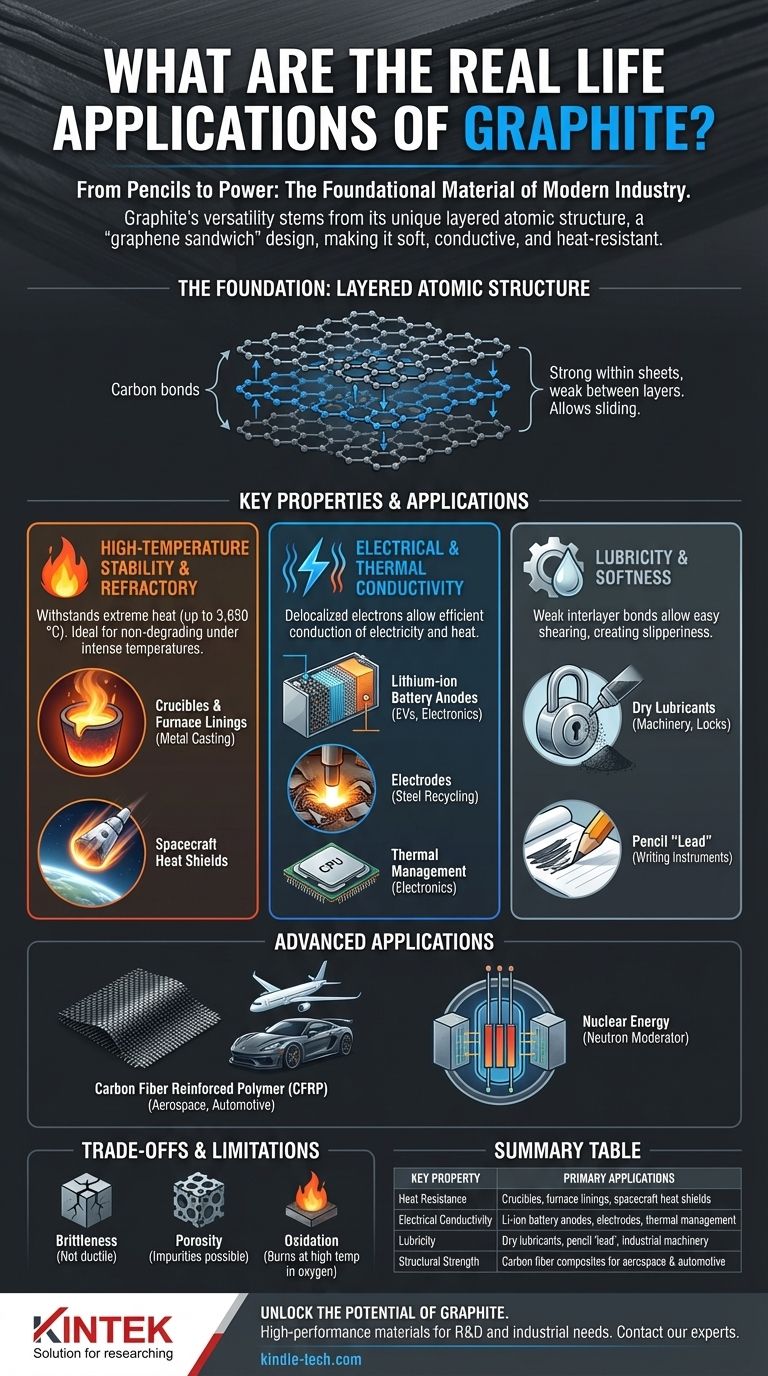
At its core, graphite is far more than just pencil lead. Its applications are foundational to modern industry, ranging from the batteries powering your phone and electric vehicles to the high-temperature crucibles used for melting steel and the heat shields on spacecraft. This versatility stems from a unique combination of seemingly contradictory properties.
Graphite's true value lies in its layered atomic structure. This "graphene sandwich" design creates a material that is simultaneously soft, conductive, and incredibly resistant to heat, making it one of the most versatile and critical non-metallic materials in modern engineering.

The Foundation: Why Graphite is So Versatile
To understand graphite's applications, you must first understand its fundamental structure. Graphite is an allotrope of carbon, meaning it's made of pure carbon atoms arranged in a specific way.
The Layered Atomic Structure
Graphite consists of vast, flat sheets of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice. These sheets, now famous as graphene, are incredibly strong internally.
However, the bonds between these sheets are extremely weak. This allows the layers to slide over one another with very little effort. This duality—strong internal sheets and weak interlayer bonds—is the key to almost all of its properties.
Property 1: High-Temperature Stability
The carbon-carbon bonds within each graphite sheet are exceptionally strong, requiring immense energy to break. This gives graphite an extremely high melting point (around 3,650 °C or 6,600 °F).
This makes it an ideal refractory material, meaning it can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading.
Property 2: Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
The electrons within graphite's carbon sheets are delocalized, meaning they are not tied to a single atom and are free to move throughout the sheet.
This mobility of electrons allows graphite to conduct electricity and heat very efficiently, rivaling some metals. This property is rare for a non-metal.
Property 3: Lubricity and Softness
The weak bonds between graphite's layers allow them to easily cleave and slide apart. This microscopic shearing action is what creates its characteristic slipperiness.
When you write with a pencil, you are shearing off thousands of these microscopic layers onto the paper. This same principle makes it an excellent dry lubricant.
Key Applications by Property
Graphite isn't a single material but a family of materials whose specific form is chosen to enhance one of its core properties for a given application.
As a Refractory Material (Heat Resistance)
Graphite's ability to withstand heat makes it essential for high-temperature industries.
It is used to make crucibles for holding molten metal, linings for blast furnaces, and molds for continuous casting of steel. Its stability ensures it doesn't melt or react with the materials it contains.
As a Conductor (Electrical and Thermal)
This is one of its fastest-growing applications. Finely processed spherical graphite is the primary anode material in most lithium-ion batteries, including those in electric vehicles and consumer electronics.
It's also used for electrodes in electric arc furnaces for steel recycling and in manufacturing heat spreaders and thermal interface materials for cooling CPUs and other powerful electronics.
As a Lubricant (Slipperiness)
In its powdered form, graphite serves as a high-performance dry lubricant. It is used in applications where wet lubricants like oil would attract dust or fail, such as in door locks, industrial machinery, and certain bearings.
The most famous application is, of course, the "lead" in pencils, which is a mixture of graphite and a clay binder.
In Advanced Composites and Nuclear Energy
Graphite fibers can be woven into a fabric and combined with a polymer resin to create carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP). This material has an incredible strength-to-weight ratio and is used in aerospace, high-performance cars, and sports equipment.
Additionally, high-purity graphite is used as a neutron moderator in some nuclear reactor designs, where it slows down neutrons to sustain a controlled nuclear chain reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging graphite's limitations is key to using it effectively.
Brittleness and Mechanical Strength
While the individual graphene sheets are strong, bulk graphite is not ductile like metal. It is a brittle material and can fracture under sharp impact or high tensile stress. It is strong under compression but weak under tension.
Porosity and Purity
Natural graphite often has a porous structure and contains impurities. For high-tech applications like semiconductors or batteries, this is unacceptable.
This has led to the development of synthetic graphite and specialized forms like isostatic graphite, which offer extremely high purity and a uniform, non-porous structure to meet strict performance requirements.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
While graphite has a high melting point, it will react with oxygen and burn away at high temperatures (typically starting around 600-700 °C). Its use in high-temperature environments often requires a vacuum or an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The term "graphite" refers to a wide range of materials. The correct choice depends entirely on your engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective refractory performance: Natural flake graphite is the standard for crucibles and furnace linings in the steel industry.
- If your primary focus is high-performance energy storage: Highly controlled synthetic or specialized spherical graphite is required for lithium-ion battery anodes.
- If your primary focus is extreme purity and structural integrity: High-purity isostatic graphite is necessary for semiconductor manufacturing equipment and nuclear applications.
- If your primary focus is lightweight structural strength: Carbon fiber, derived from specific precursors, is the basis for advanced composite materials.
Understanding graphite begins with its atomic structure, which dictates the remarkable properties that make it indispensable across a vast spectrum of modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Applications |
|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Crucibles, furnace linings, spacecraft heat shields |
| Electrical Conductivity | Lithium-ion battery anodes, electrodes for steel recycling |
| Lubricity | Dry lubricants, pencil 'lead', industrial machinery |
| Structural Strength | Carbon fiber composites for aerospace and automotive |
Unlock the potential of graphite for your laboratory or production process.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance graphite materials, including crucibles, electrodes, and high-purity synthetic graphite, tailored to meet the demanding needs of R&D and industrial applications. Our materials ensure superior thermal management, electrical conductivity, and durability.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite solutions can enhance your project's efficiency and performance.
Get in touch with our experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are Al-doped LLZO samples subjected to post-treatment? Restoring Purity for Solid Electrolyte Performance
- What is the primary function of a vacuum drying oven in LiFePO4 cathode preparation? Ensure High Battery Performance
- What is the purpose of a heating device in in-situ thermal polymerization? Optimize All-Solid-State Battery Performance
- What is the significance of the ultra-high pressure in solid-state battery assembly? Achieve Atomic-Level Contact
- In which fields is nickel foam widely used? A Key Material for Advanced Engineering
- How should carbon paper be handled during cutting? Prevent Fractures with a Delicate, Precise Approach
- What is the synthesis method of graphene? Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Approaches for Your Application
- What are the main applications of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in battery R&D? Optimize High-Energy Density Battery Performance



















