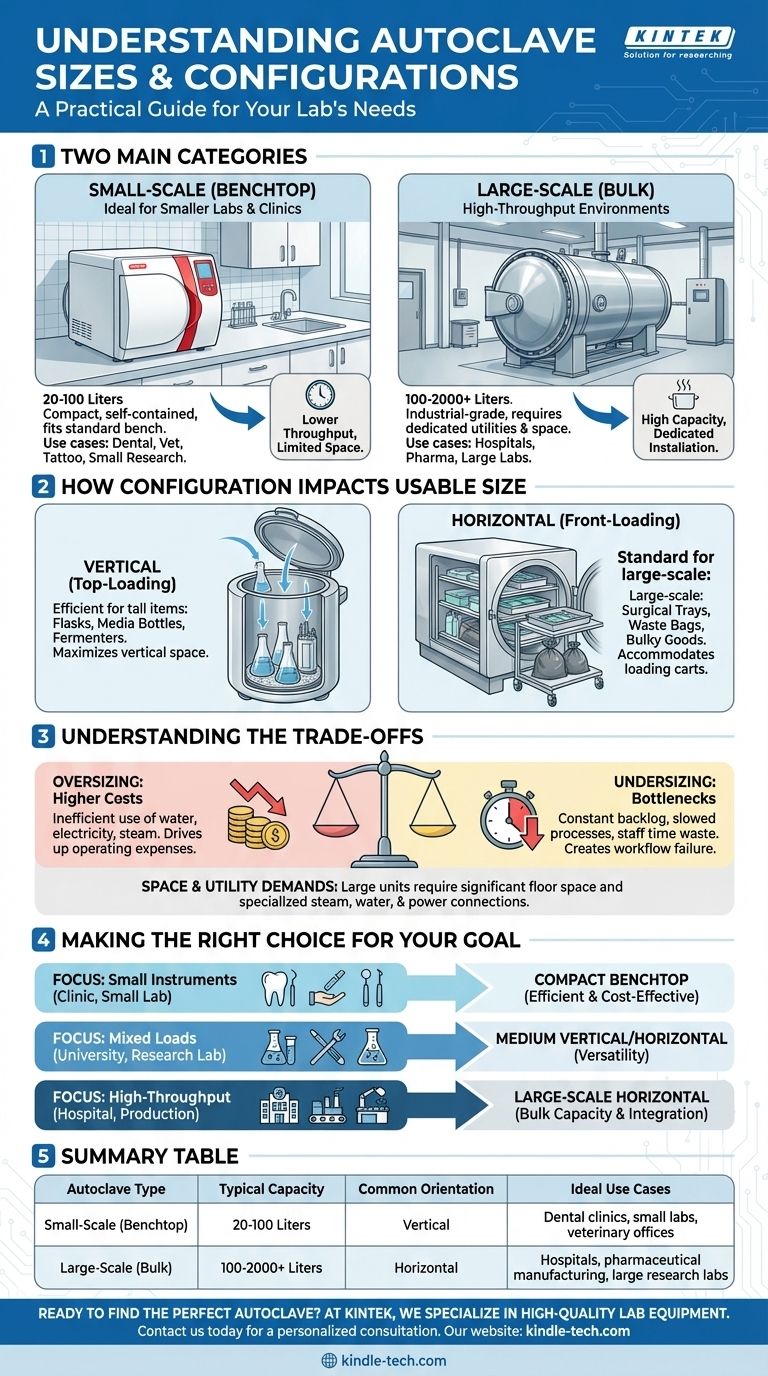
The short answer is that autoclaves are broadly classified into two main categories: small-scale (benchtop) models suitable for smaller labs and clinics, and large-scale (bulk) units designed for high-throughput environments like hospitals. The specific size and configuration you need, however, depend entirely on your intended application.
The most common mistake is focusing only on chamber volume. The correct approach is to match the autoclave's size, orientation (vertical or horizontal), and utility requirements to the specific materials you need to sterilize and your daily operational workflow.

A Practical Guide to Autoclave Sizing
Choosing an autoclave is a significant investment. Understanding the primary size categories is the first step in ensuring that investment supports, rather than hinders, your facility's efficiency.
Small-Scale (Benchtop) Autoclaves
These are compact, self-contained units designed to fit on a standard laboratory bench or countertop.
They are the go-to solution for facilities with lower throughput needs or limited space, such as dental offices, veterinary clinics, tattoo parlors, and smaller research labs.
Large-Scale (Bulk) Autoclaves
These are industrial-grade, high-capacity machines that often require dedicated rooms and specialized utility connections (steam, water, high-voltage electricity).
They are essential for high-throughput sterilization in hospitals, pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, and large-scale clinical or research laboratories where bulk materials like surgical trays, animal cages, or large volumes of media must be processed.
How Configuration Impacts Usable Size
The physical orientation of the autoclave chamber directly influences what you can sterilize effectively, regardless of the stated liter capacity.
Vertical Autoclaves
These units are top-loading, similar to a large pressure cooker. You lower items into the chamber from above.
This design is highly efficient for sterilizing tall items like flasks, media bottles, and fermenters, maximizing the use of vertical space.
Horizontal Autoclaves
These front-loading units function like a large oven, with a door that swings outward. They are often equipped with racks and shelves to accommodate loading carts.
As noted in many specifications, this configuration is standard for large-scale autoclaves. It is ideal for sterilizing wide, flat items like surgical instrument trays, bags of waste, and other bulky goods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong size has significant consequences for your budget and workflow. It's a decision that requires careful consideration of the downsides.
The Cost of Oversizing
A larger autoclave consumes more water, electricity, and steam per cycle. Running a large, half-empty chamber for a few small items is incredibly inefficient and drives up operating costs.
The Bottleneck of Undersizing
An autoclave that is too small for your needs creates a constant backlog. Staff will waste time running multiple cycles, slowing down critical laboratory or clinical processes and creating a point of failure in your workflow.
Space and Utility Demands
A large-scale autoclave is more than just a piece of equipment; it's a facility installation. It demands significant floor space, clearance for maintenance, and often requires professional installation to connect to dedicated steam, water, and electrical lines. A small benchtop unit, by contrast, may only need a standard electrical outlet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate autoclave, shift your focus from "how big is it?" to "what do I need it to do?"
- If your primary focus is sterilizing small instruments in a clinic or a small lab: A compact, small-scale benchtop autoclave offers the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing mixed loads of glassware, media, and tools in a university or research lab: A medium-sized, floor-standing vertical or horizontal unit provides the necessary versatility.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput sterilization in a hospital or production facility: A large-scale horizontal autoclave designed for bulk capacity and workflow integration is the only viable option.
Ultimately, choosing the right size autoclave is a strategic decision that directly impacts your operational efficiency and budget.
Summary Table:
| Autoclave Type | Typical Capacity | Common Orientation | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small-Scale (Benchtop) | 20-100 Liters | Vertical | Dental clinics, small labs, veterinary offices |
| Large-Scale (Bulk) | 100-2000+ Liters | Horizontal | Hospitals, pharmaceutical manufacturing, large research labs |
Ready to find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory's needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you need a compact benchtop autoclave for a small clinic or an industrial-grade bulk unit for high-throughput sterilization, our experts will help you select the right size and configuration to maximize your operational efficiency and minimize costs.
Don't let the wrong autoclave size slow down your workflow—contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the advantages of autoclaving in hospitals? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Patient Safety



















