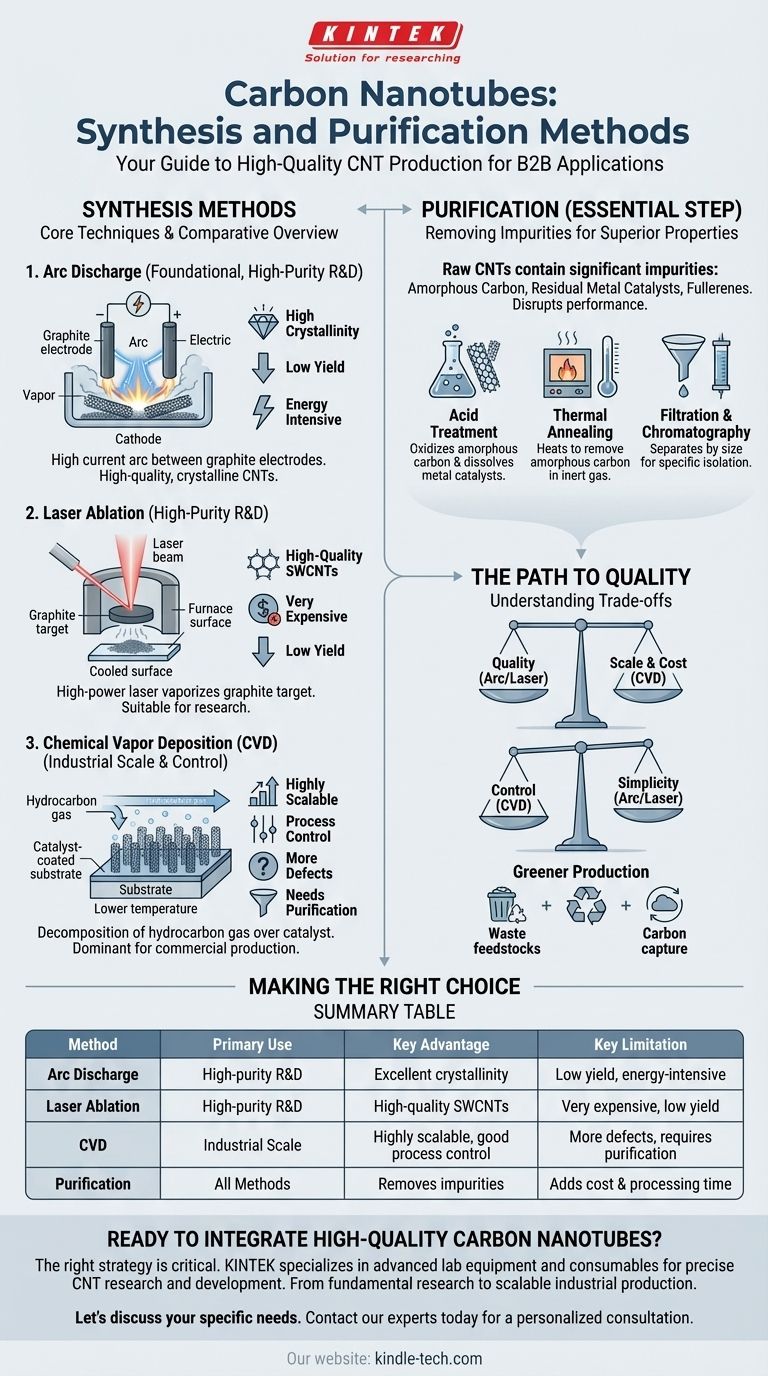
The primary methods for synthesizing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are arc discharge, laser ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While the first two were foundational, CVD is now the dominant commercial process due to its scalability and control. Regardless of the synthesis method, a subsequent purification stage is essential to remove byproducts and catalysts.
The challenge in producing carbon nanotubes isn't merely their creation, but a careful balancing act between the synthesis method and the required purification. Your choice of process directly dictates the trade-offs between production scale, material quality, and final cost.
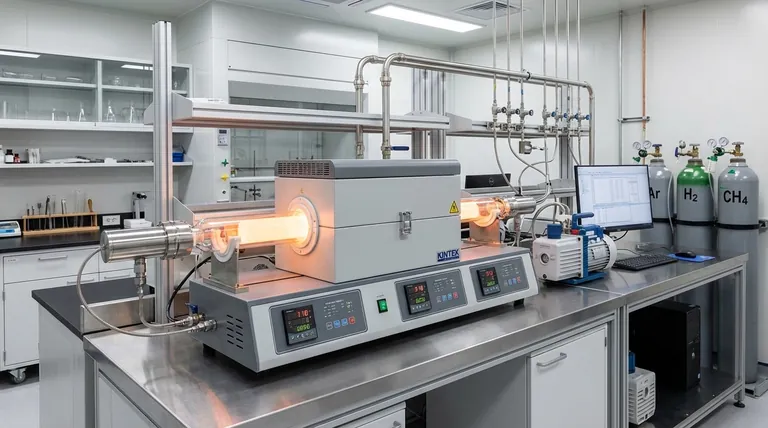

Core Synthesis Methods: A Comparative Overview
Three techniques form the foundation of CNT production. While they all produce nanotubes, they operate on different principles and are suited for different goals.
Arc Discharge
This method involves creating a high-current electric arc between two graphite electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere.
The intense heat from the arc vaporizes the carbon from the positive electrode (anode), which then condenses on the cooler negative electrode (cathode), forming nanotubes. It was one of the first techniques used and produces high-quality, highly crystalline CNTs.
Laser Ablation
In this process, a high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target, often mixed with a metal catalyst, inside a high-temperature furnace.
The laser vaporizes the carbon target, creating a plume of carbon atoms that are swept by an inert gas onto a cooler collector. Like arc discharge, this method yields high-quality CNTs but is generally expensive and has a low production rate, making it suitable for research.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the most common method for commercial-scale production. It involves decomposing a hydrocarbon gas (like methane or acetylene) over a substrate prepared with metal catalyst nanoparticles.
The process operates at much lower temperatures than arc discharge or laser ablation. The catalysts break down the hydrocarbon molecules, and the carbon atoms reassemble into nanotube structures. CVD offers superior control over CNT length, diameter, and alignment, making it highly versatile.
The Critical Step: Purification
Raw CNT material produced by any method is never pure. It contains significant impurities that degrade its exceptional mechanical and electrical properties, making purification a non-negotiable step.
Why Purification is Essential
The primary impurities include amorphous carbon, residual metal catalysts (especially from CVD), and other unwanted carbon nanoparticles like fullerenes.
These contaminants can disrupt electrical conductivity, weaken composite materials, and cause unpredictable behavior in sensitive applications like electronics or biomedical devices.
Common Purification Techniques
Several methods are used to remove these impurities, often in combination.
- Acid Treatment: Using strong acids like nitric or sulfuric acid oxidizes and washes away amorphous carbon while dissolving the metallic catalyst particles.
- Thermal Annealing: Heating the raw CNTs to high temperatures in an inert gas or vacuum helps graphitize and remove amorphous carbon.
- Filtration and Chromatography: These physical methods separate CNTs from impurities based on differences in size, allowing for the isolation of nanotubes of a specific length or diameter.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a production strategy requires understanding the inherent compromises between quality, quantity, and cost.
Quality vs. Scale
Arc discharge and laser ablation typically produce CNTs with fewer structural defects and higher crystallinity. However, their yield is low and the process is energy-intensive.
CVD excels at large-scale production and is far more economical. The trade-off is that CVD-grown CNTs often have more defects and require more aggressive purification to remove catalyst residues.
Control vs. Simplicity
The primary advantage of CVD is its process control. By adjusting the catalyst, temperature, gas flow, and pressure, manufacturers can influence the resulting nanotube diameter, length, and even vertical alignment.
Arc discharge and laser ablation offer far less control over the final product, typically producing a tangled mixture of single-walled and multi-walled nanotubes of various sizes.
The Future: Greener Production
Emerging research focuses on making CNT synthesis more sustainable. This includes developing "green" methods that use waste feedstocks, such as pyrolyzing methane or using captured carbon dioxide via electrolysis in molten salts, to reduce both cost and environmental impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final application dictates the optimal synthesis and purification strategy.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, research-grade samples: Laser ablation or arc discharge are ideal for creating highly crystalline material where production cost is not the main constraint.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the only commercially viable method due to its unmatched scalability and lower operational cost.
- If your primary focus is controlled CNT structures for electronics: CVD provides the necessary control over alignment, diameter, and density required for fabricating advanced devices.
Ultimately, mastering carbon nanotubes requires viewing synthesis and purification as two halves of a single, integrated process.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | High-purity R&D | Excellent crystallinity | Low yield, energy-intensive |
| Laser Ablation | High-purity R&D | High-quality SWCNTs | Very expensive, low yield |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Industrial Scale | Highly scalable, good process control | More defects, requires purification |
| Purification | All Methods | Removes catalysts & amorphous carbon | Adds cost and processing time |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or product development?
The right synthesis and purification strategy is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for precise CNT research and development. Our expertise supports applications from fundamental research to scalable industrial production.
Let's discuss your specific needs and how our solutions can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods



















