In nearly every industrial sector, filtration is an indispensable process used to separate particles from a fluid or gas. Its applications are vast, ranging from producing sterile pharmaceuticals and clarifying beverages to treating municipal wastewater, protecting sensitive equipment, and controlling air pollution. Filtration is the fundamental technology that ensures product quality, operational efficiency, and environmental compliance across the modern industrial landscape.
Industrial filtration is not a single process, but a versatile engineering tool used to solve critical separation challenges. The key is to match the filtration method to the specific goal, whether it's removing microscopic contaminants, recovering a valuable solid product, or clarifying a process liquid.

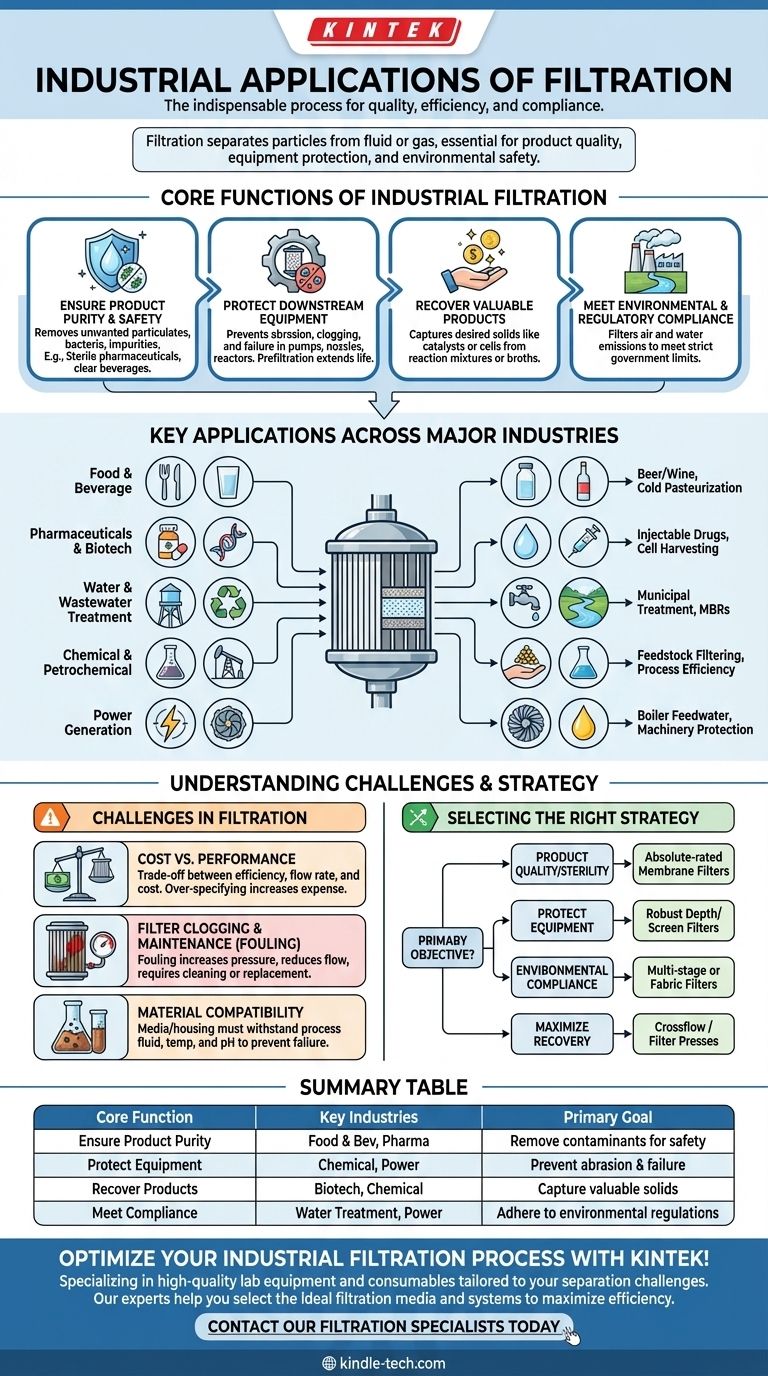
The Core Functions of Industrial Filtration
Before examining specific industries, it's crucial to understand the primary goals that drive the use of filtration. Nearly every application can be traced back to one of these four core functions.
Ensuring Product Purity and Safety
This is often the most critical function, especially in consumer-facing industries. Filtration removes unwanted particulates, microorganisms, or impurities that could compromise the final product's quality, safety, or appearance.
For example, sterile filtration in pharmaceuticals removes all bacteria to ensure a drug is safe for injection. In the food industry, it removes yeast and sediment to create a clear, stable beverage.
Protecting Downstream Equipment
Industrial processes often rely on a series of complex and expensive machines, such as pumps, nozzles, heat exchangers, and reactors. Particulates in a fluid stream can cause abrasion, clogging, and catastrophic failure of this equipment.
Prefiltration is a common strategy where a coarse filter is placed upstream to remove larger particles. This protects more sensitive, high-efficiency filters or machinery further down the line, extending their life and reducing maintenance costs.
Recovering Valuable Products
Filtration is not always about removing waste; it is often used to capture the desired product. In these applications, the solid material retained by the filter is the valuable component.
This is common in chemical manufacturing for catalyst recovery, where expensive catalysts are separated from a liquid reaction mixture to be reused. Similarly, in biotechnology, filtration is used to harvest cells from a fermentation broth.
Meeting Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Governments worldwide impose strict limits on what industries can release into the air and water. Filtration is a cornerstone technology for meeting these environmental regulations.
Wastewater treatment plants use multiple stages of filtration to remove contaminants before discharging water into rivers. Power plants and factories use large-scale "baghouses" (fabric filters) to capture particulate matter from exhaust stacks, preventing air pollution.
Key Applications Across Major Industries
With the core functions in mind, we can see how filtration is applied across a diverse range of sectors.
Food and Beverage
In this industry, filtration directly impacts product taste, appearance, and shelf life. Key applications include the clarification of beer and wine, the removal of bacteria from milk (cold pasteurization), and the purification of bottled water and soft drinks. Sugar syrups and edible oils are also filtered to ensure clarity and purity.
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
The pharmaceutical industry demands the highest level of purity. Sterile filtration using 0.22-micron filters is standard for injectable drugs and ophthalmic solutions. It is also essential for producing Water for Injection (WFI), an ultra-pure water free of microbes and endotoxins. Cell harvesting and protein purification are other critical biotech applications.
Water and Wastewater Treatment
Filtration is the backbone of both municipal and industrial water treatment. It is used at a massive scale to produce safe drinking water by removing sediment, cysts like Giardia, and other particles. In wastewater treatment, membrane bioreactors (MBRs) combine biological treatment with membrane filtration to produce high-quality effluent.
Chemical and Petrochemical Manufacturing
In chemical processing, filtration is used to remove contaminants from feedstocks, recover valuable catalysts, and purify final products. It protects sensitive equipment like reactors and distillation columns from fouling, ensuring process efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Power Generation
Power plants rely on filtration to maintain operational integrity. Boiler feedwater is heavily filtered to prevent the buildup of scale on turbine blades, a major cause of inefficiency and failure. Hydraulic and lubricating oils are also filtered to protect heavy machinery from wear.
Understanding the Challenges in Filtration
While powerful, implementing an industrial filtration system involves navigating important trade-offs and operational challenges.
The Cost vs. Performance Balance
There is a direct relationship between filtration efficiency, flow rate, and cost. A filter that can remove extremely small particles (an "absolute-rated" filter) typically has a lower flow rate and a higher cost than a coarse filter. Over-specifying a filter can lead to unnecessary capital expense and high energy consumption due to increased pressure drop.
Filter Clogging and Maintenance (Fouling)
All filters eventually clog, a phenomenon known as fouling. This increases the pressure required to push fluid through the system, reduces flow rates, and eventually requires the filter to be cleaned or replaced. Managing fouling is a primary operational concern, as it directly impacts productivity and maintenance costs.
Material Compatibility
The filter media and housing must be chemically compatible with the process fluid. An incompatible material can degrade, leaching contaminants into the product or causing the filter to fail structurally. This is especially critical when working with aggressive solvents, high temperatures, or extreme pH levels.
Selecting the Right Filtration Strategy
To apply this knowledge, focus on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is product quality and sterility: You need absolute-rated, fine-pored membrane filters, often used in series to protect the final sterile filter.
- If your primary focus is protecting equipment: A robust, depth-style or screen filter designed to remove larger particulates is often the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Your choice will be dictated by regulations, often involving multi-stage systems for wastewater or large-scale fabric filters for air emissions.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product recovery: You should evaluate crossflow filtration systems or filter presses that are specifically designed for efficient solid-liquid separation and cake washing.
Ultimately, viewing filtration as a strategic separation tool is the first step toward designing a more robust, efficient, and profitable industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Core Function | Key Industries | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Ensure Product Purity | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals | Remove contaminants for safety and quality |
| Protect Equipment | Chemical, Power Generation | Prevent abrasion, clogging, and failure |
| Recover Products | Biotechnology, Chemical Manufacturing | Capture valuable solids from liquids |
| Meet Compliance | Water Treatment, Power Generation | Adhere to environmental regulations |
Optimize your industrial filtration process with KINTEK!
Filtration is the backbone of product quality, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Whether you need to ensure sterility in pharmaceuticals, protect sensitive machinery in chemical processing, or recover valuable catalysts, the right filtration strategy is critical.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your separation challenges. Our experts can help you select the ideal filtration media and systems to maximize efficiency, reduce downtime, and meet your specific industrial needs.
Contact our filtration specialists today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK solutions can enhance your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of reactive sputtering? Create High-Performance Ceramic Coatings
- How many types of sputtering are there? A Guide to DC, RF, and Advanced Techniques
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What are the effects of magnetron sputtering? Achieve High-Quality, Durable Thin Films for Your Lab


















