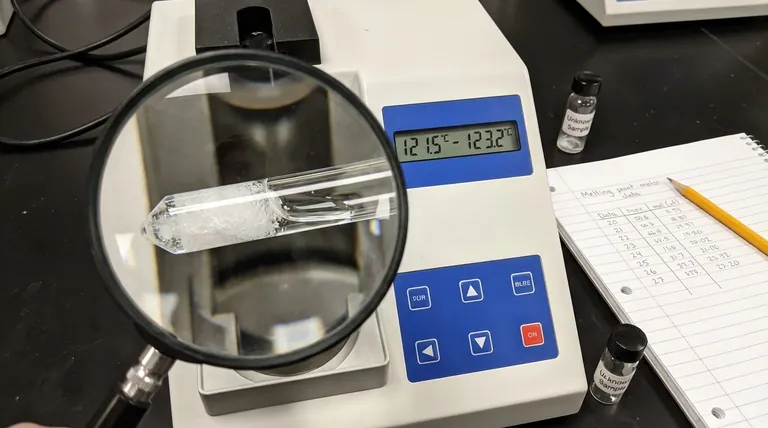
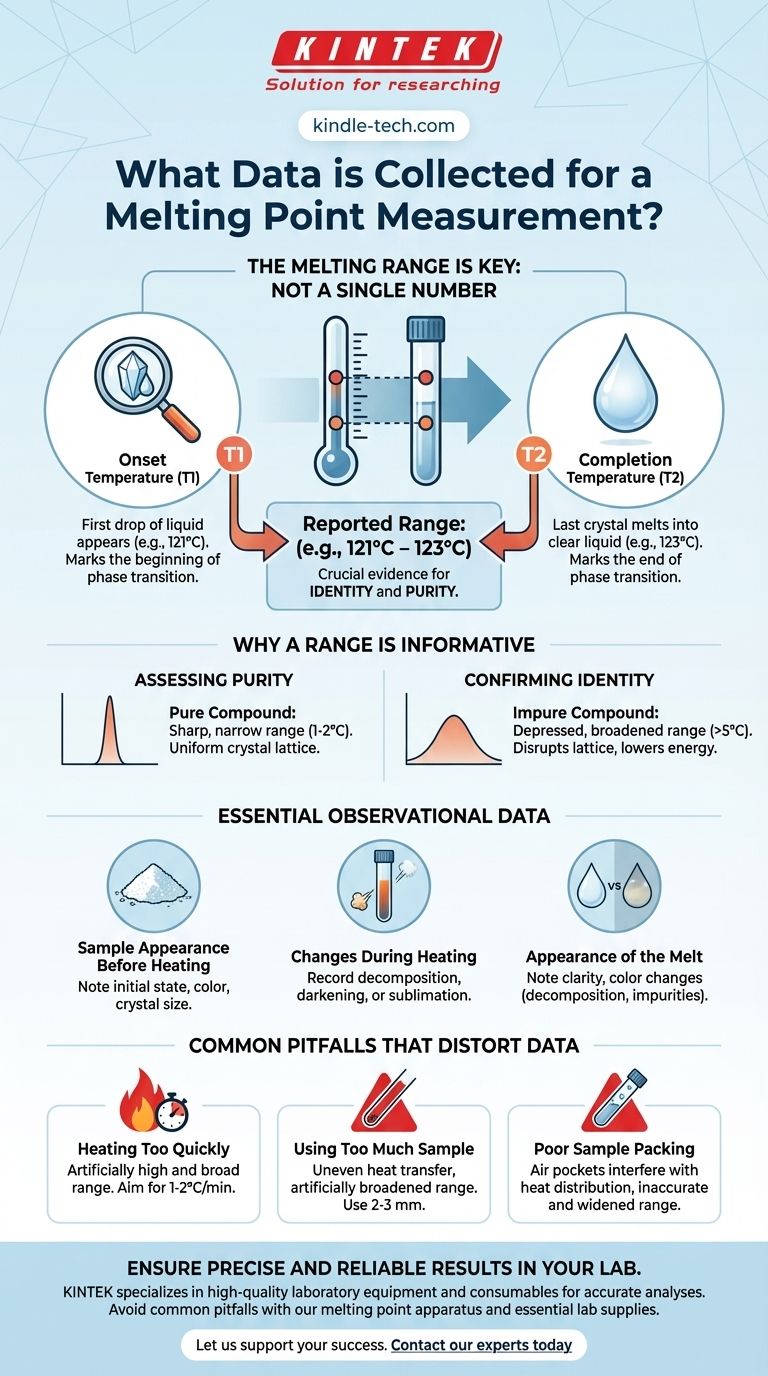
In practice, the essential data collected for a melting point measurement is a temperature range, not a single number. This range consists of two key points: the temperature at which the first drop of liquid appears (the onset of melting) and the temperature at which the last crystal of the solid melts into a clear liquid (the completion of melting).
The core purpose of collecting a melting point range is to use it as a powerful diagnostic tool. This data simultaneously provides crucial evidence for both the identity and the purity of a crystalline solid.

The Two Critical Data Points of a Melting Range
The melting "point" is more accurately described as a melting "range." The quality of this range is what provides the most valuable information.
The Onset Temperature (T1)
This is the first temperature recorded. It is the exact point when you observe the very first drop of liquid forming within the solid sample, often seen as a "sweating" of the crystals. This temperature marks the beginning of the phase transition.
The Completion Temperature (T2)
This is the second and final temperature recorded. It represents the point at which the last solid particle melts, leaving the entire sample as a transparent liquid. This marks the end of the phase transition.
How the Data is Reported
The final data is always reported as a range, listing the onset temperature first and the completion temperature second. For example, a result would be documented as 121°C – 123°C.
Why This Range Is More Informative Than a Single Point
A single temperature value provides very little context. The characteristics of the range—specifically its width and its agreement with known values—are what make the measurement so useful.
Assessing Purity
The width of the melting range is a primary indicator of a substance's purity. A pure crystalline compound will have a very sharp, narrow melting range, typically spanning only 1-2°C.
The presence of impurities disrupts the compound's uniform crystal lattice. This disruption lowers the energy required to start breaking the structure apart, resulting in a depressed (lower) and broadened (wider) melting range.
Confirming Identity
The measured melting range is compared against a literature value, which is the accepted melting point for a pure substance. If your experimentally determined range is sharp, narrow, and matches the literature value, it provides strong evidence that your compound is what you believe it to be.
Essential Observational Data to Record
Beyond the two temperatures, a thorough analysis includes recording key visual observations that provide critical context for the data.
Sample Appearance Before Heating
Note the initial state and color of your sample. Is it a white, crystalline powder? Are the crystals large or small? This serves as a baseline for any changes that occur.
Changes During Heating
It is crucial to record any phenomena other than simple melting. The sample might decompose, indicated by darkening, charring, or gas evolution. It could also sublime, disappearing as it turns from a solid directly into a gas.
The Appearance of the Melt
As the sample melts, note the appearance of the liquid. A pure sample should yield a clear, colorless liquid (unless the compound itself is colored). Cloudiness or color changes can indicate decomposition or the presence of insoluble impurities.
Common Pitfalls That Distort Data
Accurate data collection depends on avoiding common procedural errors. These mistakes can render your results misleading or useless.
Heating Too Quickly
This is the most common error. If the sample is heated too fast, the thermometer reading will not keep up with the actual temperature of the sample. This lag leads to an observed melting range that is artificially high and broad. A rate of 1-2°C per minute is standard.
Using Too Much Sample
Overloading the capillary tube results in poor and uneven heat transfer throughout the sample. This causes different parts of the sample to melt at different times, which artificially broadens the melting range. A small amount of finely ground powder (2-3 mm high) is sufficient.
Poor Sample Packing
If the sample is not packed tightly at the bottom of the capillary tube, air pockets will interfere with heat distribution. This also leads to an inaccurate and widened melting range.
Interpreting Your Results
Once you have collected your data, the interpretation depends entirely on your analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is determining purity: A narrow melting range (1-2°C) that aligns with the literature value indicates high purity. A broad range (e.g., > 5°C) that is lower than the literature value signals the presence of significant impurities.
- If your primary focus is identifying an unknown: A sharp melting range that precisely matches the literature value for a known compound is strong, corroborating evidence for its identity.
- If you observe decomposition or sublimation: Your recorded temperature should be reported as a "decomposition point" or "sublimation temperature," not a true melting point, as it reflects thermal instability.
Ultimately, the careful collection of a melting point range is a fundamental, efficient, and data-rich technique for characterizing any crystalline solid.
Summary Table:
| Key Data Point | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Onset Temperature (T1) | Temperature when the first drop of liquid appears | Marks the beginning of melting |
| Completion Temperature (T2) | Temperature when the last crystal melts | Marks the end of the phase transition |
| Reported Range (T1 – T2) | The full melting range (e.g., 121°C – 123°C) | Indicates purity (narrow range = pure) and identity (matches literature) |
| Observational Data | Visual changes (decomposition, color, clarity) | Provides context for thermal stability and impurity detection |
Ensure precise and reliable results in your lab.
Accurate melting point measurement is fundamental for identifying compounds and confirming their purity. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables designed to deliver the precision and reliability your analyses demand. From melting point apparatus to essential lab supplies, our products help you avoid common pitfalls like uneven heating and temperature lag.
Let us support your laboratory's success. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your specific needs and achieve consistent, trustworthy data in every experiment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment



















