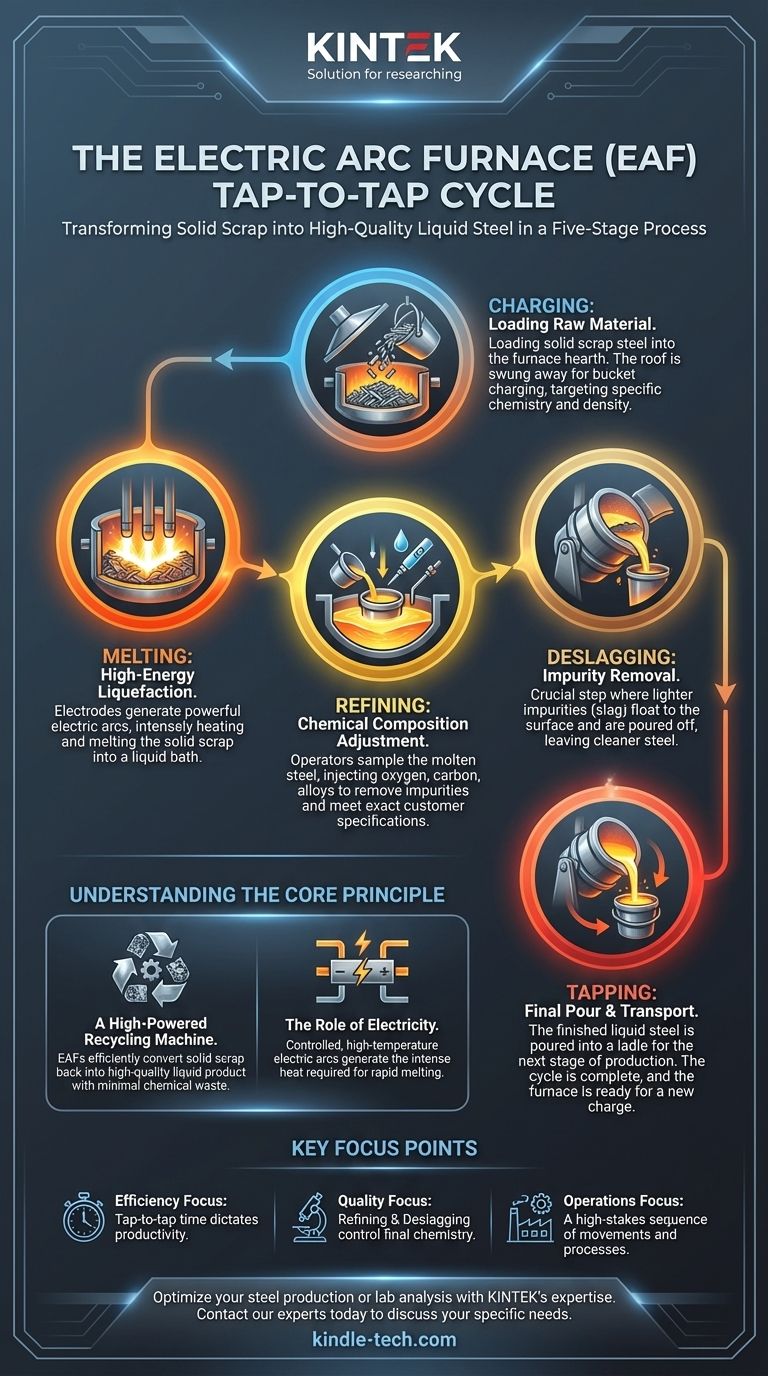
The operational cycle of an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is known as the tap-to-tap cycle. This highly efficient process consists of five distinct stages: charging, melting, refining, deslagging, and tapping. Each phase is a critical step in transforming solid scrap metal into high-quality liquid steel.
An electric arc furnace doesn't just melt metal; it executes a precise, high-energy sequence to recycle scrap into a refined product with a specific chemical composition, all within a cycle that is measured from the moment steel is poured out (tapped) to the next.

A Detailed Breakdown of the EAF Cycle
The entire tap-to-tap cycle is a carefully choreographed process designed for speed and quality control. It begins with a cold, empty furnace and ends with it ready for the next charge.
Stage 1: Furnace Charging
Charging is the process of loading the raw material, primarily scrap steel, into the furnace.
The furnace roof, which holds the electrodes, is swung away to allow large buckets to drop the scrap directly into the main vessel or hearth. This initial charge is carefully selected to achieve a target chemistry and density.
Stage 2: Melting
This is the most energy-intensive stage, where an immense amount of electricity is used to melt the solid scrap.
Three graphite or carbon electrodes are lowered through holes in the furnace roof. A powerful electric arc is struck between the electrodes and the scrap metal, generating intense heat that melts the charge into a liquid bath.
Stage 3: Refining
Once the steel is molten, the focus shifts from melting to adjusting its chemical composition.
During refining, operators take samples of the molten bath to check its chemistry. They may inject oxygen, carbon, and other alloys to remove impurities and bring the steel to the exact specification required by the customer.
Stage 4: Deslagging
This crucial step involves removing impurities, known as slag, from the molten steel.
The impurities, which are lighter than steel, float to the surface to form a liquid slag layer. The furnace is carefully tilted to pour this slag off through a slag door, leaving behind the cleaner, refined liquid steel.
Stage 5: Tapping
Tapping is the final stage, where the finished liquid steel is poured out of the furnace.
The furnace is tilted in the opposite direction of deslagging, allowing the molten steel to flow out through a drain hole, or taphole, into a ladle. This ladle then transports the steel to the next stage of the production process, and the EAF is ready to be charged again, beginning a new cycle.
Understanding the Core Principle
The EAF process is fundamentally different from traditional primary steelmaking. Its efficiency and purpose are defined by its core components and its role as a recycler.
A High-Powered Recycling Machine
An EAF is essentially a powerful recycling unit. Its primary function is to take a solid, cold material (scrap steel) and convert it back into a high-quality liquid product with minimal chemical waste.
The main furnace vessel is a steel casing lined with refractory material designed to withstand the extreme temperatures. The entire structure sits on a cradle that can be tilted by hydraulic or electric drives, enabling the precise actions of deslagging and tapping.
The Role of Electricity
The process relies entirely on electrical energy supplied through massive copper busbars to the electrodes. The ability to generate a controlled, high-temperature arc is what makes the rapid melting of tons of steel possible.
Key Focus Points of the EAF Process
To understand the cycle, consider which aspect is most relevant to your goal.
- If your primary focus is on efficiency: The "tap-to-tap time" is the single most important metric, as it dictates the furnace's productivity.
- If your primary focus is on material quality: The refining and deslagging stages are the most critical, as this is where the final product chemistry is precisely controlled.
- If your primary focus is on operations: The entire cycle is a high-stakes sequence of mechanical movements (tilting, roof swinging) and intense electrical and chemical processes.
The electric arc furnace cycle is a masterclass in controlled, high-energy manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Charging | Loading scrap steel into the furnace | Prepare the raw material for melting |
| 2. Melting | Using electric arcs to melt the scrap | Create a liquid steel bath |
| 3. Refining | Injecting oxygen/carbon, adding alloys | Achieve the target chemical composition |
| 4. Deslagging | Tilting furnace to remove impurities | Purify the molten steel by removing slag |
| 5. Tapping | Pouring finished steel into a ladle | Transfer the final product for casting |
Optimize your steel production or lab analysis with KINTEK's expertise.
Whether you are operating an EAF or analyzing the resulting steel, KINTEK provides the durable lab equipment and consumables you need for precise temperature control, accurate sampling, and reliable material testing. Our furnaces, electrodes, and refractory materials are designed to withstand the extreme conditions of metal production and quality control.
Let us help you enhance efficiency and quality in your laboratory or production facility.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















