Graphite rods are defined by their exceptional ability to conduct heat and electricity, often surpassing common metals like steel and lead. Their unique combination of thermal, electrical, and chemical properties makes them highly effective in specialized industrial applications, particularly those involving extreme temperatures.
Graphite's primary value lies in its dual-role as a high-performance conductor (both thermal and electrical) and a chemically stable material. Understanding which form of graphite to use—pure or composite—is critical for harnessing these properties effectively for a specific application.

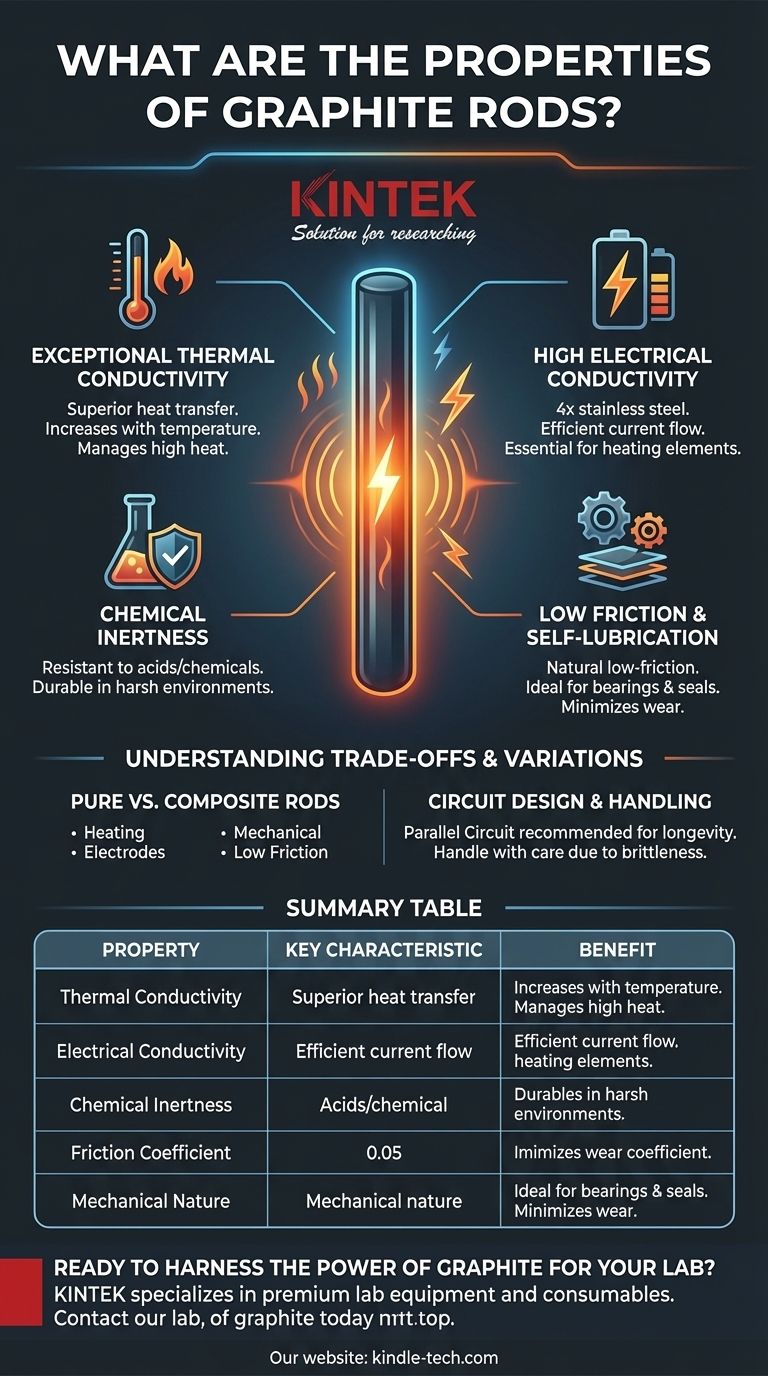
Core Properties of Graphite Rods
Graphite's atomic structure, a layered lattice of carbon atoms, is the source of its most significant characteristics. These properties make it a valuable material where metals might fail.
Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor. Its ability to transfer heat is greater than that of steel, iron, and lead.
Uniquely, its thermal conductivity tends to increase with temperature up to a certain point, a behavior opposite to most metals. This makes it ideal for managing heat in high-temperature environments.
High Electrical Conductivity
The material is also a superior electrical conductor. A graphite rod's conductivity can be four times higher than stainless steel and twice that of carbon steel.
This property is fundamental to its use in applications like heating elements and electrodes, where efficient current flow is essential.
Chemical Inertness
Graphite is highly resistant to corrosion and does not react with most acids or other chemicals.
This stability allows it to be used in harsh chemical environments where other materials would quickly degrade. When blended with materials like PTFE (Teflon), this inertness is further enhanced.
Low Friction and Self-Lubrication
The layered structure of graphite allows layers to slide over one another easily, giving it a natural low-friction, or self-lubricating, quality.
This is especially true for composite rods, which are often used for bearings and seals where they cause minimal wear to mating surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends on selecting the right type and understanding its operational limits.
Brittleness and Mechanical Stress
Unlike metals, graphite is a brittle material. It lacks ductility and can fracture under sudden mechanical shock or impact. This must be considered in any design where physical stress is a factor.
Pure vs. Composite Rods
The term "graphite rod" can refer to pure graphite or a composite. Pure graphite is typically used for heating elements and electrodes. Composite rods, such as those blended with PTFE and carbon, are engineered for mechanical applications requiring low friction and wear resistance.
Handling Electrical Loads
When using graphite rods as heating elements, it is crucial to increase voltage gradually. A sudden surge can cause thermal shock and damage the rod.
Circuit Design for Longevity
For applications with multiple heating elements, connecting graphite rods in a parallel circuit is strongly recommended over a series connection. In a series circuit, a change in resistance in one rod affects the entire chain, often leading to rapid degradation and a shorter lifespan for all components. Parallel circuits isolate each rod, ensuring more stable and prolonged operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct type of graphite rod and implementing it properly is key to success. Your primary goal will dictate your choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating: Use pure graphite rods and ensure you implement a slow voltage ramp-up and a parallel circuit design to maximize lifespan.
- If your primary focus is electrical conduction or electrodes: Leverage graphite's high conductivity but design mountings and connections that protect the brittle rods from mechanical shock.
- If your primary focus is low-friction mechanical parts: Choose a PTFE-graphite composite rod for its superior wear resistance and self-lubricating properties.
Ultimately, understanding graphite's fundamental properties is the first step toward leveraging its power in demanding technical applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent, increases with temperature | Superior heat management in high-temp environments |
| Electrical Conductivity | 4x higher than stainless steel | Efficient current flow for heating elements & electrodes |
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to most acids and chemicals | Durability in harsh, corrosive environments |
| Friction Coefficient | Low, self-lubricating | Ideal for bearings and seals with minimal wear |
| Mechanical Nature | Brittle, lacks ductility | Requires careful handling to avoid fracture from shock |
Ready to harness the power of graphite for your lab?
Graphite rods are essential for high-temperature furnaces, electrochemical cells, and specialized lab equipment. Choosing the right type—pure or composite—is critical for performance and longevity.
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the ideal graphite rods for your specific application, ensuring optimal conductivity, thermal management, and chemical resistance.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and get a personalized solution that enhances your lab's efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What technical advantages do carbon graphite electrodes offer for electroactive biofilms? Optimize Your Bio-Research
- How should a graphite electrode be cleaned and stored after an experiment? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What are the properties and applications of a graphite disk electrode? Precision Tools for Electroanalysis
- What are the potential risks when using a graphite electrode in electrochemical tests? Avoid Decomposition and Contamination
- Why is a high-purity graphite rod preferred as a counter electrode? Ensure Uncontaminated Electrochemical Analysis



















