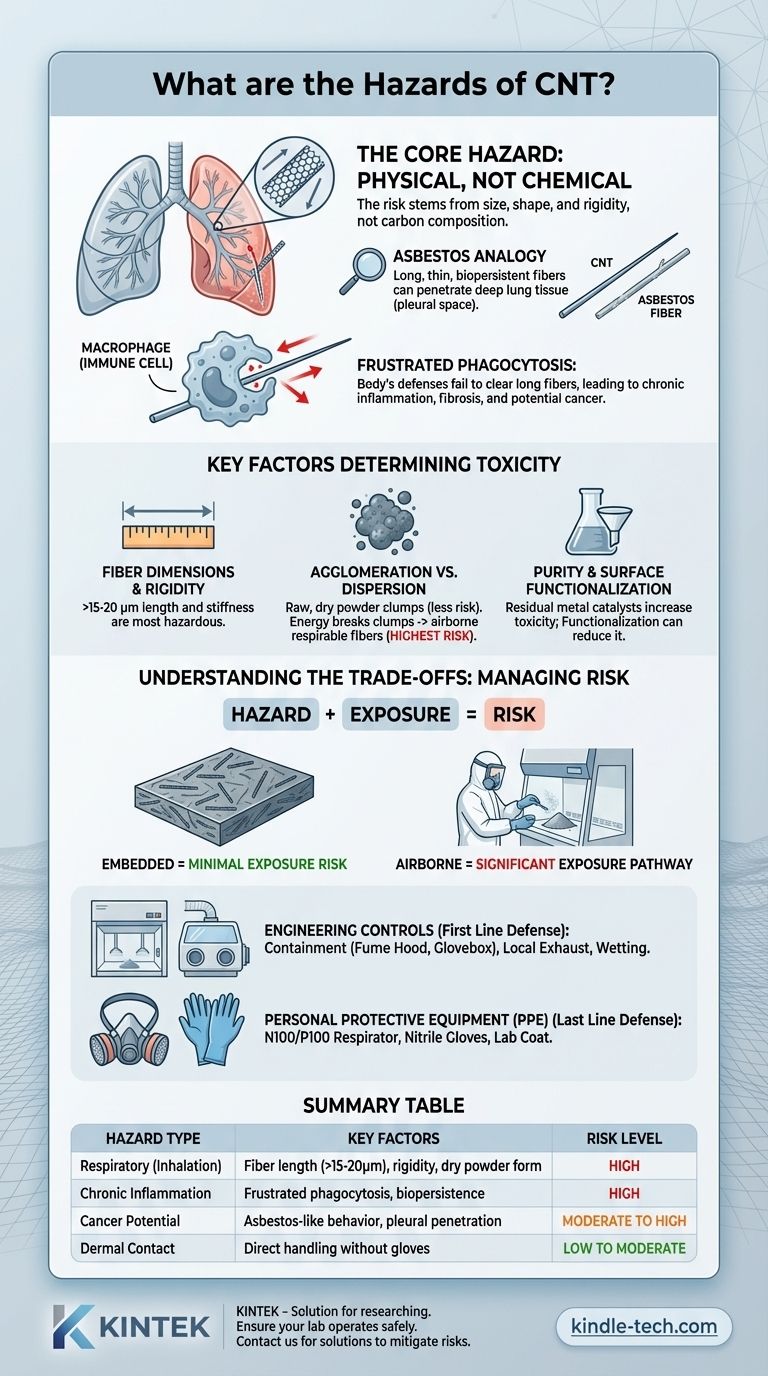
The primary hazards of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) are not chemical but physical, stemming from their size, shape, and rigidity. When inhaled, certain types of long, thin, and stiff CNTs can behave like asbestos fibers, posing a significant risk of chronic lung inflammation, fibrosis (scarring), and potentially cancer, as the body's immune cells cannot effectively clear them.
The central takeaway is that the risk from CNTs is overwhelmingly a respiratory hazard driven by the physical dimensions of the fibers, not their carbon composition. The potential for harm is highest when handling raw, dry CNT powders that can become airborne, and is significantly lower when they are embedded within a solid polymer matrix.

The Core Hazard: A Physical, Not Chemical, Threat
The toxicity of CNTs is a classic example of how a material's form, rather than its chemical makeup, can determine its biological impact. Carbon itself is generally benign, but shaping it into a nanoscale fiber changes the rules.
The Asbestos Analogy Explained
The most pressing concern arises from the similarity between some CNTs and asbestos fibers. Both are characterized by a high aspect ratio (very long and thin) and can be biopersistent, meaning they resist breaking down inside the body.
This structural similarity leads to a similar toxicological outcome. Long, needle-like fibers can penetrate deep into the lung tissue, specifically reaching the pleural space—the thin membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity. This is the same mechanism that leads to mesothelioma, a rare and aggressive cancer strongly linked to asbestos exposure.
Frustrated Phagocytosis: Why the Body's Defenses Fail
Your lungs are protected by immune cells called macrophages, which act as a cleanup crew, engulfing and removing foreign particles. However, macrophages have a size limit.
When a macrophage encounters a CNT fiber that is too long to be fully ingested, a process called frustrated phagocytosis occurs. The cell repeatedly tries and fails to engulf the fiber, triggering a continuous inflammatory response. This chronic inflammation can lead to the formation of granulomas (masses of immune cells), fibrosis, and an increased risk of cancer over time.
Key Factors Determining CNT Toxicity
It is critical to understand that not all CNTs are equally hazardous. The risk is highly dependent on several physical properties.
Fiber Dimensions and Rigidity
Length is the most critical factor. Generally, fibers longer than 15-20 micrometers are too large for macrophages to clear and are associated with the most severe asbestos-like effects.
Rigidity also plays a key role. Stiff, needle-like CNTs are more capable of physically piercing cell membranes and driving inflammatory responses compared to flexible, tangled nanotubes which are less pathogenic.
Agglomeration vs. Dispersion
In their raw, dry powder form, CNTs tend to clump together into larger agglomerates. These clumps are often too large to be inhaled deep into the lungs.
The greatest risk occurs when energy is applied—such as through sonication or air currents—that breaks these clumps apart, releasing individual, respirable fibers into the air. This is why processes involving the handling of dry powders are the most hazardous.
Purity and Surface Functionalization
The manufacturing process for CNTs often leaves behind residual metal catalyst nanoparticles (like iron, nickel, or cobalt). These metallic impurities can have their own inherent toxicity and may contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation.
Conversely, intentionally modifying the surface of CNTs (functionalization) can sometimes reduce their toxicity by changing how they interact with cells or by making them less biopersistent.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Managing Risk in Practice
The presence of a hazard does not automatically equal risk. Risk is a function of both the inherent hazard of the material and the level of exposure to it.
The Hazard vs. Exposure Equation
A highly hazardous material (like long, rigid CNTs) poses little risk if it is fully contained. For example, CNTs embedded within a solid composite material are not airborne and therefore present a minimal exposure risk.
The risk becomes significant only when these materials are machined, abraded, or processed in a way that releases the fibers into the air, creating an exposure pathway.
Engineering Controls: The First Line of Defense
The most effective way to manage CNT risk is to prevent exposure in the first place. Engineering controls are designed to contain the material at its source.
This includes working with CNT powders inside ventilated enclosures like a fume hood or a glovebox, and using local exhaust ventilation to capture any dust generated during handling. Wetting the powder to create a slurry or paste can also dramatically reduce its potential to become airborne.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): The Last Line of Defense
When engineering controls cannot completely eliminate the risk of exposure, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential.
For CNTs, this primarily means respiratory protection. A simple surgical mask is insufficient. A properly fitted respirator with a P100 or N100 filter is required to capture nanoscale particles. Nitrile gloves and lab coats should also be used to prevent dermal contact.
How to Apply This to Your Work
Your safety strategy should be directly informed by your specific application and the form of the CNT material you are using.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Treat all novel or uncharacterized CNT powders as highly hazardous respiratory agents. Work exclusively within certified engineering controls.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or integration: Concentrate safety efforts on points where dry CNTs are handled. Once the CNTs are integrated into a liquid resin or solid matrix, the inhalation risk is dramatically reduced.
- If your primary focus is safety management: Develop a risk management plan based on the "asbestos model." Prioritize eliminating airborne exposure and assume any respirable fiber could be pathogenic until proven otherwise.
Ultimately, harnessing the revolutionary properties of carbon nanotubes safely requires a proactive and informed approach to risk management.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Type | Key Factors | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory (Inhalation) | Fiber length (>15-20μm), rigidity, dry powder form | High |
| Chronic Inflammation | Frustrated phagocytosis, biopersistence | High |
| Cancer Potential | Asbestos-like behavior, pleural penetration | Moderate to High |
| Dermal Contact | Direct handling without gloves | Low to Moderate |
Ensure your lab operates safely with cutting-edge materials. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for handling nanomaterials like Carbon Nanotubes safely and efficiently. Our products help you mitigate risks and maintain compliance with the highest safety standards. Contact us today to learn how we can support your laboratory's needs and enhance your safety protocols.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Is biomass renewable or renewable? A Deep Dive into Sustainable Energy's Carbon Cycle
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently
- What is a thick film circuit? A Durable, High-Power Hybrid Electronics Solution
- What role does a magnetic stirrer play in electrochemical dye degradation? Maximize Kinetics & Mass Transfer Efficiency
- How do separate internal compartments in ultra-low freezers improve efficiency? Enhance Stability and Reduce Costs
- What is the product of slow pyrolysis? Tailor-Made Biochar, Oil, and Syngas from Biomass
- How do you clean a filter press? A Step-by-Step Guide to Efficient Filter Cake Removal
- What are two different uses of a water bath in biological investigations? Precise Temperature Control for Reliable Results



















