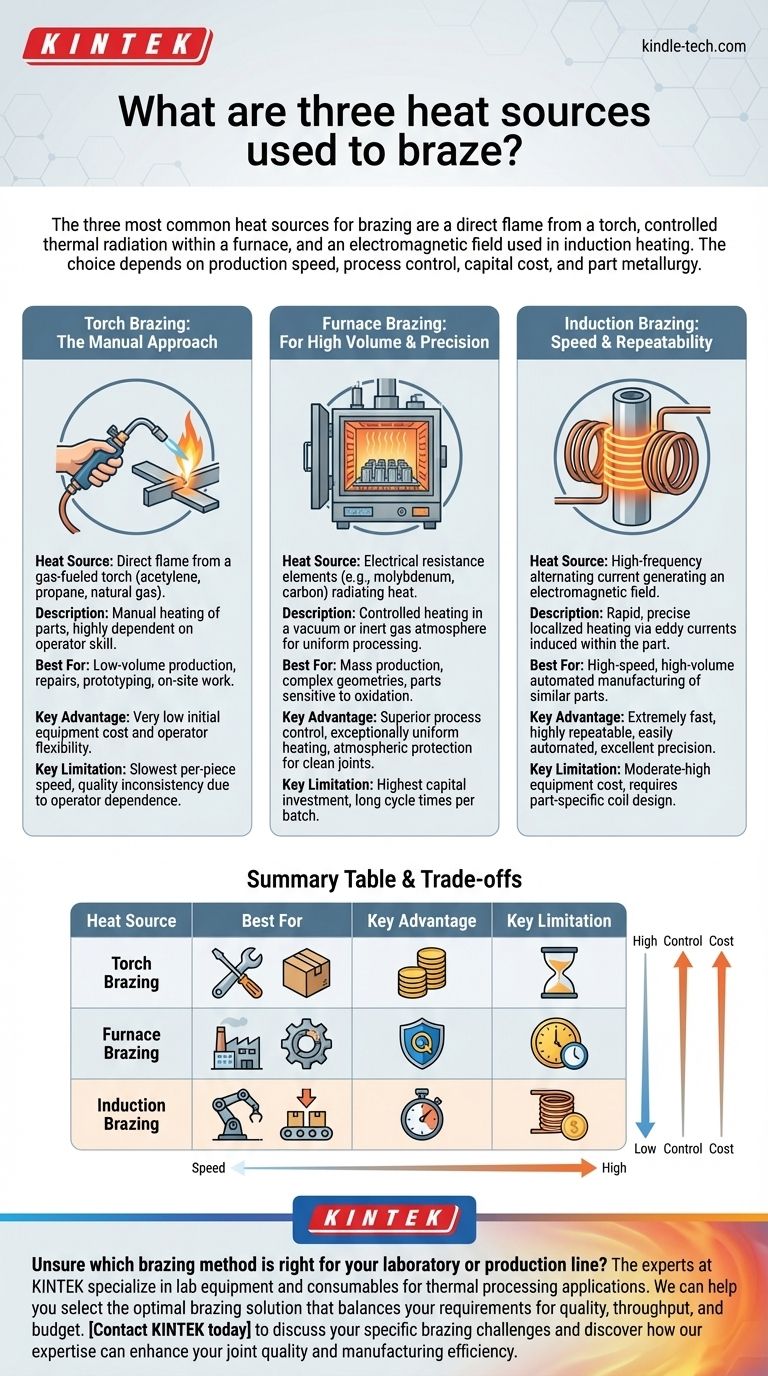
The three most common heat sources for brazing are a direct flame from a torch, controlled thermal radiation within a furnace, and an electromagnetic field used in induction heating. While each can successfully melt a filler metal to create a joint, they are designed for vastly different applications, production volumes, and levels of precision.
The specific heat source you choose for brazing is less about the heat itself and more about the application. The decision is a strategic trade-off between production speed, process control, capital cost, and the specific metallurgy of the parts being joined.

A Closer Look at Brazing Heat Sources
Brazing requires heating two or more base metals to a temperature above the melting point of a filler metal, but below the melting point of the base metals. The method by which this heat is delivered is fundamental to the quality, speed, and cost of the operation.
Torch Brazing: The Manual Approach
Torch brazing is the most common manual method, using the direct flame from a gas-fueled torch. The fuel is typically a combination of a flammable gas (like acetylene, propane, or natural gas) and oxygen or air.
The operator manually heats the parts to be joined and applies the filler metal. This method's success is highly dependent on the skill of the operator to heat the assembly uniformly and avoid overheating.
Furnace Brazing: For High Volume and Precision
Furnace brazing is an ideal method for mass production and for parts with complex geometries. The entire assembly is placed inside a furnace and heated in a controlled cycle.
The heat source within the furnace is typically electrical resistance elements, often made of molybdenum or carbon, which radiate heat throughout the chamber. This provides exceptionally uniform heating for the entire part.
A key advantage is the ability to control the furnace's atmosphere. By using an inert gas or creating a vacuum, the process prevents oxidation, resulting in clean, strong joints without the need for flux. As the references note, furnaces can be batch-type for smaller runs or continuous for high-volume production.
Induction Brazing: Speed and Repeatability
Induction brazing uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This generates a powerful and precise electromagnetic field.
When a metal part is placed within this field, the field induces electrical eddy currents within the part itself. The resistance to these currents generates rapid, localized heat exactly where it is needed for the joint.
This method is extremely fast, with heating cycles often lasting only a few seconds. It is highly repeatable and easily automated, making it perfect for high-speed, high-volume manufacturing lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Control vs. Cost
Choosing a heat source is not just a technical decision; it is an economic one. Each method presents a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages.
Cost and Initial Investment
Torch brazing has a very low initial equipment cost, making it accessible for repairs, prototyping, and low-volume work.
Induction brazing requires a moderate to high investment in a power supply and custom-designed coils.
Furnace brazing represents the highest capital investment due to the cost of the furnace, atmospheric controls, and installation.
Production Speed and Volume
The fastest process per-piece is induction brazing, making it a cornerstone of automated manufacturing.
Torch brazing is the slowest per-piece and is limited by the speed of a manual operator.
Furnace brazing has a long cycle time per batch (often hours), but because it can process hundreds or thousands of parts at once, its overall throughput for mass production is very high.
Process Control and Quality
Furnace brazing offers the highest level of process control. The controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation and ensures uniform heating, leading to the highest quality joints, especially for sensitive materials or complex assemblies.
Induction brazing provides excellent control and unmatched repeatability, virtually eliminating part-to-part variation in automated settings.
Torch brazing offers the lowest process control, as quality is directly tied to operator skill and consistency.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on your project's specific goals. A clear understanding of your priorities will point you to the correct method.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or repair: Torch brazing offers the lowest initial cost and greatest flexibility for a variety of jobs.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, automated manufacturing of similar parts: Induction brazing provides unmatched speed, precision, and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies or materials sensitive to oxidation: Furnace brazing in a controlled atmosphere or vacuum is the definitive solution for maximum quality and strength.
Understanding these core heating methods empowers you to select a brazing process that aligns perfectly with your technical and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Heat Source | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Low-volume, repairs, prototyping | Low equipment cost, operator flexibility | Slow, dependent on operator skill |
| Furnace Brazing | High-volume, complex assemblies, oxidation-sensitive materials | Superior process control, uniform heating, atmospheric protection | High capital cost, long cycle times |
| Induction Brazing | High-speed automated production, repeatable joints | Extremely fast, precise localized heating, excellent repeatability | Moderate-high equipment cost, requires part-specific coil design |
Unsure which brazing method is right for your laboratory or production line? The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables for thermal processing applications. We can help you select the optimal brazing solution that balances your requirements for quality, throughput, and budget.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific brazing challenges and discover how our expertise can enhance your joint quality and manufacturing efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining



















