At its core, a lyophilizer is a specialized machine, also known as a freeze-dryer, designed to remove water from a substance without damaging its structure. It achieves this by first freezing the material solid, then creating a powerful vacuum and applying a small amount of heat, which causes the frozen water to turn directly into a gas in a process called sublimation.
While simple dehydration uses heat that can shrink and damage delicate products, lyophilization bypasses the liquid water phase entirely. This preserves the material's original structure, bio-activity, and chemistry, making it the gold standard for preserving high-value substances.

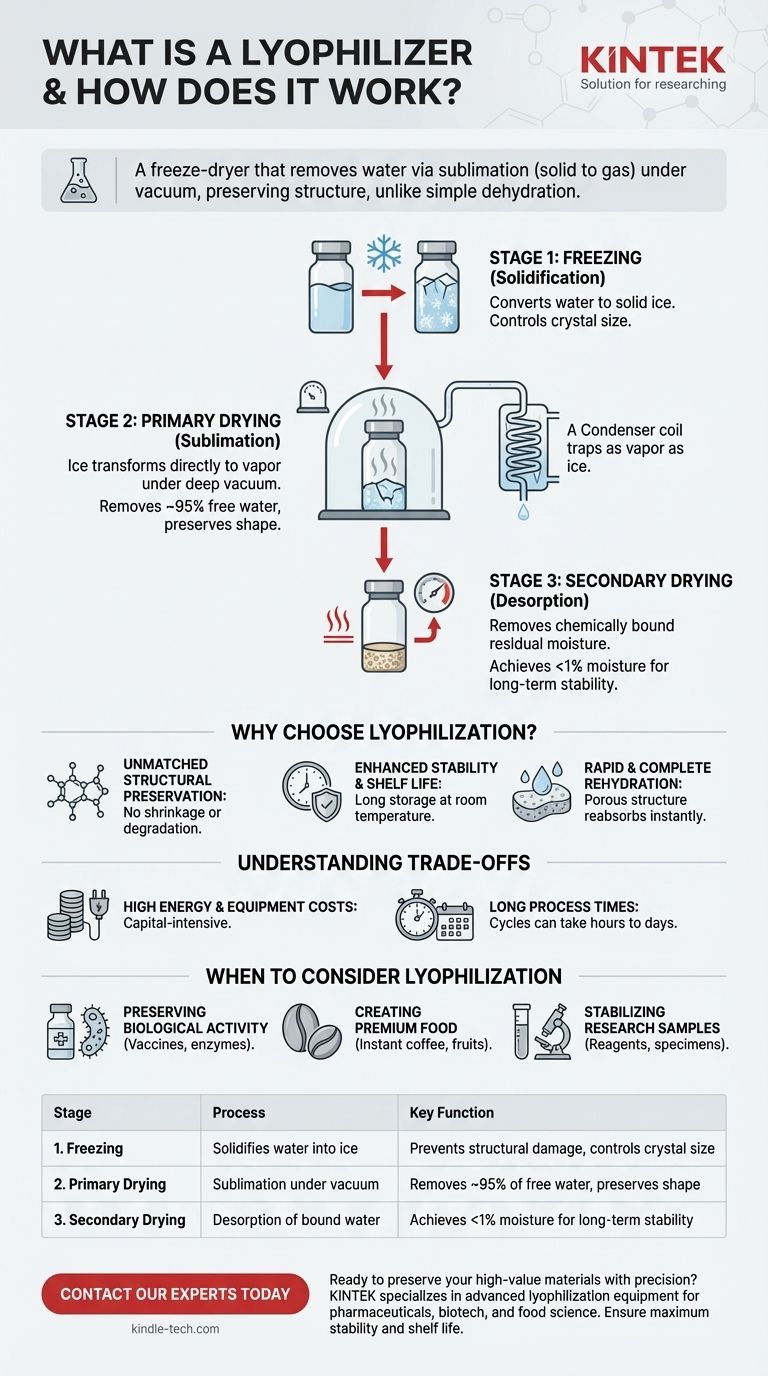
The Science of Freeze-Drying: A Three-Stage Process
Understanding how a lyophilizer works requires breaking the process down into its three distinct stages. Each stage is precisely controlled to ensure the final product is perfectly preserved.
Stage 1: Freezing (Solidification)
The first and most critical step is to completely freeze the material. The goal is to convert all the water within the product into solid ice.
The rate of freezing is crucial as it determines the size of the ice crystals that form. Slower freezing creates larger crystals, which can be easier to sublimate, while faster freezing creates smaller crystals, which may be better for preserving delicate cellular structures.
Stage 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
This is the heart of the lyophilization process. After freezing, the material is placed under a deep vacuum, lowering the pressure well below the "triple point" of water.
At this extremely low pressure, water can no longer exist as a liquid. A controlled amount of heat is then gently applied to the shelves holding the material. This heat does not melt the ice; instead, it provides the necessary energy for the ice to sublimate—transforming directly from a solid into a water vapor.
This vapor is then drawn out of the chamber and collected on a condenser coil, which is kept at an even colder temperature, trapping the removed water as ice once again. This stage removes up to 95% of the water.
Stage 3: Secondary Drying (Desorption)
After all the free ice has been sublimated, a small amount of residual moisture remains, chemically bound to the molecules of the material.
To remove this final fraction of water, the temperature is raised slightly higher and the vacuum is often increased. This breaks the bonds between the water molecules and the product, a process called desorption, ensuring the final material is exceptionally dry and stable.
Why Choose Lyophilization Over Simple Dehydration?
While heating is a much simpler way to remove water, lyophilization is chosen for high-value applications because its benefits are significant and often unachievable by other means.
Unmatched Structural Preservation
Because the water is removed from a solid state, the product’s underlying molecular and physical structure is left intact, like a rigid scaffold.
This prevents the shrinkage, cracking, and degradation common with heat-based drying, resulting in a lightweight, porous product that retains its original shape and volume.
Enhanced Stability and Shelf Life
The extremely low water content achieved through lyophilization—often less than 1%—effectively halts biological and chemical degradation.
Without water, microbial growth is inhibited and enzymatic reactions that would spoil the product cease. This allows sensitive materials like vaccines or probiotics to be stored for years at room temperature.
Rapid and Complete Rehydration
The porous, sponge-like structure created by the sublimation process means the final product can reabsorb water almost instantly.
This property is essential for products like injectable pharmaceuticals that need to be reconstituted quickly and completely, or for high-end instant foods that should return to their original texture and flavor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, lyophilization is not a universal solution. It involves significant trade-offs that make it suitable only for specific applications.
High Energy and Equipment Costs
Lyophilizers are complex pieces of machinery. Creating and maintaining deep vacuums and extremely cold temperatures is an energy-intensive process.
The initial capital investment for the equipment is substantially higher than for a conventional oven or dehydrator, making it cost-prohibitive for low-value bulk materials.
Long Process Times
Freeze-drying is a slow, deliberate process. Depending on the product, its thickness, and the amount of water to be removed, a single cycle can take anywhere from several hours to multiple days. This low throughput is a major consideration for manufacturing timelines.
When to Consider Lyophilization
Choosing this technology depends entirely on the nature of your material and your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: Lyophilization is the industry standard for stabilizing vaccines, enzymes, pharmaceuticals, and microbes because it avoids heat denaturation.
- If your primary focus is creating premium-quality, long-shelf-life food: It is the best method for retaining the flavor, nutrition, and texture of products like high-end instant coffee, fruits for cereal, and astronaut meals.
- If your primary focus is stabilizing delicate research samples: It creates a stable, lightweight powder from chemical reagents or biological specimens that is easy to store, transport, and precisely reconstitute.
By understanding its principles, you can determine if this powerful preservation technique is the right solution for your high-value materials.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Process | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Freezing | Solidifies water into ice | Prevents structural damage, controls crystal size |
| 2. Primary Drying | Sublimation under vacuum | Removes ~95% of free water, preserves shape |
| 3. Secondary Drying | Desorption of bound water | Achieves <1% moisture for long-term stability |
Ready to preserve your high-value materials with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced lyophilization equipment and consumables for laboratories in pharmaceuticals, biotech, and food science. Our solutions ensure maximum stability, extended shelf life, and complete rehydration for your most sensitive products. Contact our experts today to find the perfect freeze-drying system for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Which industries commonly use lab freeze dryers? Preserve Sensitive Materials with Lyophilization
- What is the technical definition of freeze drying? A Deep Dive into Lyophilization and Sublimation
- What are the characteristics of benchtop freeze dryers? A Guide for Lab R&D and Small-Batch Processing
- What happens during the primary drying phase of freeze drying? Master the Sublimation Process
- What is the difference between freeze drying and lyophilization? Unveiling the Same Powerful Preservation Process



















