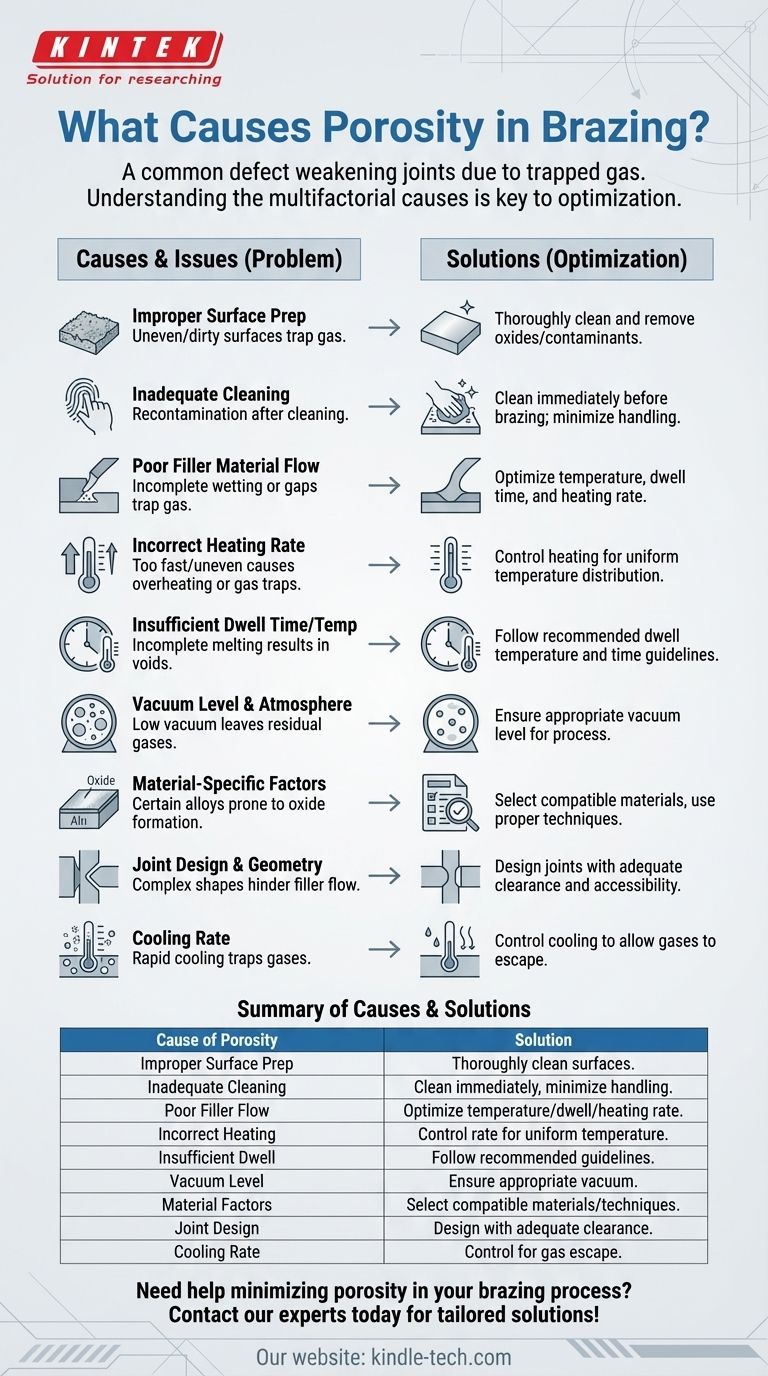
Porosity in brazing is a common defect that can significantly weaken the joint and compromise its integrity. It occurs when gas or air becomes trapped within the brazed joint, forming voids or bubbles. The causes of porosity are multifaceted and can be attributed to factors such as improper surface preparation, inadequate cleaning, poor filler material flow, incorrect heating rates, and insufficient dwell time or temperature. Understanding these causes is essential for optimizing the brazing process and ensuring high-quality, durable joints.

Key Points Explained:
-
Improper Surface Preparation:
- Surface preparation is critical for achieving strong brazed joints. If the surfaces to be joined are not flat, smooth, or free from contaminants, capillary action and filler material flow can be hindered. This can lead to incomplete wetting and the formation of voids.
- Oxide films, oil, grease, or other residues on the surface can prevent proper bonding, trapping gases and causing porosity.
- Solution: Ensure thorough cleaning and surface preparation, including the removal of oxide layers and contaminants, before brazing.
-
Inadequate Cleaning:
- Cleaning effectiveness depends on the material, atmospheric conditions, and handling. If the material is not cleaned properly or is exposed to contaminants after cleaning, porosity can occur.
- Solution: Clean the materials immediately before brazing and minimize handling to prevent recontamination.
-
Poor Filler Material Flow:
- Filler material must flow evenly and completely into the joint to form a strong bond. If the filler material does not wet the surfaces properly or if there are gaps in the joint, gas can become trapped, leading to porosity.
- Solution: Optimize the brazing parameters, such as temperature, dwell time, and heating rate, to ensure proper filler material flow.
-
Incorrect Heating Rate:
- Heating too quickly or unevenly can cause localized overheating or insufficient heating, leading to incomplete melting of the filler material or trapped gases.
- Solution: Control the heating rate to ensure uniform temperature distribution and proper melting of the filler material.
-
Insufficient Dwell Time or Temperature:
- The dwell temperature and time are critical for achieving complete brazing. If the temperature is too low or the dwell time is too short, the filler material may not fully melt or flow, resulting in voids.
- Solution: Follow recommended dwell temperature and time guidelines for the specific materials and filler alloy being used.
-
Vacuum Level and Atmosphere:
- In vacuum brazing, the vacuum level must be sufficient to remove gases from the joint area. If the vacuum level is too low, residual gases can cause porosity.
- Solution: Ensure the vacuum level is appropriate for the materials and brazing process being used.
-
Material-Specific Factors:
- The type of base metal and filler alloy can influence porosity. For example, aluminum alloys are prone to oxide formation, which can trap gases if not properly removed.
- Solution: Select compatible materials and use appropriate cleaning and brazing techniques for the specific alloy.
-
Joint Design and Geometry:
- The shape and size of the parts being joined can affect filler material flow and gas entrapment. Complex geometries or narrow gaps may increase the risk of porosity.
- Solution: Design joints with adequate clearance and accessibility for filler material flow.
-
Cooling Rate:
- Rapid cooling can trap gases within the joint, while slow cooling allows gases to escape. Improper cooling rates can contribute to porosity.
- Solution: Control the cooling rate to allow gases to escape without compromising joint strength.
By addressing these factors and optimizing the brazing process, porosity can be minimized, resulting in stronger, more reliable joints.
Summary Table:
| Cause of Porosity | Solution |
|---|---|
| Improper Surface Preparation | Thoroughly clean and prepare surfaces, removing oxides and contaminants. |
| Inadequate Cleaning | Clean materials immediately before brazing and minimize handling. |
| Poor Filler Material Flow | Optimize brazing parameters (temperature, dwell time, heating rate). |
| Incorrect Heating Rate | Control heating rate for uniform temperature distribution. |
| Insufficient Dwell Time/Temp | Follow recommended dwell temperature and time guidelines. |
| Vacuum Level & Atmosphere | Ensure appropriate vacuum level for the materials and process. |
| Material-Specific Factors | Select compatible materials and use proper cleaning/brazing techniques. |
| Joint Design & Geometry | Design joints with adequate clearance and accessibility for filler flow. |
| Cooling Rate | Control cooling rate to allow gases to escape without weakening the joint. |
Need help minimizing porosity in your brazing process? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















