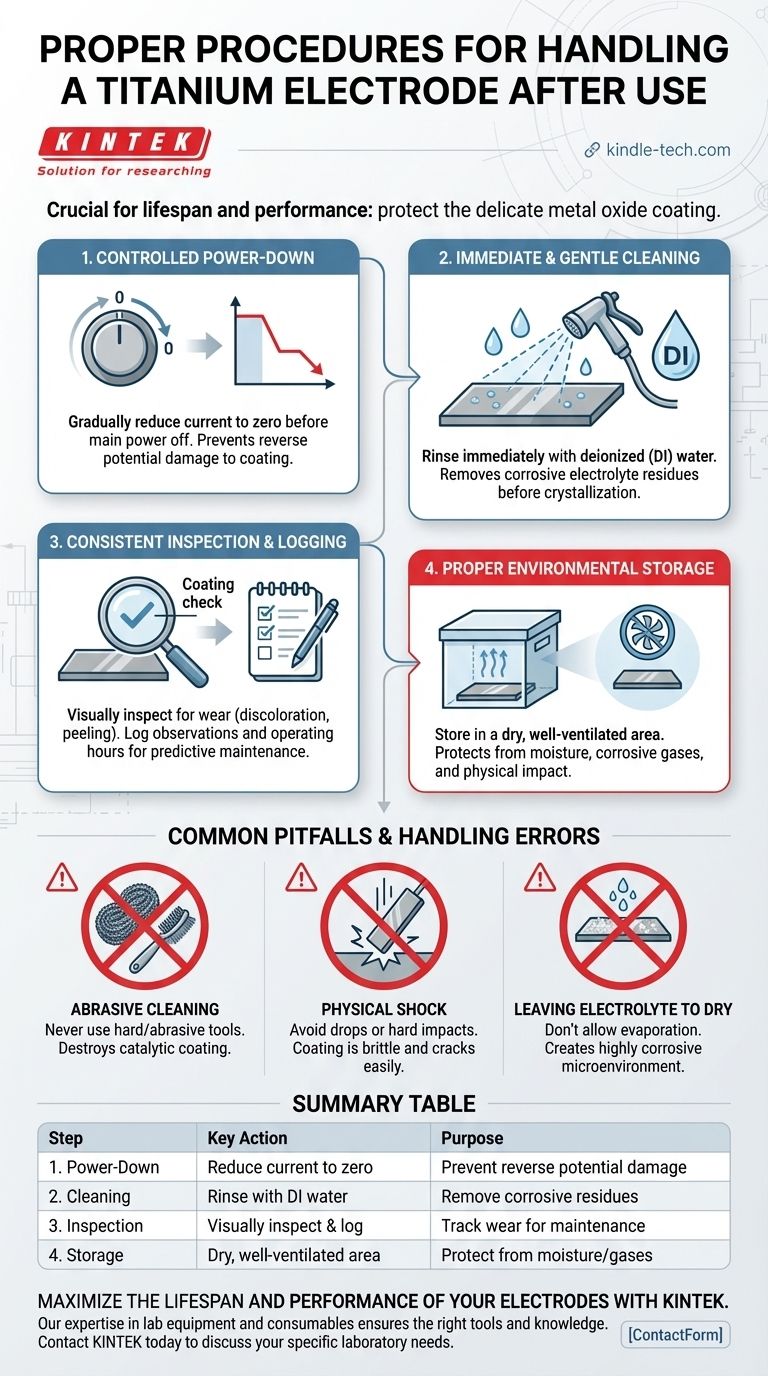
Proper handling after use is the single most critical factor in determining the lifespan and performance of a titanium electrode. The correct procedure involves four distinct steps: a controlled power-down, immediate cleaning with deionized water, thorough inspection for wear, and storage in a dry, controlled environment. Failing to follow this protocol can permanently damage the electrode's delicate catalytic coating, leading to premature failure and costly replacement.
The core principle of post-use care is to protect the electrode's precious metal oxide coating. This layer is responsible for its catalytic activity and corrosion resistance, and every step—from shutdown to storage—is designed to prevent the physical and chemical damage that degrades it.

The Core Post-Use Protocol
Following a systematic, four-step process after every use cycle is essential for preserving the electrode's integrity and ensuring consistent performance.
Step 1: Controlled Power-Down
The shutdown sequence is not trivial; it is your first line of defense against electrical damage.
First, gradually reduce the current to zero before turning off the main power supply. A sudden power cut can induce a reverse potential across the electrode, which can strip or damage the active coating.
Step 2: Immediate and Gentle Cleaning
Residual electrolyte is the primary enemy of a resting electrode. It must be removed immediately.
Rinse the electrode surface thoroughly with deionized (DI) water. This removes salts and other residues before they can crystallize and corrode the surface. This step must be performed promptly after removing the electrode from the cell.
Step 3: Consistent Inspection and Logging
Treat the electrode as a critical asset whose condition must be tracked over time.
Visually inspect the coating for any changes, such as discoloration, peeling, or scratches. Log these observations along with the total operating hours. This data is invaluable for predictive maintenance and understanding the electrode's wear cycle.
Step 4: Proper Environmental Storage
The storage environment can either preserve or degrade the electrode.
Store the electrode in a dry and well-ventilated area. It must be kept away from moisture and any corrosive gases that could react with the coating. Ensure it is placed securely to prevent physical impact.
Common Pitfalls and Handling Errors
Mistakes in handling are a common cause of premature electrode failure. Awareness is the key to prevention.
The Myth of Abrasive Cleaning
Never use hard or abrasive tools like steel wool, wire brushes, or scrapers to clean the electrode surface. This will permanently scratch and destroy the catalytic coating, rendering the electrode useless.
If gentle rinsing with DI water is insufficient, use a soft cloth or sponge, but only with extreme care.
The Danger of Physical Shock
The coating on a titanium electrode is a thin, ceramic-like layer that can be brittle.
Dropping the electrode or allowing it to strike a hard surface can cause the coating to chip or crack. Handle it with the same care you would afford laboratory glassware.
Leaving Electrolyte to Dry
Allowing electrolyte to evaporate on the electrode surface is highly detrimental.
As the water evaporates, the concentration of salts and acids increases dramatically, creating a highly corrosive microenvironment that will aggressively attack the coating. This is why immediate rinsing is non-negotiable.
Applying This to Your Workflow
Your specific priorities will determine which aspects of this protocol demand the most attention.
- If your primary focus is maximizing operational lifespan: Make the immediate post-use cleaning and proper dry storage your most rigid, non-negotiable habits.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process consistency: Prioritize the inspection and logging step to track performance degradation and anticipate when replacement is needed.
- If your primary focus is preventing catastrophic failure: Master the controlled power-down procedure and enforce strict rules against physical shock or short-circuiting.
Ultimately, disciplined handling is the most effective investment you can make in the long-term reliability of your process.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Power-Down | Gradually reduce current to zero | Prevents reverse potential damage to coating |
| 2. Cleaning | Rinse immediately with deionized water | Removes corrosive electrolyte residues |
| 3. Inspection | Visually inspect and log coating condition | Tracks wear for predictive maintenance |
| 4. Storage | Store in a dry, well-ventilated area | Protects from moisture and corrosive gases |
Maximize the lifespan and performance of your electrodes with KINTEK.
Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you have the right tools and knowledge for proper electrode maintenance. Whether you need high-quality replacement electrodes, specialized cleaning solutions, or technical support to optimize your workflow, our team is here to help.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Ultra-Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Electrode Lead for High-Precision Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using a spiral platinum wire? Optimize Your Electrochemical Precision
- What are the advantages of using a Platinum (Pt) electrode for zirconium testing? Ensure High-Precision Data Integrity
- Why is platinum a good counter electrode? For Superior Chemical Inertness and Electron Transfer
- Why is a platinum electrode typically selected as the auxiliary or counter electrode? Unlock Precise Data Accuracy
- What is the function of a platinum electrode as an auxiliary electrode? Ensure Precise Nickel Coating Corrosion Testing



















