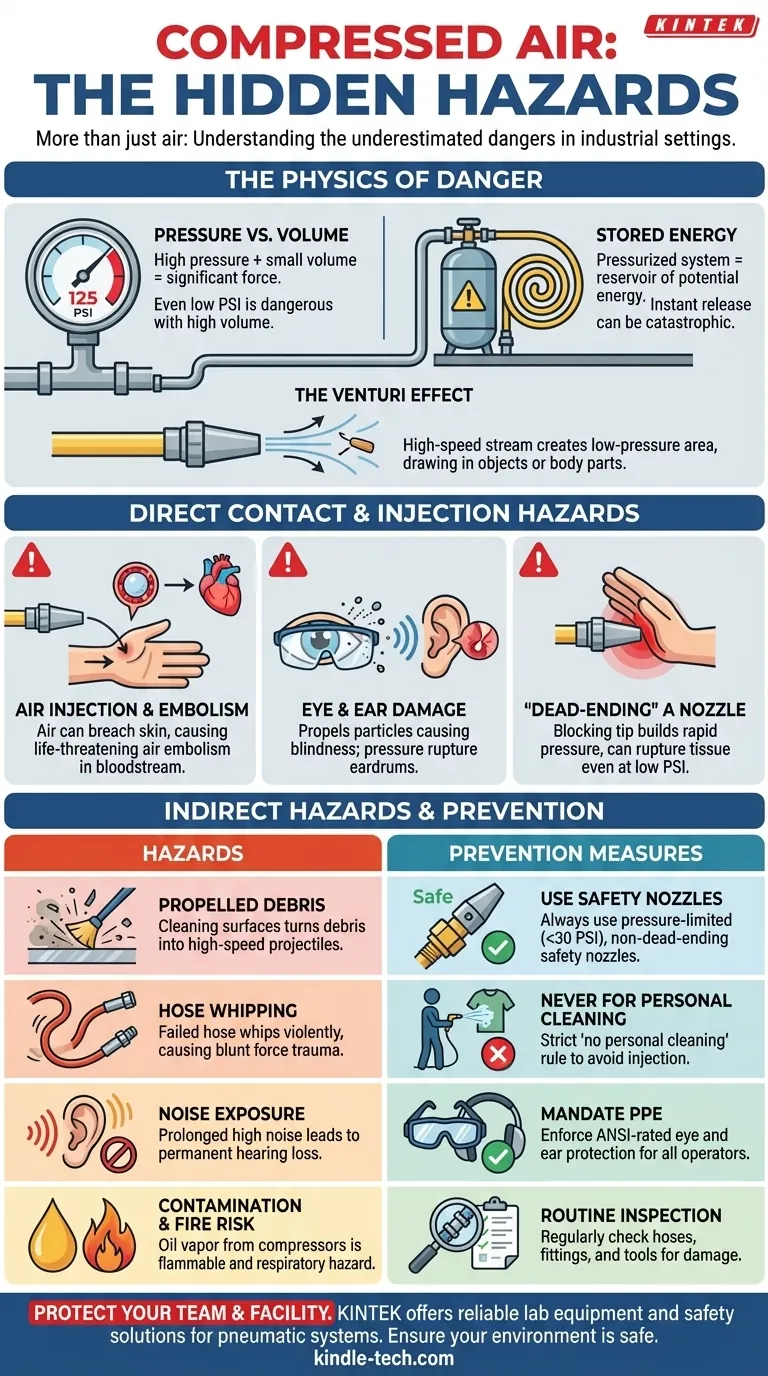
The Physics of a Hidden Danger
To mitigate the risks, you must first understand the properties that make compressed air hazardous. The danger is a direct result of storing a large amount of energy in a small volume.
Pressure vs. Volume
A standard industrial air system running at 100-125 PSI (pounds per square inch) exerts significant force. Even systems at a seemingly low 15-30 PSI can be dangerous, especially when the volume of air released is high.
Stored Energy
A pressurized air system is a reservoir of stored potential energy. If a component like a hose, tank, or fitting fails, this energy is released instantaneously and violently, creating an explosion or a whipping hose with enough force to cause fatal injury.
The Venturi Effect
When compressed air is released from a nozzle, the high-speed stream creates a low-pressure area around it (the Venturi effect). This can paradoxically cause nearby objects, including body parts, to be drawn into the powerful airstream, increasing the risk of injury.
Direct Contact and Injection Hazards
The most severe injuries occur when compressed air directly contacts the body. These are medical emergencies that are often misunderstood by workers.
Air Injection and Embolism
If a compressed air stream breaches the skin, air can be forced directly into the tissue and bloodstream. This can create an air embolism—an air bubble in a blood vessel—which can travel to the heart or brain, causing a heart attack, stroke, or immediate death. An injection injury may show little external damage, masking a life-threatening internal condition.
Eye and Ear Damage
A blast of compressed air, even from a distance, can easily rupture an eardrum. More commonly, it propels tiny, unseen particles of dust, metal, or debris at high velocity, causing severe eye damage or blindness. This is the single most common injury associated with compressed air.
"Dead-Ending" a Nozzle
Blocking the tip of an air nozzle with a finger or thumb is exceptionally dangerous. This "dead-ending" causes the air pressure to build rapidly against the skin, and it can rupture tissue and force its way into the body at pressures as low as 10-15 PSI.
Indirect and Environmental Hazards
Beyond direct contact, compressed air creates a hazardous environment through its effect on surrounding objects and the equipment itself.
Propelled Debris
Using compressed air for cleaning surfaces is a primary source of injury. It turns dust, dirt, metal shavings, and other small fragments into high-speed projectiles that threaten the operator and anyone nearby.
Hose Whipping
A disconnected or failed air hose will whip around violently and unpredictably. The metal fitting at the end of a whipping hose acts like a flail, capable of causing blunt force trauma, fractures, and deep lacerations.
Noise Exposure
Air compressors and pneumatic tools generate high levels of noise. Without proper hearing protection, prolonged exposure can lead to permanent hearing loss.
Contamination and Fire Risk
Air from oil-lubricated compressors can contain a fine mist of oil. This oil vapor can be flammable or explosive under certain conditions and is also a respiratory hazard if inhaled in significant quantities.
Common Misconceptions and Oversights
Effective safety relies on dispelling common myths that lead to complacency.
"It's Only Low Pressure"
Many assume that pressures under 30 PSI are safe. While OSHA regulations permit pressures up to 30 PSI for cleaning only if the nozzle is a safety-type that cannot be dead-ended, any un-regulated pressure can propel debris or cause injection. The 30 PSI rule is a specific regulatory minimum, not a universal "safe" threshold.
Using Air for Personal Cleaning
Never use compressed air to clean dust or debris from clothing or skin. This practice is a direct cause of severe injection injuries and is explicitly forbidden in nearly all industrial safety programs.
Ignoring Small Leaks
A hissing leak is not just an efficiency loss; it is a symptom of a potential failure point. That same fitting or hose could be degrading and may eventually fail catastrophically.
Improper Fittings and Hoses
Using incorrect or damaged fittings, clamps, or hoses is a leading cause of violent system failure. All components must be rated for the system's maximum pressure and be correctly installed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Protecting your team requires moving from awareness to active prevention. Your approach should be tailored to your specific role and responsibilities.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Mandate and enforce the use of ANSI-rated safety glasses and hearing protection, and provide rigorous training on the specific danger of air injection.
- If your primary focus is facility management: Implement a routine inspection program for all hoses, fittings, and connectors, and ensure all air-powered tools use safety retainers for their attachments.
- If your primary focus is writing safety policy: Enforce a strict "no personal cleaning" rule and ensure all cleaning stations use engineered safety nozzles that are pressure-limited (below 30 PSI) and cannot be dead-ended.
By treating compressed air with the respect its stored energy deserves, you transform a potential hazard into a powerful and efficient tool.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Specific Risks | Key Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Bodily Injury | Air injection, embolism, tissue damage | Use safety nozzles, never use for cleaning skin/clothing |
| Eye & Ear Damage | Propelled debris, noise-induced hearing loss | Mandate ANSI-rated safety glasses and hearing protection |
| Equipment Failure | Hose whipping, violent explosions | Implement routine inspections, use pressure-rated components |
| Environmental Hazards | Oil contamination, fire risk, propelled debris | Prohibit personal cleaning, use engineered safety systems |
Protect your team and your facility from compressed air hazards. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including safety solutions for pneumatic systems. Our expertise helps laboratories like yours maintain a safe and compliant working environment. Contact us today to discuss your specific safety needs and ensure your compressed air systems are secure.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- What is terpene distillate? A Guide to High-Potency, Flavored Cannabis Oil
- What is the effect of temperature on hydrogen embrittlement? The Critical Role of Temperature in Material Failure
- How do I prepare my house for bed bug heat treatment? A Guide to Ensuring Total Elimination
- What are the safety issues with nanomaterials? Navigating the Unique Risks of Nanoscale Materials
- What is the temperature range for annealing? Master Material-Specific Heat Treatment
- How is thin film thickness measured? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Films
- What is bio-oil production and uses? A Guide to Liquid Biomass for Energy & Chemicals
- What chemicals are used in heat treatment? Master the Quenching Process for Optimal Metal Properties



















