Beyond a simple number on a datasheet, the melting point of a substance has several critical limitations you must understand. Its value is not an absolute constant but is highly sensitive to the purity of the sample, the precision of the measuring instrument, and the specific technique used during measurement. Furthermore, some materials do not exhibit a sharp, clear melting point at all, but instead decompose or soften over a wide temperature range.
The primary limitation of melting point determination is that it is not an intrinsic, fixed property but rather a conditional one. Viewing it as a definitive identifier without considering sample purity and measurement context can lead to significant errors in material analysis and process control.
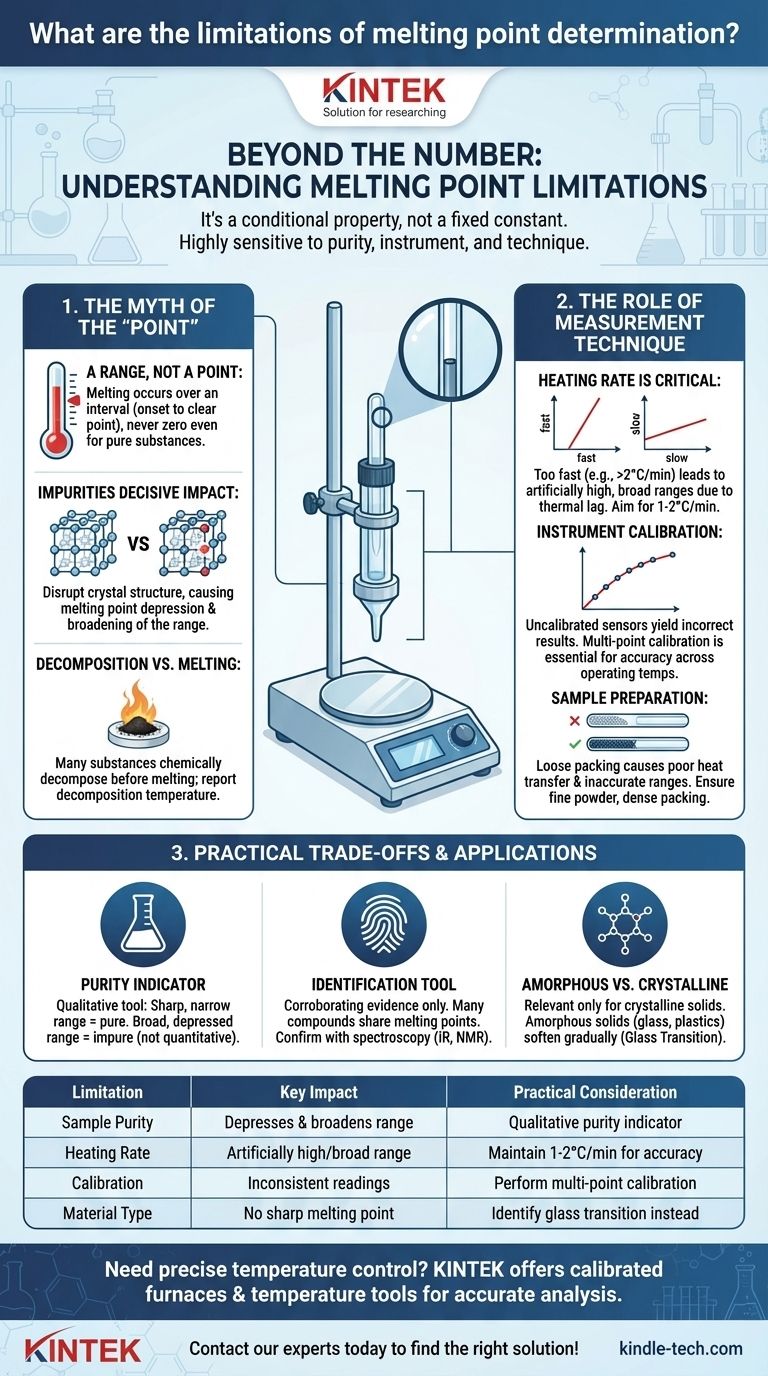
The Myth of the "Melting Point"
The term itself suggests a single, discrete temperature, which is the first misconception to address. In practice, melting is a process that occurs over a temperature interval.
It's a Range, Not a Point
Even for a very pure substance, melting does not happen instantaneously. It begins at one temperature (onset) and is complete at another (clear point). For highly pure, crystalline compounds, this melting range may be very narrow (less than 1-2°C), but it is never zero.
The Decisive Impact of Impurities
This is the most common and significant limitation. Impurities disrupt the crystal lattice of a substance, which almost always results in two effects: a depression of the melting point and a broadening of the melting range. A small amount of a contaminant can cause a noticeable drop and a wide, indistinct melting process.
When Substances Decompose, Not Melt
Many organic compounds and polymers do not have a true melting point. As you heat them, they chemically decompose or char before they can transition into a liquid state. In these cases, a "decomposition temperature" is reported, which is often variable and dependent on the heating rate.
The Role of Measurement Technique
How you perform the measurement is just as important as the substance itself. Inconsistent technique is a major source of unreliable data.
Heating Rate Is Critical
If the sample is heated too quickly, the temperature of the heating block or bath will rise faster than the sample's temperature can equilibrate. This lag causes the observed melting range to be artificially high and often broader than it should be. A slow, controlled heating rate (e.g., 1-2°C per minute) is essential for accuracy.
Instrument Calibration and Accuracy
The thermometer or sensor used to measure the temperature must be accurately calibrated. An uncalibrated instrument can produce consistently incorrect results, rendering the data useless for anything other than relative comparisons.
As seen in industrial applications like ceramic furnaces, single-point calibration (e.g., using silver) may be insufficient. For processes requiring accuracy across a wide spectrum, multi-point calibration is necessary to ensure the instrument is reliable at both low and high operating temperatures.
Sample Preparation and Packing
The way a solid sample is packed into a capillary tube can affect the result. A loosely packed sample will have poor heat transfer, leading to an inaccurate and broad melting range. The sample must be finely powdered and densely packed to ensure uniform heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Knowing these limitations allows you to use melting point data effectively while avoiding common misinterpretations.
As an Indicator of Purity
Melting point is an excellent qualitative indicator of purity. A sharp, narrow melting range that matches the literature value suggests a pure compound. Conversely, a broad, depressed range is a strong sign of impurity. However, it is a poor quantitative tool; you cannot accurately determine the percentage of impurity from the melting range alone.
As a Tool for Identification
A measured melting point can help confirm the identity of a known compound or narrow the possibilities for an unknown one. However, it is not a definitive confirmation. Many different compounds have similar or identical melting points. Therefore, it should always be used as corroborating evidence alongside other analytical techniques like spectroscopy (IR, NMR) or chromatography.
Amorphous vs. Crystalline Solids
Melting point is only relevant for crystalline solids, which have an ordered, long-range atomic structure. Amorphous solids, like glass and many plastics, lack this structure. They do not have a sharp melting point but instead soften gradually over a wide temperature range, a phenomenon known as the glass transition.
How to Apply This to Your Analysis
Your interpretation of melting point data should depend entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is assessing purity: Look at the breadth of the melting range. A narrow range (e.g., <2°C) is your key indicator of high purity.
- If your primary focus is compound identification: Use the melting point as one piece of evidence to be confirmed with more specific analytical methods.
- If your primary focus is process control: Prioritize rigorous and regular multi-point instrument calibration across your entire relevant operating temperature range.
Ultimately, treating melting point as a diagnostic range rather than a single, absolute number unlocks its true analytical power.

Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Practical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Purity | Depresses and broadens melting range | Use as qualitative purity indicator |
| Heating Rate | Artificially high/broad range | Maintain 1-2°C/min for accuracy |
| Instrument Calibration | Inconsistent temperature readings | Perform multi-point calibration |
| Material Type (e.g., amorphous) | No sharp melting point | Identify glass transition instead |
Need precise temperature control for your lab analysis? At KINTEK, we understand that accurate melting point determination is critical for assessing purity and ensuring process reliability. Our high-quality lab equipment, including calibrated furnaces and temperature measurement tools, is designed to deliver the consistency and accuracy your laboratory demands. Don't let measurement limitations compromise your results—contact our experts today to find the right solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- How does vacuum arc melting equipment facilitate Ti-Cr-Al-Nb alloy prep? Precision High-Temp Melting Explained
- What is the primary function of a vacuum arc melting furnace in RHEA preparation? Achieving Extreme Thermal Fusion
- What is AC frame? Decoding the Two Meanings in Wi-Fi and Video

















