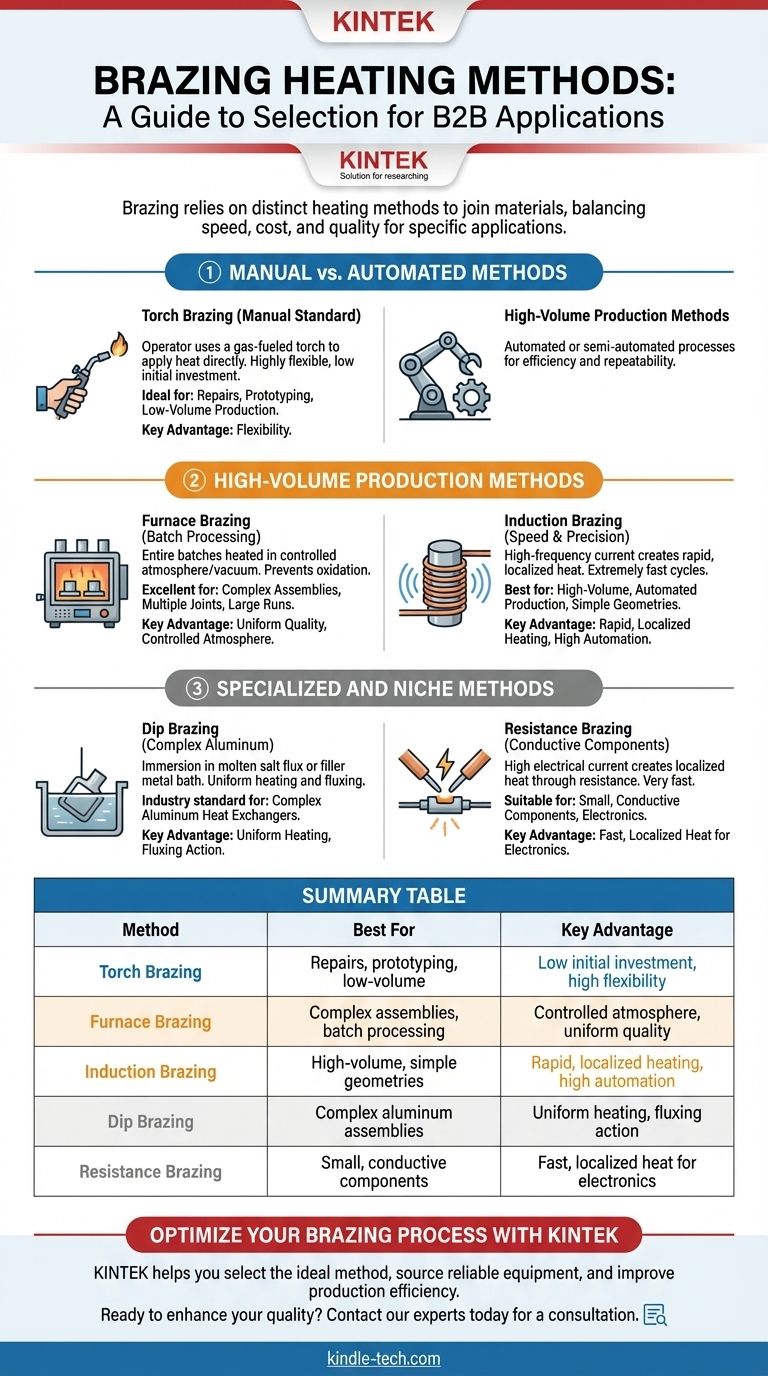
Brazing relies on several distinct heating methods, each with a specific purpose and application. The most common methods include torch brazing, furnace brazing, induction brazing, dip brazing, and resistance brazing, all designed to heat a workpiece above the filler metal's melting point but below the base metal's melting point. The choice of method depends entirely on the materials, joint design, production volume, and required quality.
The core challenge isn't just knowing the different ways to heat a joint, but understanding how each method impacts production speed, cost, and final quality. Selecting the right method is a critical engineering decision that balances initial investment against per-piece cost and repeatability.
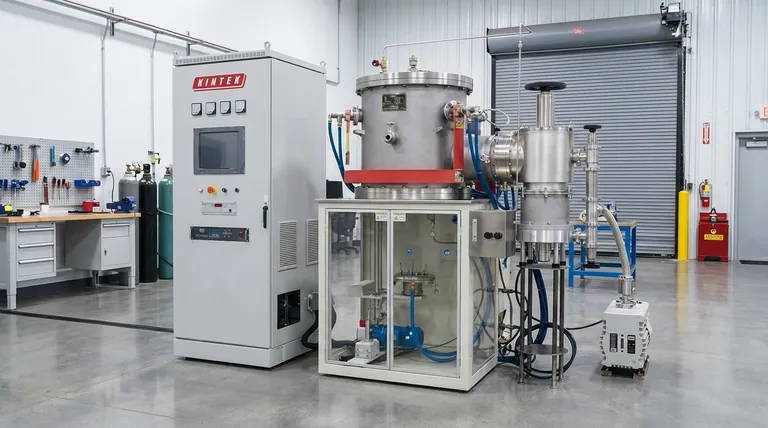

Manual vs. Automated Methods
The first major distinction between brazing methods is the level of operator control versus automation. This choice directly influences flexibility, speed, and consistency.
Torch Brazing: The Manual Standard
Torch brazing is the most common manual heating method. An operator uses a gas-fueled torch (such as oxy-acetylene or air-propane) to apply heat directly to the parts being joined.
This method is highly flexible and requires a low initial investment, making it ideal for repairs, prototyping, and low-volume production. However, its quality and consistency are entirely dependent on the skill of the operator.
High-Volume Production Methods
When repeatability and high throughput are required, automated or semi-automated processes are necessary. These methods are designed for efficiency in a production environment.
Furnace Brazing: For Batch Processing
In furnace brazing, components are pre-assembled with the filler metal placed at the joints. Entire batches of these assemblies are then loaded into a furnace and heated in a controlled atmosphere or vacuum.
The protective atmosphere prevents oxidation, often eliminating the need for flux. This method is superb for complex assemblies with multiple joints that must be brazed simultaneously, ensuring high quality and uniformity across large production runs.
Induction Brazing: For Speed and Precision
Induction brazing uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a powerful electromagnetic field that rapidly and precisely heats the conductive workpiece placed within it.
This process is extremely fast, with heating cycles often lasting only a few seconds. Its localized heating minimizes distortion and is perfect for high-volume, automated production of parts with simple, repeatable joint geometries.
Specialized and Niche Methods
Some applications have unique requirements that demand highly specialized heating techniques.
Dip Brazing: For Complex Aluminum Assemblies
Dip brazing involves immersing the entire assembly into a bath of molten salt flux or, less commonly, molten filler metal. The bath heats the part uniformly and provides the fluxing action simultaneously.
This method is the industry standard for producing complex aluminum heat exchangers and other intricate aluminum assemblies. It allows for hundreds of joints to be made at once with excellent quality.
Resistance Brazing: For Conductive Components
Resistance brazing generates heat by passing a high electrical current through the joint area via electrodes. The resistance of the components to the current flow creates intense, localized heat.
This technique is very fast and suitable for joining small, electrically conductive components. It's often used in the electrical and electronics industries for attaching contacts or terminals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single heating method is universally superior. Your decision must be based on a clear understanding of the compromises involved.
Cost: Initial Investment vs. Per-Piece
Torch brazing has a very low initial cost but a high labor cost per piece.
Furnace and induction systems require a significant capital investment but offer a very low cost per piece at high production volumes, making them cost-effective in the long run.
Speed and Volume
Torch brazing is the slowest method and is only suitable for low-volume work.
Induction brazing offers the fastest heating cycle for a single joint, making it a champion of high-speed, single-piece flow production.
Furnace brazing is slower per cycle, but its ability to process hundreds of parts in a single batch makes it highly efficient for mass production.
Joint Quality and Repeatability
Manual methods like torch brazing are entirely dependent on operator skill, leading to potential inconsistencies.
Automated methods like furnace and induction brazing offer superior control over heating rates and temperature, resulting in highly repeatable, high-quality joints.
How to Select the Right Method
Your choice should be guided by your project's specific demands for speed, cost, and quality.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or repair work: Torch brazing offers the best flexibility and lowest initial cost.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable joints on simple parts: Induction brazing provides unmatched speed and automation potential.
- If your primary focus is brazing complex assemblies with multiple joints: Furnace brazing in a controlled atmosphere delivers the highest quality and consistency.
- If your primary focus is joining complex aluminum components like heat exchangers: Dip brazing is the specialized, industry-standard solution.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select a heating method that ensures both the quality and efficiency of your brazed joints.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Repairs, prototyping, low-volume | Low initial investment, high flexibility |
| Furnace Brazing | Complex assemblies, batch processing | Controlled atmosphere, uniform quality |
| Induction Brazing | High-volume, simple geometries | Rapid, localized heating, high automation |
| Dip Brazing | Complex aluminum assemblies | Uniform heating, fluxing action |
| Resistance Brazing | Small, conductive components | Fast, localized heat for electronics |
Optimize Your Brazing Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right brazing heating method is critical for achieving strong, repeatable joints while controlling costs. Whether you need the flexibility of torch brazing for prototypes or the high-volume efficiency of an induction or furnace system, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory and production needs.
We help you:
- Select the ideal brazing method for your specific materials and joint design.
- Source reliable lab equipment and consumables for consistent, high-quality results.
- Improve production efficiency with solutions tailored to your volume and quality requirements.
Ready to enhance your brazing quality and efficiency? Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can be your partner in laboratory excellence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What are the defects in sintered parts? Avoid Warping, Cracking, and Porosity Issues
- What is the sintering time? A Critical Process Variable for Material Density and Strength



















