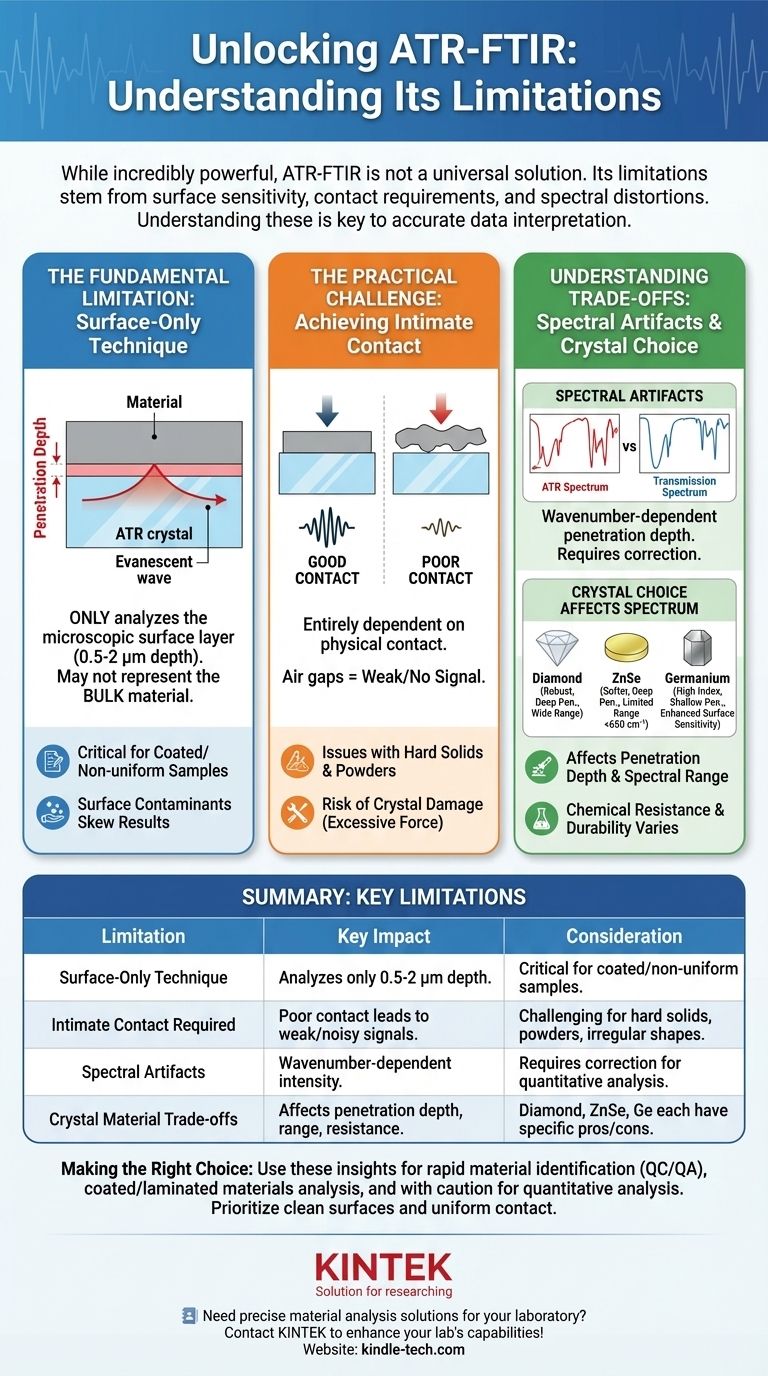
While incredibly powerful, ATR-FTIR is not a universal solution. Its primary limitations stem from its nature as a surface-sensitive technique, the absolute requirement for intimate sample-crystal contact, and potential spectral distortions that can complicate quantitative analysis. Understanding these constraints is essential for generating and correctly interpreting your data.
The core challenge of ATR-FTIR is knowing you are only analyzing a microscopic layer at the immediate surface. Results may not represent the bulk material, and obtaining a high-quality spectrum is entirely dependent on physical contact with the analysis crystal.

The Fundamental Limitation: It's a Surface-Only Technique
Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) works by creating an "evanescent wave" that penetrates a very short distance out of the measurement crystal and into your sample. This is both its greatest strength and its most significant limitation.
Understanding the Evanescent Wave
The penetration depth of this wave is typically only 0.5 to 2 microns (µm). For context, a human hair is about 70 µm thick.
This means you are not analyzing the entire sample. You are exclusively collecting chemical information from the microscopic layer that is in direct contact with the crystal.
When Surface vs. Bulk Matters
This surface sensitivity is a critical factor for any sample that is not perfectly uniform. Your analysis will be skewed or misleading if the surface is different from the interior.
Common examples include coated polymers, oxidized metals, weathered plastics, or any material with a surface contaminant like a mold-release agent or fingerprint oil. The ATR spectrum will preferentially, or even exclusively, show the surface layer, not the bulk material underneath.
The Practical Challenge: Achieving Intimate Contact
The evanescent wave cannot travel through air. Therefore, obtaining a good spectrum is entirely dependent on achieving firm, uniform, and intimate contact between the sample and the ATR crystal.
The "Contact is King" Principle
If there are air gaps between your sample and the crystal, the IR beam will not interact with your sample in those areas, resulting in a weak, noisy, or completely absent signal.
This is the most common cause of poor-quality ATR-FTIR spectra.
Issues with Difficult Sample Forms
This requirement poses a challenge for certain types of samples.
Hard, inflexible solids or irregularly shaped objects may only touch the crystal at a few high points, leading to a very weak signal. Likewise, coarse or fluffy powders can be difficult to press into uniform contact without significant pressure.
The Risk of Crystal Damage
Most ATR accessories use a pressure clamp to ensure good contact. However, applying excessive force, especially with a hard or abrasive sample, can scratch, fracture, or permanently damage the ATR crystal. These crystals, particularly diamond, are extremely expensive to replace.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Crystal and Spectral Artifacts
The instrument's configuration and the physics of the technique itself introduce variables that you must be aware of to correctly interpret your results.
How Crystal Choice Affects Your Spectrum
The ATR crystal material—most commonly Diamond, Zinc Selenide (ZnSe), or Germanium (Ge)—is not inert. Each has different properties that impact your analysis.
- Penetration Depth: The refractive index of the crystal changes the penetration depth. Germanium (Ge) has a high refractive index and provides the shallowest depth of penetration (~0.7 µm), making it ideal for highly absorbing samples (like carbon-filled rubber) or for enhancing surface sensitivity. Diamond and ZnSe offer deeper penetration (~2 µm).
- Spectral Range: Crystals are not transparent across the entire IR spectrum. ZnSe, for example, is not usable below approximately 650 cm⁻¹, obscuring that region of the spectrum.
- Durability & Chemical Resistance: Diamond is incredibly hard and chemically inert, making it a robust, all-purpose choice. ZnSe is much softer, scratches easily, and is damaged by acids and strong chelators.
Wavenumber-Dependent Penetration Depth
A critical artifact of ATR is that the penetration depth is not constant; it is dependent on the wavelength of light. The depth is greater at lower wavenumbers (longer wavelengths).
This causes bands at the low-wavenumber end of the spectrum (e.g., below 1000 cm⁻¹) to appear relatively more intense in an ATR spectrum compared to a traditional transmission spectrum of the same material. While correctable with software, this distortion can confuse analysts accustomed to transmission library spectra.
Challenges in Quantitative Analysis
Because of the variability in sample contact, pressure, and the wavenumber-dependent penetration depth, using ATR-FTIR for precise quantitative analysis is challenging.
While it can be done, it requires rigorous calibration curves and highly consistent sample preparation. For most applications, it is best considered a qualitative or semi-quantitative technique.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Use your understanding of these limitations to guide your experimental approach and interpretation.
- If your primary focus is rapid material identification (QC/QA): ATR-FTIR is often ideal due to its speed and ease of use, but be mindful that you are only verifying the surface composition.
- If you are analyzing coated, laminated, or potentially degraded materials: Recognize that ATR-FTIR will preferentially see the outermost layer, which may require complementary techniques to understand the bulk.
- If you need precise quantitative measurements: Proceed with caution, as ATR-FTIR requires extensive calibration and control over pressure and contact to yield reliable quantitative data.
- If you are getting a weak or noisy spectrum: Your first troubleshooting step should always be to ensure clean surfaces and improve the physical contact between your sample and the ATR crystal.
Understanding these limitations is the key to transforming ATR-FTIR from a simple tool into a precise and powerful analytical method.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Surface-Only Technique | Analyzes only 0.5-2 µm depth; may not represent bulk material. | Critical for coated, oxidized, or non-uniform samples. |
| Intimate Contact Required | Poor contact leads to weak/noisy signals; risk of crystal damage. | Challenging for hard solids, powders, or irregular shapes. |
| Spectral Artifacts | Wavenumber-dependent intensity; differs from transmission spectra. | Requires correction for accurate qualitative/quantitative analysis. |
| Crystal Material Trade-offs | Affects penetration depth, spectral range, and chemical resistance. | Diamond, ZnSe, and Germanium each have specific advantages/limitations. |
Need precise material analysis solutions for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the right tools to overcome analytical challenges like those posed by ATR-FTIR. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure accurate, reliable results for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What is treatment through pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Valuable Resources with Thermal Decomposition
- What is the use of pyrolysis oil? A Versatile Fuel and Chemical Feedstock
- What is heat treatment for small parts? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What is the purpose of glass sample tubes and rod holders in biofuel corrosion studies? Enhance Research Accuracy
- Is a filter press better than a clarifier? Choose the Right Tool for Your Separation Goal
- What is the long-term stability of viral analytes in plasma stored at -70°C? Proven for Decades of Research
- What is the composition of bio-oil fast pyrolysis? Unlocking Its Potential as a Renewable Chemical Feedstock
- How does a high-speed homogenizer prepare m-BN and PNF dispersions? Achieve Uniform Molecular-Level Integration


















