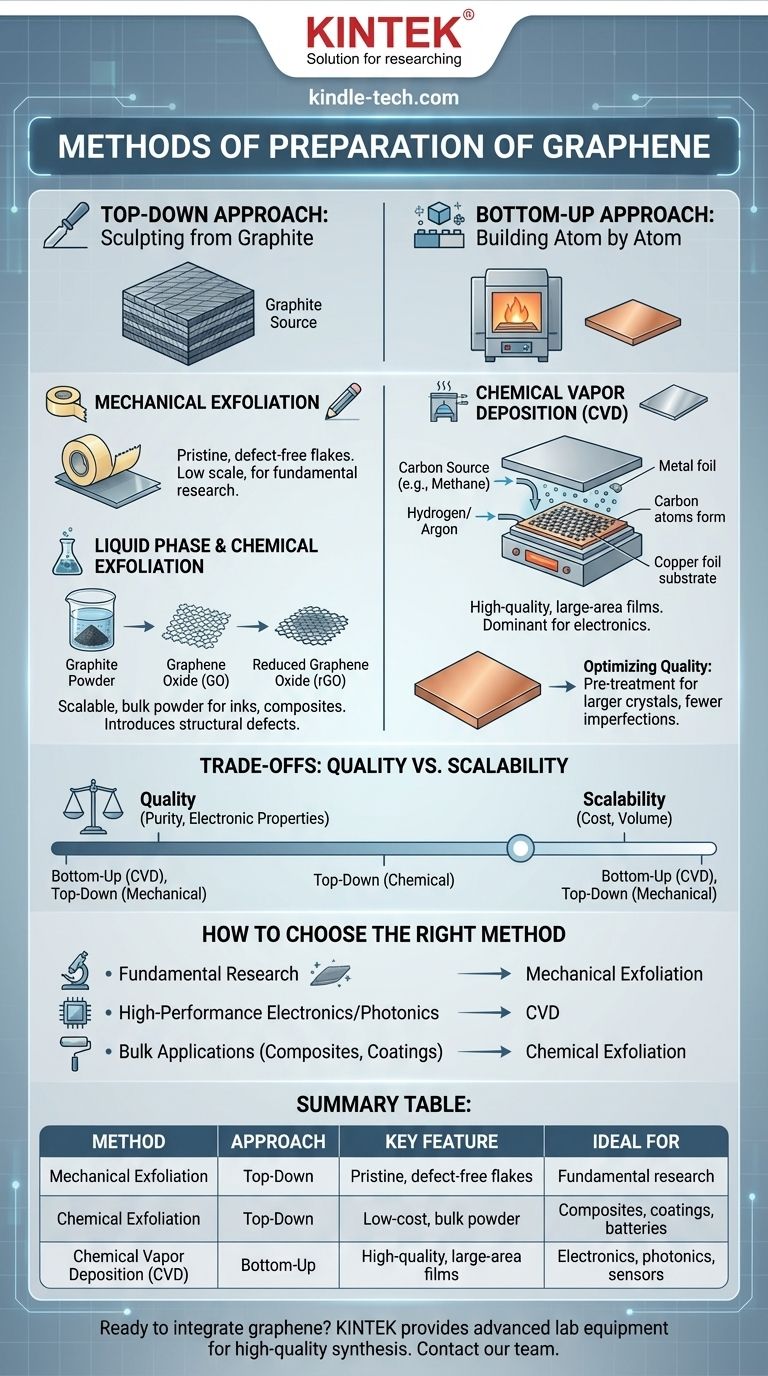
Graphene is prepared using two fundamentally different strategies: "top-down" methods that start with bulk graphite and break it down, and "bottom-up" methods that construct the graphene sheet atom by atom. The most popular method for producing the large, high-quality sheets needed for electronics is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a bottom-up technique.
The choice between graphene preparation methods is a critical trade-off. "Top-down" approaches prioritize low-cost scalability for bulk materials, while "bottom-up" approaches deliver the superior quality and control required for advanced research and electronics.

The "Top-Down" Approach: Sculpting from Graphite
Top-down synthesis is conceptually similar to carving a sculpture from a block of stone. You begin with a large, inexpensive starting material—graphite—and use physical or chemical force to remove material until you are left with individual or few-layered graphene sheets.
Mechanical Exfoliation
This is the original method used to first isolate graphene, famously using simple adhesive tape to peel layers from a piece of graphite. It produces pristine, nearly defect-free graphene flakes.
However, mechanical exfoliation is not scalable. It yields very small quantities and offers little control over the size or location of the flakes, limiting its use almost exclusively to fundamental academic research.
Liquid Phase & Chemical Exfoliation
This more scalable approach uses chemical processes to overcome the forces holding the graphite layers together. Often, this involves oxidizing the graphite to create graphene oxide (GO), which separates easily in water.
The graphene oxide is then "reduced" back toward pure graphene. While this method can produce large quantities of graphene powder suitable for inks, composites, and coatings, the chemical process often introduces structural defects that can impair its electrical properties.
The "Bottom-Up" Approach: Building Atom by Atom
Bottom-up synthesis is like building a structure with individual bricks. These methods start with carbon-containing molecules and assemble them on a substrate, offering much greater control over the final structure and quality of the graphene sheet.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the dominant method for producing high-quality, large-area graphene films. The process involves heating a substrate, typically a copper or nickel foil, in a vacuum furnace.
A carbon-containing gas, such as methane, is then introduced. The high temperature causes the gas to decompose, and the carbon atoms arrange themselves into a single atomic layer on the surface of the metal foil.
Optimizing Quality in CVD
Scientists are constantly refining CVD techniques to improve graphene quality. For example, pre-treating the copper substrate with chemicals can reduce its catalytic activity and smooth its surface.
This allows for the growth of larger, more uniform graphene crystals with fewer imperfections, which is critical for demanding applications like high-performance transistors and sensors.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Scalability
No single method is universally "best." The right choice depends entirely on the intended application, as each method presents a different balance of quality, cost, and scale.
Purity and Defects
Mechanical exfoliation and well-controlled CVD produce the highest-quality graphene with the fewest defects, preserving its exceptional electronic properties. Chemical methods, while scalable, almost always introduce structural flaws.
Scale and Cost
Chemical exfoliation is the most cost-effective method for producing graphene in bulk (kilogram quantities), but it comes in the form of a powder or flakes, not a continuous sheet. CVD can produce large-area sheets (measured in square meters) but requires expensive, specialized equipment.
Final Form Factor
The output of the method is a critical differentiator. Top-down methods typically produce a powder of graphene or graphene oxide flakes. Bottom-up CVD produces a continuous, thin film of graphene that must be transferred from its growth substrate to a target substrate.
How to Choose the Right Method
Your end goal dictates the ideal preparation strategy. By defining your primary need, you can select the most logical approach.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine material: Mechanical exfoliation provides the highest-quality flakes, though in very small quantities.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or photonics: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the industry standard for producing large, high-purity graphene sheets.
- If your primary focus is bulk applications like composites, coatings, or batteries: Chemical exfoliation methods offer the best balance of scalability and low cost for producing large volumes.
Understanding these core production pathways is the first step toward effectively harnessing graphene's potential for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Approach | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Top-Down | Pristine, defect-free flakes | Fundamental research |
| Chemical Exfoliation | Top-Down | Low-cost, bulk powder | Composites, coatings, batteries |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Bottom-Up | High-quality, large-area films | Electronics, photonics, sensors |
Ready to integrate graphene into your research or product development? The right preparation method is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment, including CVD systems and consumables, necessary for high-quality graphene synthesis. Our experts can help you select the right tools for your specific application, whether you're focused on fundamental research or scaling up for production.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's graphene innovation journey.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production



















