The primary safety precautions during heat treatment are a multi-layered system designed to control extreme temperatures, hazardous atmospheres, chemical exposures, and material handling risks. This involves a strict combination of specialized Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), robust engineering controls like furnace interlocks and ventilation, and rigorous administrative procedures such as Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) and comprehensive operator training.
Heat treatment safety is not merely about avoiding burns. It's about systematically managing high-energy environments by understanding that the greatest risks often come from invisible hazards like toxic gases, flammable atmospheres, and the immense potential energy stored in hot materials.
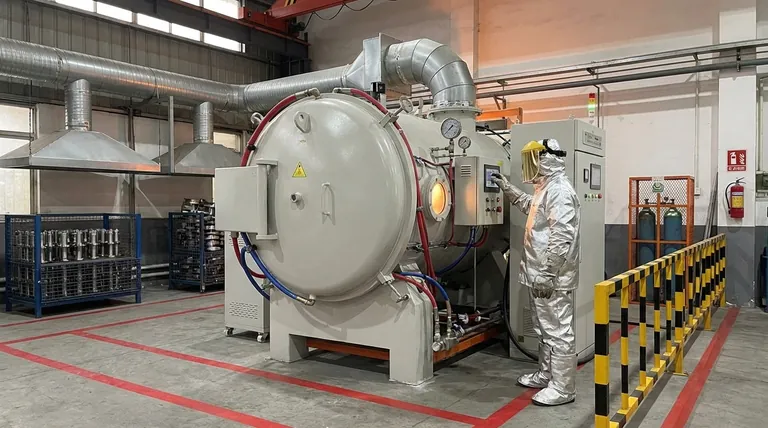

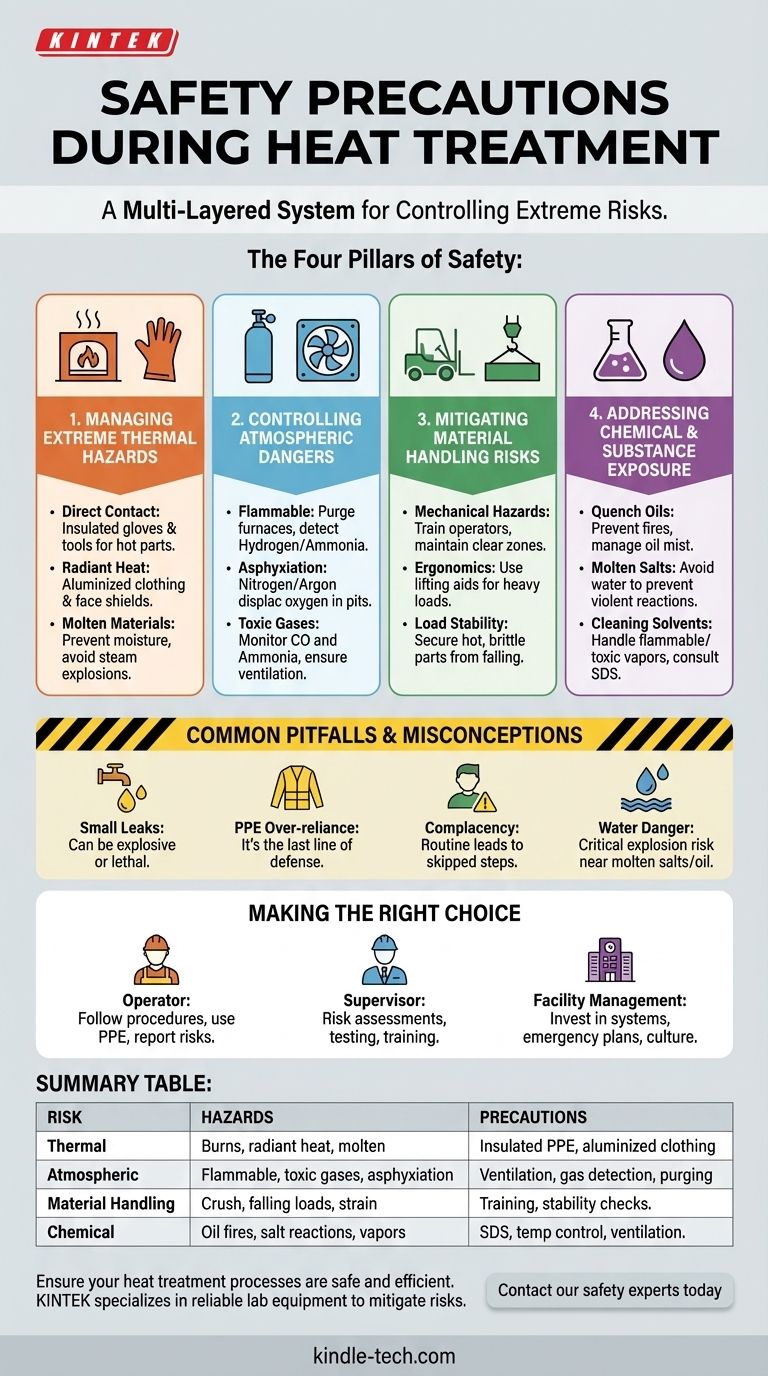
The Four Pillars of Heat Treatment Safety
Effective safety protocols are built on understanding and controlling the four primary categories of risk inherent to heat treating operations.
1. Managing Extreme Thermal Hazards
The most obvious danger is the extreme heat from furnaces, parts, and quenching media. This risk extends beyond simple contact burns.
- Direct Contact: Touching hot parts, fixtures, or furnace interiors can cause severe, life-altering burns instantly. Insulated gloves and tools are non-negotiable.
- Radiant Heat: The intense infrared radiation from an open furnace door can cause serious skin burns and eye damage from a distance. Aluminized clothing and proper face shields are required for these tasks.
- Molten Materials: Processes using molten salt or metals present an extreme thermal and splash hazard. Any moisture contamination can cause a violent steam explosion, ejecting molten material over a wide area.
2. Controlling Atmospheric Dangers
What you can't see is often the most dangerous element. The atmospheres inside heat treatment furnaces are engineered for metallurgical purposes but can be lethal.
- Flammable Atmospheres: Gases like hydrogen, dissociated ammonia, or endothermic gas are highly explosive. Proper ventilation, furnace purging procedures, and gas detection systems are critical to prevent catastrophic explosions.
- Inert Gas Asphyxiation: Gases like nitrogen and argon, used to prevent oxidation, can displace oxygen in enclosed areas. A leak in a pit furnace or a poorly ventilated room can lead to asphyxiation in minutes, often without warning.
- Toxic Gases: Carburizing and nitriding processes use gases that can be toxic. Carbon monoxide (CO) is a byproduct of endothermic gas, and ammonia (NH3) is used in nitriding. Both require continuous monitoring and emergency ventilation.
3. Mitigating Material Handling Risks
Heat treatment involves moving heavy, awkward, and often very hot or brittle materials in and out of equipment.
- Mechanical Hazards: Cranes, forklifts, and charging machines present significant crush and impact risks. Proper operator training and maintaining clear zones of operation are essential.
- Ergonomics and Load Stability: Manually loading and unloading baskets can cause strain injuries. Furthermore, hot or freshly quenched parts can be brittle or shift unexpectedly, creating a risk of falling materials.
4. Addressing Chemical and Substance Exposure
The process involves more than just heat and metal. Various chemicals are used that carry their own distinct risks.
- Quench Oils: These oils operate at high temperatures and present a significant fire hazard if their flash point is exceeded or if hot parts are not fully submerged. Inhalation of oil mist is also a long-term respiratory health concern.
- Molten Salts: Beyond the burn risk, salt baths can be chemically reactive. The accidental introduction of water or incompatible materials can cause violent reactions.
- Cleaning Solvents: Parts are often cleaned before treatment. The vapors from cleaning solvents can be flammable or toxic, requiring careful handling and ventilation. Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for any chemical used.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Building a true culture of safety means moving beyond the checklist and understanding the common failure points.
The "It's Just a Small Leak" Fallacy
A small, seemingly insignificant leak of process gas is an emergency. A minor hydrogen leak can accumulate to form an explosive mixture, while a quiet nitrogen leak can silently create a lethal, oxygen-deficient atmosphere.
Over-reliance on PPE
Personal Protective Equipment is the last line of defense, not the first. If an operator is relying solely on their PPE to stay safe, the underlying hazard has not been properly controlled by engineering or procedural solutions.
Complacency with Routine Tasks
Familiarity can lead to complacency. Operators who have performed a task thousands of times may be tempted to take shortcuts, such as bypassing a safety interlock or failing to properly purge a furnace. This is a leading cause of major incidents.
The Extreme Danger of Water
Water is one of the greatest single threats in a heat treatment facility. Its presence near molten salt baths or hot quench oil tanks is a critical risk, as the rapid conversion to steam is powerful enough to be explosive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
A robust safety program requires a commitment at every level of the organization, with specific responsibilities tailored to each role.
- If you are an operator or technician: Your primary focus is on meticulous adherence to procedure, correctly using all required PPE for every task, and immediately reporting any condition you believe to be unsafe.
- If you are a supervisor or engineer: Your primary focus is on conducting regular risk assessments, ensuring all engineering controls are functional through periodic testing, and providing clear, continuous training on both normal and emergency procedures.
- If you are responsible for facility management: Your primary focus is on investing in and maintaining modern safety systems like gas detection and ventilation, establishing clear and practiced emergency action plans, and fostering a proactive safety culture that empowers everyone to stop work if they see a risk.
Ultimately, a proactive and systematic approach to safety transforms a high-risk environment into a controlled, predictable, and productive operation.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Hazards | Essential Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Hazards | Contact burns, radiant heat, molten materials | Insulated PPE, aluminized clothing, moisture control |
| Atmospheric Dangers | Flammable/explosive gases, asphyxiation, toxic fumes | Ventilation, gas detection systems, furnace purging |
| Material Handling | Crush injuries, falling loads, ergonomic strain | Proper crane/forklift training, load stability checks |
| Chemical Exposure | Quench oil fires, molten salt reactions, solvent vapors | Consult SDS, temperature control, ventilation |
Ensure your heat treatment processes are safe and efficient. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for all your laboratory needs. Our expertise helps you mitigate risks and maintain a secure working environment. Contact our safety experts today to discuss your specific requirements and how we can support your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the most common applications of FTIR? Identify Materials from Polymers to Pharmaceuticals
- What are the applications of thin film technology? Powering Electronics, Energy, and Innovation
- What are the advantages of powder metallurgy process? Achieve Cost-Effective, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is the process of debinding? A Guide to Safe, Effective Binder Removal
- How long does it take for THC to evaporate? The Real Science Behind Potency Loss
- What is the function of 3D motion mixing equipment in powder preparation? Ensure Uniformity for Laser Cladding
- What protective roles do Sealing Gaskets and Support Grids play in oil-water separation? Ensure High-Pressure Integrity
- What heating treatment can be used to strengthen the structure of a metal? Master Hardening, Tempering & More



















