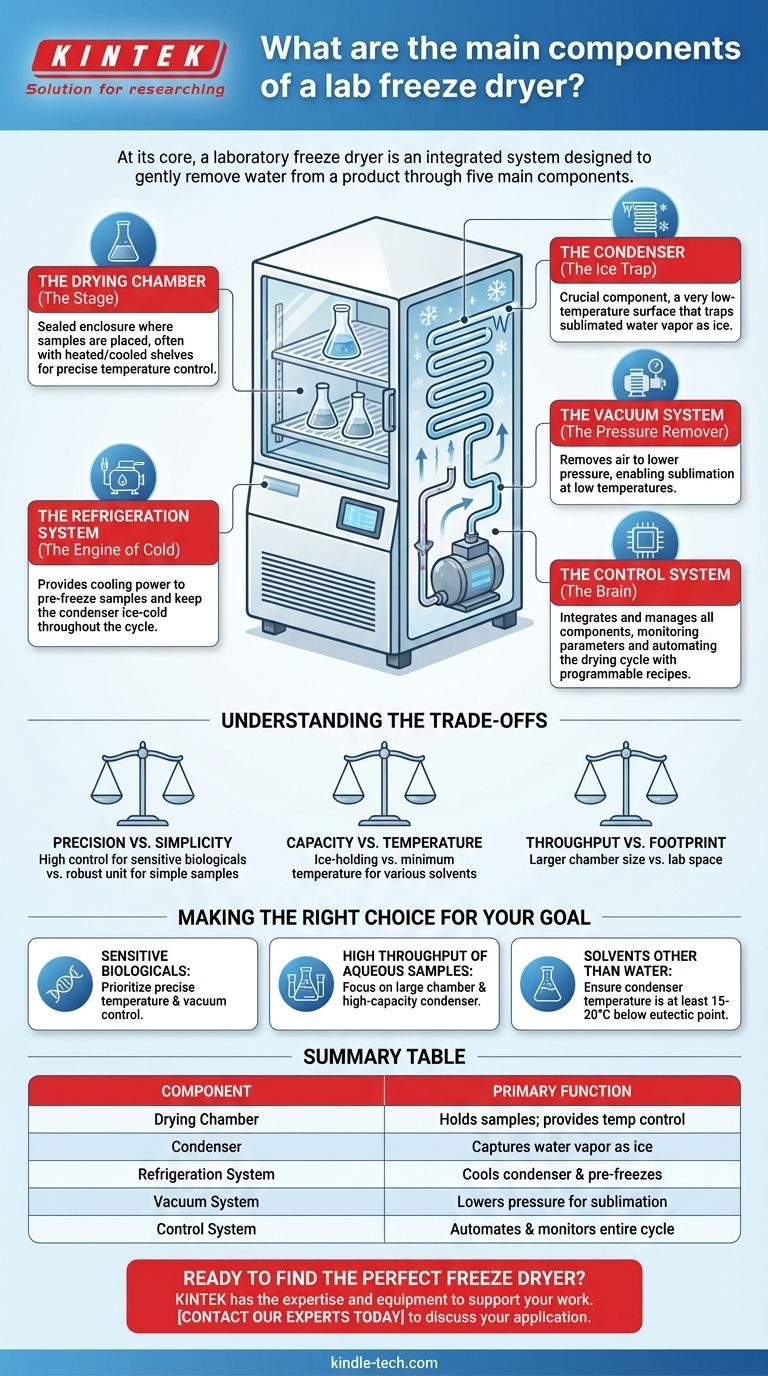
At its core, a laboratory freeze dryer is an integrated system designed to gently remove water from a product. It achieves this through a precise interplay between five main components: a drying chamber, a condenser (or cold trap), a refrigeration system, a vacuum system, and an electronic control system.
Understanding a freeze dryer is not just about knowing its parts, but about recognizing how they work in concert. The process hinges on a fundamental principle: lowering pressure to a point where ice can turn directly into vapor, which is then captured, preserving the integrity of the original material.

The Core Systems: A Functional Breakdown
The magic of freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is sublimation—the transition of a substance directly from a solid to a gas phase. Each component plays a critical role in controlling this process to protect sensitive samples.
The Drying Chamber (The Stage)
The drying chamber is where your samples are placed. It is a sealed enclosure that can be a simple manifold for flasks or a more complex cabinet with shelves.
These shelves can often be heated or cooled, providing precise temperature control for the material throughout the primary and secondary drying phases.
The Condenser (The Ice Trap)
The condenser is arguably the most critical component. It is a surface or coil maintained at an extremely low temperature, often much colder than the sample itself.
Its sole purpose is to attract and capture the water vapor that sublimates from the sample, trapping it as ice. This creates a pressure differential that continuously draws vapor away from the product, driving the drying process forward.
The Refrigeration System (The Engine of Cold)
This system is the workhorse that provides the cooling power for the entire unit. It typically uses one or more compressors to achieve very low temperatures.
The refrigeration system is responsible for two key tasks: pre-freezing the samples into a solid state and, most importantly, keeping the condenser ice-cold throughout the drying cycle.
The Vacuum System (The Pressure Remover)
The vacuum system, centered around a vacuum pump, removes air and other non-condensable gases from the drying chamber and condenser.
By reducing the system's pressure to a deep vacuum, it lowers the temperature at which ice sublimates. This allows water to be removed at temperatures low enough to prevent damage to delicate biological or chemical structures.
The Control System (The Brain)
The control system integrates and manages all other components. It monitors critical parameters like temperature and pressure and automates the drying cycle.
Modern systems allow for programmable recipes, ensuring that complex, multi-step drying processes are repeatable and precise, which is essential for sensitive or valuable samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a freeze dryer involves more than just a list of parts. The specifications of each component create critical trade-offs that impact performance and suitability.
Precision vs. Simplicity
A sophisticated control system offers precise temperature and vacuum control, which is vital for sensitive biologicals. However, this adds complexity and cost compared to a simpler unit designed for more robust materials.
Condenser Capacity and Temperature
The condenser's ice-holding capacity determines how much water it can trap before it needs to be defrosted, impacting run times. Its minimum temperature dictates what types of solvents can be trapped effectively; lower temperatures are required for solvents with lower freezing points.
Throughput vs. Footprint
The size of the drying chamber dictates your sample volume. A larger chamber or a pilot-plant model allows for higher throughput but requires significantly more lab space and power than a compact benchtop unit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application should guide your evaluation of a freeze dryer's components.
- If your primary focus is preserving sensitive biologicals: Prioritize a unit with highly precise temperature and vacuum control systems to prevent product collapse or damage.
- If your primary focus is high throughput of simple aqueous samples: Focus on a large drying chamber and a high-capacity condenser to maximize batch size and minimize downtime.
- If your primary focus is working with solvents other than water: Ensure the condenser can reach a temperature at least 15-20°C colder than the eutectic point (freezing point) of your solvent.
By understanding how these core components function and interact, you can select a system perfectly matched to your scientific objectives.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Drying Chamber | Holds samples; provides temperature-controlled shelves. |
| Condenser (Cold Trap) | Captures sublimated water vapor as ice. |
| Refrigeration System | Cools the condenser and pre-freezes samples. |
| Vacuum System | Lowers pressure to enable sublimation at low temperatures. |
| Control System | Automates and monitors the entire freeze-drying cycle. |
Ready to find the perfect freeze dryer for your lab's needs?
Whether you're preserving sensitive biologicals, scaling up for high throughput, or working with specialized solvents, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your work. Our range of laboratory freeze dryers is designed for precision, reliability, and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and let us help you select the ideal lyophilization solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is a lyophilizer and how does it work? Unlock Superior Preservation for High-Value Materials
- What role do laboratory freeze dryers play in the food industry? Unlock Superior Food Preservation
- What are the overall benefits of freeze drying technology across industries? Achieve Unparalleled Product Preservation
- What is collapse in freeze drying? A Critical Failure Event Explained
- What is the basic process of freeze drying? A Guide to Lyophilization Stages and Benefits



















