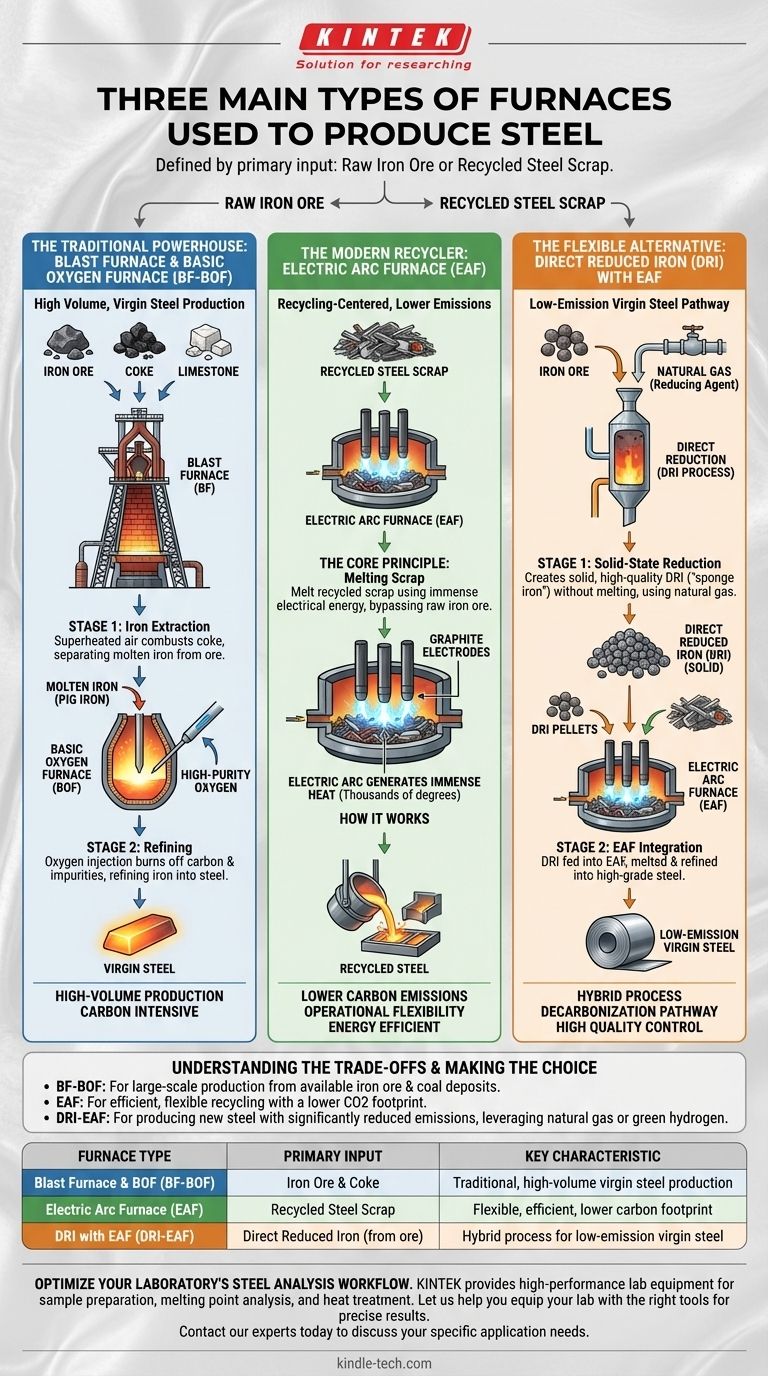
At the heart of modern industry, steel is produced using one of three primary furnace configurations. These methods are the integrated Blast Furnace and Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF) route, the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) route, and a hybrid process involving Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) that feeds an Electric Arc Furnace. Each pathway is defined by its primary input material, whether it be raw iron ore or recycled steel scrap.
The fundamental difference between the three major steelmaking methods lies in their raw materials. The traditional BF-BOF process makes new steel from iron ore, the EAF process recycles existing steel scrap, and the DRI-EAF process provides a modern way to make new steel with the flexibility of an EAF.

The Traditional Powerhouse: Blast Furnace & Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF)
This integrated two-stage process is the classic method for producing high volumes of steel from raw, natural materials.
The Core Principle
The BF-BOF route is designed for virgin steel production. It first extracts iron from iron ore in a Blast Furnace and then refines that iron into steel in a Basic Oxygen Furnace.
Stage 1: The Blast Furnace (BF)
The process begins by feeding iron ore, coke (a high-carbon fuel derived from coal), and limestone into the top of a massive Blast Furnace. Superheated air is "blasted" into the bottom, causing the coke to combust and creating the intense heat and chemical reactions needed to separate molten iron from its ore.
Stage 2: The Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF)
This hot, liquid iron (often called "hot metal" or "pig iron") is then transferred to a Basic Oxygen Furnace. A lance is lowered into the vessel to inject high-purity oxygen, which initiates a chemical reaction that burns off excess carbon and other impurities, refining the iron into steel.
The Modern Recycler: The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
The Electric Arc Furnace represents a fundamentally different and more modern approach to steelmaking, centered on recycling.
The Core Principle
The EAF's primary function is to melt recycled steel scrap and other metallic inputs using an enormous amount of electrical energy. This method bypasses the need for raw iron ore and coke entirely.
How It Works
A charge of scrap steel is loaded into the furnace. Large graphite electrodes are then lowered, and a powerful electric arc is struck between them and the scrap metal. This arc generates immense heat—reaching thousands of degrees—that rapidly melts the scrap into liquid steel.
Key Characteristics
Because it avoids the chemical reduction of iron ore, the EAF process has significantly lower direct carbon emissions than the BF-BOF route. It is also more flexible, allowing for smaller production scales that can be started and stopped more easily.
The Flexible Alternative: Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) with EAF
This hybrid method bridges the gap between virgin steel production and the more efficient EAF technology, offering a pathway to create new steel with a smaller environmental footprint.
The Core Principle
Direct Reduction creates a solid, virgin iron product from iron ore without melting it. This material, known as DRI or "sponge iron," serves as a high-quality, low-impurity feedstock for an Electric Arc Furnace.
The EAF Connection
The solid DRI is then continuously fed into an EAF, often alongside traditional scrap steel. There, it is melted down and refined into high-grade steel, combining the virgin material benefits of the BF-BOF route with the efficiency of an EAF.
Why It Matters
The DRI process typically uses natural gas as its chemical reducing agent instead of coke. This decouples virgin steel production from coal, providing a critical pathway for lowering the industry's carbon emissions, especially as producers look to substitute natural gas with green hydrogen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between these methods is not arbitrary; it is dictated by economics, available raw materials, and environmental objectives.
Input Dictates the Process
The core distinction is simple: if you have access to vast iron ore and coal deposits, the BF-BOF route is the traditional choice for high-volume production. If you have a steady supply of recycled scrap, the EAF is far more efficient.
The Environmental Angle
The reliance on coke makes the BF-BOF process highly carbon-intensive. The EAF route, powered by an increasingly green electrical grid, is the dominant method for steel recycling with a much lower CO2 footprint. The DRI-EAF route is a critical technology for decarbonizing virgin steel production.
Quality and Control
The BF-BOF process offers precise control over the final steel chemistry because it starts with known inputs. The quality of EAF steel can vary with the quality of the scrap being recycled, a challenge that the addition of pure, virgin DRI helps overcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is large-scale production from raw materials: The integrated Blast Furnace and Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF) route is the established, high-volume method.
- If your primary focus is recycling and operational flexibility: The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the most energy-efficient and cost-effective choice for processing scrap steel.
- If your primary focus is producing new steel with lower carbon emissions: The Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) to EAF pathway is the leading modern alternative to traditional blast furnaces.
Understanding these fundamental production pathways is key to navigating the economics and environmental future of steel.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Input Material | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Blast Furnace & BOF (BF-BOF) | Iron Ore & Coke | Traditional, high-volume virgin steel production |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Recycled Steel Scrap | Flexible, efficient, lower carbon footprint |
| DRI with EAF (DRI-EAF) | Direct Reduced Iron (from ore) | Hybrid process for low-emission virgin steel |
Optimize Your Laboratory's Steel Analysis Workflow
Understanding steel production is critical for quality control and material testing. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces for sample preparation, melting point analysis, and heat treatment, tailored to the needs of metallurgical laboratories.
Let us help you equip your lab with the right tools for precise and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and discover the perfect solution from KINTEK.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens when metal is annealed? A Guide to Softer, More Workable Metals
- What are the advantages of metal sintering? Achieve Cost-Effective, Complex Metal Parts
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- How does heat treatment affect the mechanical properties of metals? Optimize Hardness, Toughness, and Ductility
- What is the difference between batch type and continuous type furnace? Choose the Right Heat Treatment Process
- How does air-cooling in high-temp furnaces affect alloy hardness? Expert Insights on Normalizing Processes
- What is catalytic pyrolysis? A Guide to Upgrading Bio-Oil Quality
- What is the function of a high-temperature sintering furnace? Powering Refractory Synthesis and Structural Integrity



















