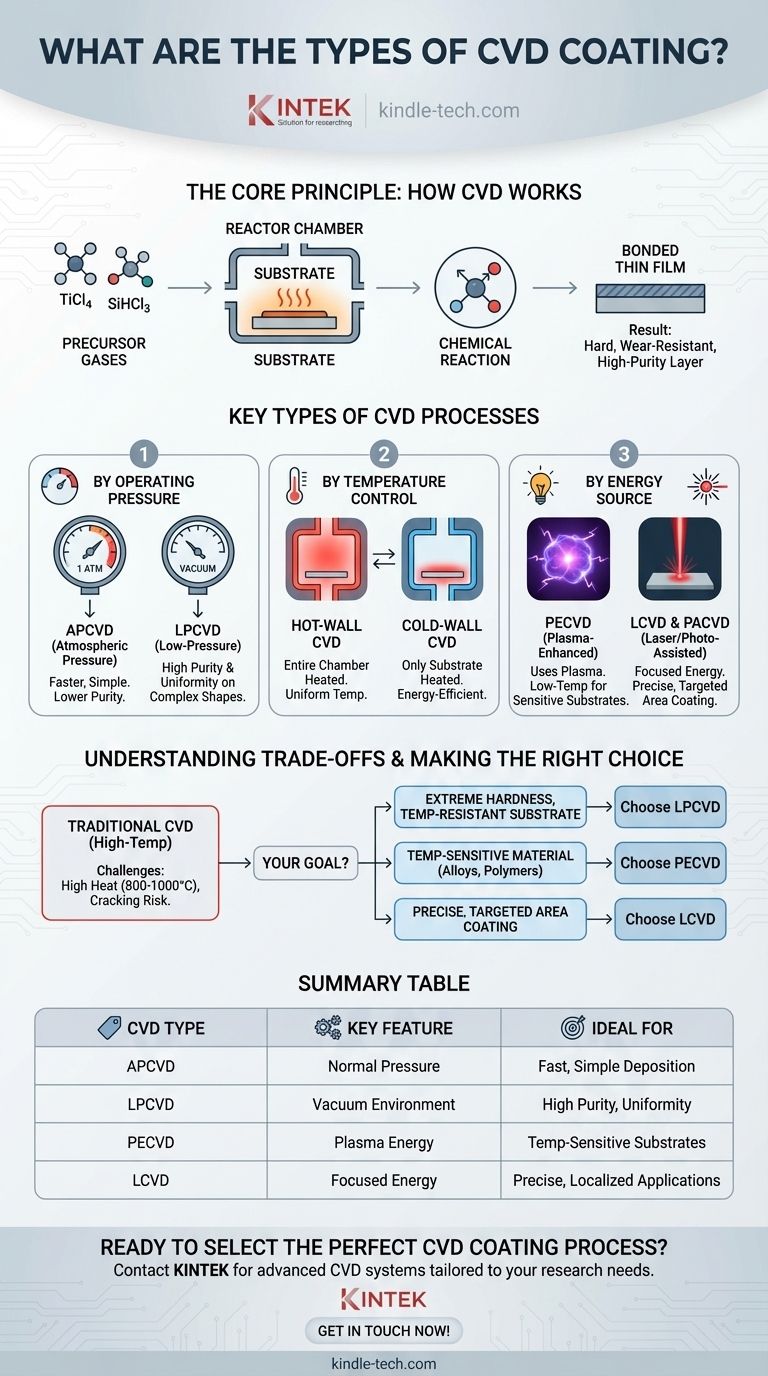
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not a single technology but a family of processes. The primary types are distinguished by their operating pressure, temperature control, and the type of energy used to initiate the chemical reaction. Key variants include Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD), Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), and methods using lasers or light for energy.
The crucial insight is that different CVD methods exist to overcome specific limitations. The choice between them is a deliberate engineering trade-off, balancing the need for lower temperatures, higher purity, or better uniformity against process complexity and cost.
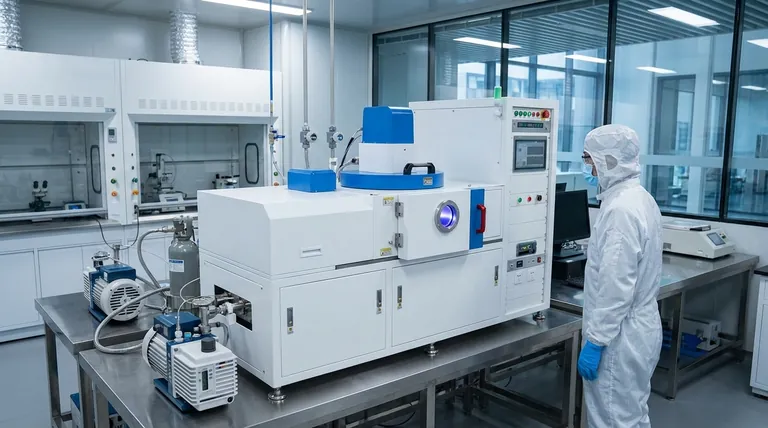

The Core Principle: How CVD Works
Before categorizing the types, it's essential to understand the fundamental process they all share. CVD is a method for applying a thin, durable film onto a surface through a controlled chemical reaction.
The Role of Precursors
The process begins with one or more volatile precursor gases, which contain the atoms of the desired coating material. For example, titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) is a common precursor for titanium-based coatings, while trichlorosilane (SiHCl3) is used for silicon deposition.
The Chemical Reaction
These precursor gases are introduced into a reactor chamber containing the object to be coated, known as the substrate. The substrate is heated, and this thermal energy causes the precursor gases to react or decompose on its surface, depositing a solid thin film.
The Result: A Bonded Thin Film
The resulting coating—such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) or silicon—is not merely sitting on the surface; it is chemically bonded to the substrate. This creates an extremely hard, wear-resistant, and high-purity layer.
The Key Types of CVD Processes
The variations in the CVD process are designed to optimize the coating for different substrates and performance requirements. They are typically classified by the conditions inside the reactor.
Classification by Operating Pressure
The pressure inside the reactor dramatically affects the quality and uniformity of the coating.
- Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD): This process operates at normal atmospheric pressure. It is simpler and faster but can sometimes result in lower film purity and uniformity compared to other methods.
- Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD): By operating under a vacuum, LPCVD reduces unwanted gas-phase reactions. This allows for excellent coating uniformity and the ability to coat complex shapes evenly.
Classification by Reactor Temperature Control
How heat is applied to the substrate and the chamber is another critical distinction.
- Hot-Wall CVD: In this configuration, the entire reactor chamber is heated. This provides excellent temperature uniformity across the substrate but can lead to wasteful deposition on the chamber walls.
- Cold-Wall CVD: Here, only the substrate itself is heated, while the chamber walls remain cool. This method is more energy-efficient and minimizes unwanted coating on the reactor components.
Classification by Energy Source
To accommodate heat-sensitive materials, some CVD processes use alternative energy sources instead of relying solely on high temperatures.
- Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): This is a pivotal variant. PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma (an ionized gas), which provides the energy for the chemical reaction. This allows the deposition to occur at much lower temperatures, making it suitable for substrates that cannot withstand traditional CVD heat.
- Laser-Assisted (LCVD) & Photo-Assisted CVD (PACVD): These highly specialized methods use a focused energy source—a laser or ultraviolet light—to initiate the reaction. Their key advantage is the ability to deposit a coating onto a very specific, targeted area of the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Traditional CVD
While powerful, the conventional high-temperature CVD process has significant limitations that drive the need for the variants described above.
The High-Temperature Limitation
Standard CVD processes operate at very high temperatures, often between 800°C and 1000°C. This restricts its use to substrates that can withstand such heat without deforming or melting, such as cemented carbides.
Risk of Cracking and Peeling
Because the coating is applied at a high temperature, significant tensile stress can build up as the part cools down. This can lead to fine cracks in the coating, which may cause it to peel or flake off under external impact or stress.
Unsuitability for Interrupted Processes
This risk of cracking makes traditional CVD less suitable for tools used in interrupted cutting applications, such as milling. The constant, non-uniform impact can exploit the micro-cracks and cause premature coating failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct CVD process requires aligning the method's capabilities with your material's limitations and your product's performance needs.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness on a temperature-resistant substrate: Traditional high-temperature LPCVD is often the most robust and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like an alloy or polymer: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the necessary alternative, as it operates at significantly lower temperatures.
- If your primary focus is depositing a film on a very specific, targeted area: Laser-Assisted CVD (LCVD) provides the highest degree of spatial control for precision applications.
Understanding these fundamental process variations is the key to selecting the ideal coating strategy for your specific material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| CVD Type | Acronym | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Pressure CVD | APCVD | Operates at normal pressure | Fast, simple deposition |
| Low-Pressure CVD | LPCVD | Vacuum environment for high purity | Excellent uniformity on complex shapes |
| Plasma-Enhanced CVD | PECVD | Uses plasma for low-temperature deposition | Temperature-sensitive substrates (alloys, polymers) |
| Laser-Assisted CVD | LCVD | Focused energy for precise targeting | High-precision, localized coating applications |
Ready to select the perfect CVD coating process for your lab's materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including advanced CVD systems tailored to your specific research and production needs. Whether you require the high-temperature robustness of LPCVD or the precision of PECVD for sensitive substrates, our experts are here to help you achieve superior coating results.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















