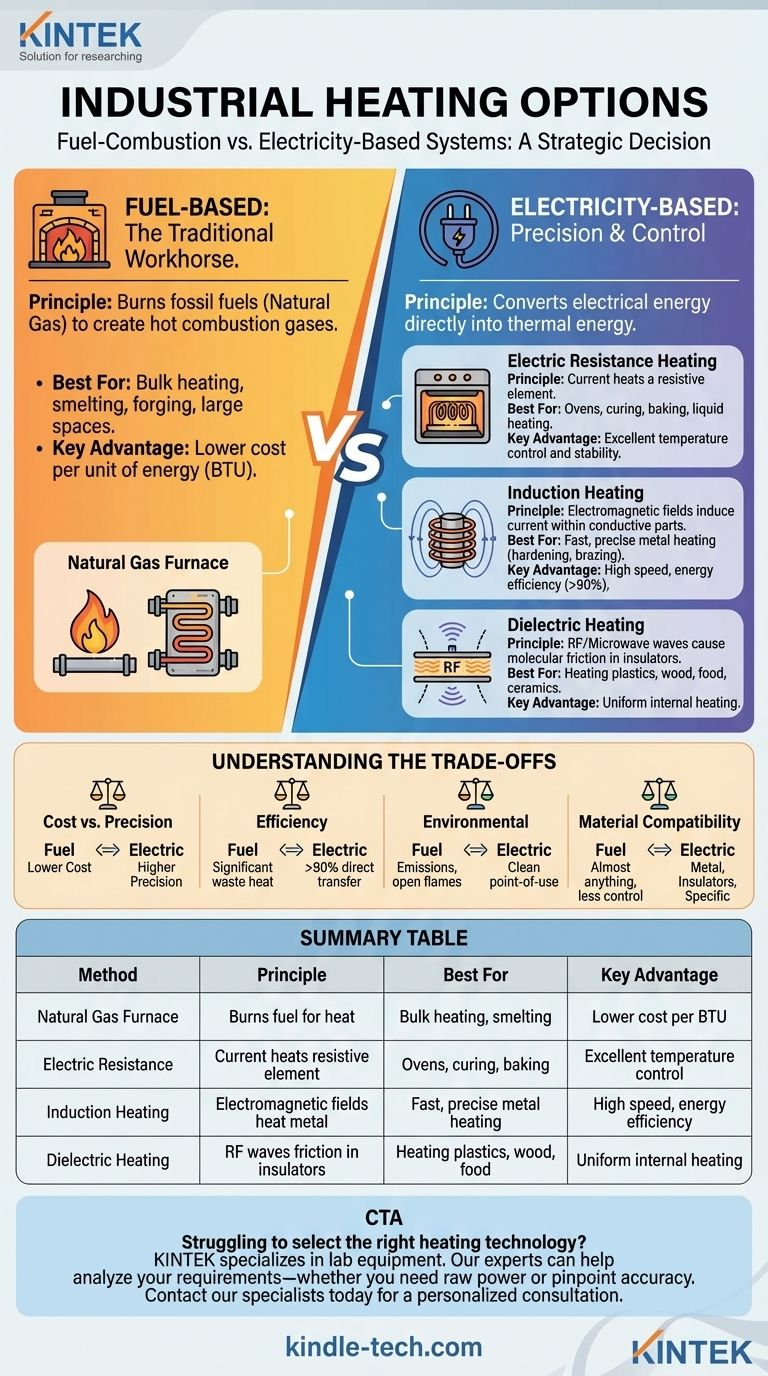
At the highest level, industrial heating is divided into two primary categories: fuel-combustion systems and electricity-based systems. While traditional natural gas furnaces remain a common option for large-scale applications, many modern industrial processes now rely on generating heat from electricity, often through methods like electric resistance heating for greater precision and efficiency.
The choice between industrial heating methods is rarely about raw power alone. It is a strategic decision that balances operational cost, required temperature precision, environmental impact, and the specific physical properties of the material you need to heat.

Fuel-Based Heating: The Traditional Workhorse
Traditional heating methods rely on the combustion of fossil fuels, most commonly natural gas, to generate thermal energy. This approach is powerful and well-understood.
How Natural Gas Furnaces Work
A natural gas furnace operates on a straightforward principle: it burns fuel to create hot combustion gases. This heat is then transferred to the target material, either directly or indirectly through a medium like air or water.
Primary Applications
These systems excel in applications requiring massive amounts of heat where pinpoint precision is not the primary concern. Common uses include smelting, forging, large-scale drying of bulk materials, and heating large industrial spaces.
Key Advantages
The primary advantage is often a lower cost per unit of energy (BTU), depending on local natural gas prices. The technology is mature, and the equipment can generate extremely high temperatures for heavy industrial tasks.
Electricity-Based Heating: Precision and Control
Electric heating has become the standard for manufacturing processes that demand repeatability, control, and cleanliness. It converts electrical energy into thermal energy directly where it is needed.
Electric Resistance Heating
This is the most common form of electric heating. It works by passing an electric current through a resistive material (a heating element), which generates heat due to the resistance, much like a stovetop or toaster.
This method is used in countless applications, from industrial ovens for curing and baking to immersion heaters for liquids and band heaters for pipes and nozzles.
Induction Heating
Induction is a highly efficient, non-contact heating method. It uses a powerful, high-frequency electromagnetic field to induce an electric current directly within a conductive part, causing it to heat from the inside out.
Because it heats the part itself and not the surrounding air, it is incredibly fast, precise, and energy-efficient. It is ideal for processes like surface hardening, brazing, and heat-treating metal components.
Dielectric Heating
Also known as radio frequency (RF) or microwave heating, this method is designed for heating electrically insulating materials. It uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves that cause the molecules within the material to rapidly rotate, generating uniform internal heat.
This is the technology of choice for applications like curing glues in woodworking, preheating plastics before molding, and processing food products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right system requires an objective look at the fundamental differences in cost, efficiency, and capability.
Cost vs. Precision
Natural gas is often cheaper per unit of energy, but fuel-based systems are less precise. Electricity offers unparalleled temperature control, which reduces defects and improves product consistency, offsetting its potentially higher energy cost.
Efficiency and Heat Transfer
Electric methods are typically far more efficient at the point of use. Induction and dielectric heating transfer over 90% of their energy directly into the part, whereas a significant portion of a furnace's energy is lost as waste heat to the surrounding environment.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
Fuel combustion inherently produces emissions like CO2 and requires handling flammable fuels and managing hot exhaust gases. Electric heating is clean at the point of use and eliminates the risks associated with open flames or combustion byproducts.
Material Compatibility
The material being heated is a critical factor. Induction only works on electrically conductive materials (metals), while dielectric heating is designed specifically for insulators like plastic, wood, and ceramics. A furnace can heat almost anything, but often with less control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your optimal solution depends entirely on the specific goals of your industrial application.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating with low precision requirements: A natural gas furnace is often the most cost-effective solution for raw power.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repeatable heating of metal parts: Induction heating offers unmatched speed, control, and energy efficiency.
- If your primary focus is precise and uniform temperature control for ovens: Electric resistance heating provides excellent stability for processes like curing, drying, or baking.
- If your primary focus is rapidly and uniformly heating non-metallic materials: Dielectric or microwave heating is the specialized and highly effective choice.
Ultimately, selecting the right industrial heating technology is about precisely matching the method to your material, budget, and operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Method | Principle | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas Furnace | Burns fuel to generate heat | Bulk heating, smelting, forging | Lower cost per BTU (energy unit) |
| Electric Resistance | Current heats a resistive element | Ovens, curing, baking, liquid heating | Excellent temperature control and stability |
| Induction Heating | Electromagnetic fields heat conductive parts | Fast, precise metal heating (hardening, brazing) | High speed, energy efficiency (>90%) |
| Dielectric Heating | RF waves cause molecular friction in insulators | Heating plastics, wood, food, ceramics | Uniform internal heating |
Struggling to select the right heating technology for your lab or production line? The optimal choice balances cost, precision, material compatibility, and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory heating needs. Our experts can help you analyze your specific process requirements—whether you need the raw power of a furnace or the pinpoint accuracy of electric heating—to enhance your operational efficiency and product quality. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover the perfect heating solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play during the re-austenitization of 17-4 PH? Transform SLM Performance
- What is the importance of precise programmed temperature control in a high-temperature furnace? Master Co-Sintering
- Why do ceramics need to be sintered? Unlock Strength and Durability Through High-Temperature Fusion
- What is the sintering process of coating? Building Durable, Solid Layers from Powder
- What is ashing in chemistry? Enhance Analytical Accuracy with Ashing Techniques



















