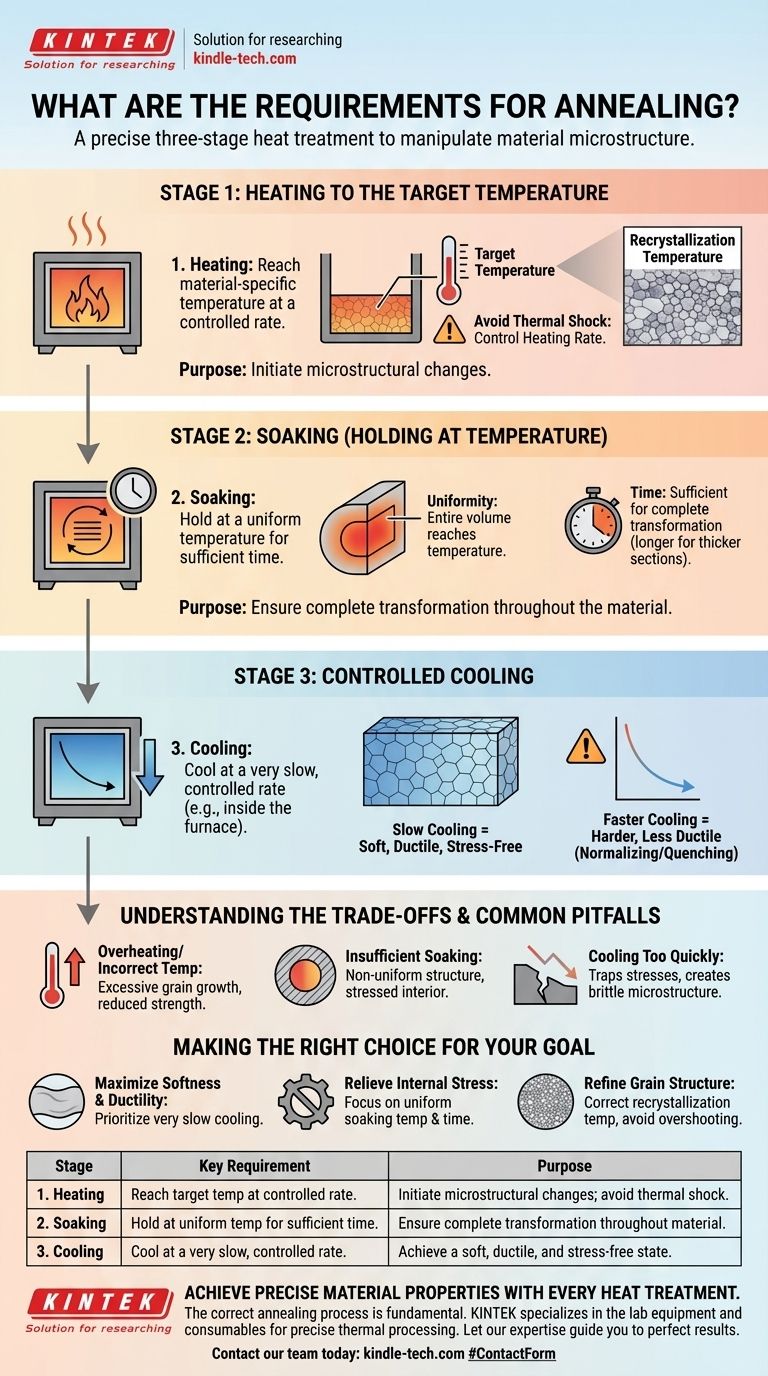
At its core, annealing is a three-stage heat treatment process. The fundamental requirements are to heat the material to a specific temperature, hold it there for a sufficient duration to ensure temperature uniformity, and then cool it at a controlled, typically slow, rate. Each of these stages is critical for achieving the desired changes in the material's internal structure.
The purpose of annealing is not simply to heat and cool a material. It is a precise method of manipulating a material’s microstructure to relieve internal stresses, increase ductility, and refine its grain structure, effectively making it softer and more workable.

The Three Critical Stages of Annealing
Annealing can be broken down into three distinct and equally important phases. Success depends on precise control over each one.
Stage 1: Heating to the Target Temperature
The first step is heating the material in a furnace. The target temperature, known as the annealing temperature, is highly specific to the material and the desired outcome.
For metals, this temperature is typically related to its recrystallization temperature—the point at which new, strain-free grains begin to form. For ceramics or glass, it's a temperature that allows internal stresses to relax without deforming the part.
The heating rate must also be controlled. Heating too quickly can induce thermal shock and cause cracking, especially in brittle materials like ceramics or large, complex metal parts.
Stage 2: Soaking (Holding at Temperature)
Once the material reaches the target temperature, it is "soaked" or held at that temperature for a set period. The primary requirements for this stage are time and uniformity.
As noted, the temperature inside the furnace must be uniform. This ensures that the entire volume of the material—from the surface to the core—reaches the same temperature and undergoes the same structural transformation.
The soaking time must be sufficient for the desired metallurgical changes to complete. Thicker sections require longer soaking times than thinner ones to achieve full-temperature penetration and complete microstructural change.
Stage 3: Controlled Cooling
The cooling stage is arguably what most defines annealing. After soaking, the material must be cooled at a very slow and controlled rate.
This is often achieved by simply turning off the furnace and letting the part cool down with the furnace over many hours. This slow cooling allows large, coarse grains to form, which results in a soft, ductile, and stress-free state.
The cooling rate directly determines the final properties. A faster cooling rate would be a different type of heat treatment (like normalizing or quenching) and would produce a harder, less ductile material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While annealing is a powerful process, imprecise control can lead to undesirable outcomes.
The Risk of Overheating or Incorrect Temperature
Using a temperature that is too high can cause excessive grain growth. While annealing aims to refine grains, overheating creates overly large grains that can reduce the material's strength and toughness.
Conversely, not heating to a high enough temperature will result in an incomplete transformation, failing to relieve stresses or soften the material as intended.
The Problem with Insufficient Soaking
If the soaking time is too short, the core of the material may never reach the target temperature. This results in a non-uniform structure where only the surface is properly annealed, leaving the interior hard and stressed.
The Impact of Cooling Rate
The most common mistake is cooling the material too quickly. This traps stresses and creates a harder, more brittle microstructure than desired. True annealing is fundamentally a slow-cooling process. Any deviation from this changes the nature of the treatment entirely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters for annealing must be tailored to your material and objective.
- If your primary focus is to maximize softness and ductility: Prioritize a very slow cooling rate, such as leaving the component to cool inside the furnace overnight.
- If your primary focus is to relieve internal stress from manufacturing: Concentrate on achieving a uniform soaking temperature and holding it long enough for the entire part to equalize.
- If your primary focus is to refine the grain structure after heavy cold working: Pay close attention to reaching the correct recrystallization temperature without overshooting it, which could cause unwanted grain growth.
By understanding these core requirements, you can precisely control a material's properties to meet the demands of your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Heating | Reach material-specific temperature at a controlled rate. | Initiate microstructural changes; avoid thermal shock. |
| 2. Soaking | Hold at a uniform temperature for a sufficient time. | Ensure complete transformation throughout the material. |
| 3. Cooling | Cool at a very slow, controlled rate (e.g., inside the furnace). | Achieve a soft, ductile, and stress-free state. |
Achieve precise material properties with every heat treatment.
The correct annealing process is fundamental to your product's performance and reliability. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for precise thermal processing, from durable furnaces with uniform temperature control to essential accessories.
Let our expertise guide you to perfect results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory annealing requirements and how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification



















